What is the square of 56?
3136
3200
3225
3250
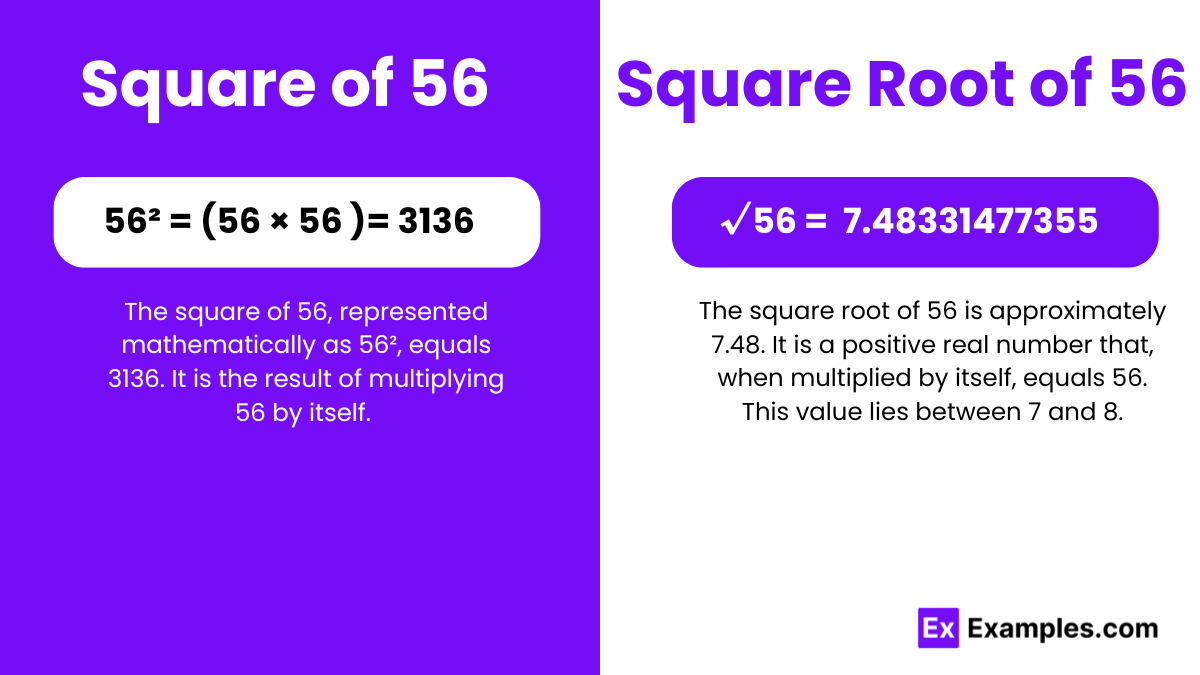
To calculate the square number of 56, you simply multiply 56 by itself:
Therefore, the square of 56 is 3136. This straightforward calculation is a building block for more complex mathematical operations and concepts, including algebraic equations, geometric formulas, and statistical models.
Or
√56 = 7.483
The square root of 56, denoted as √56, equals approximately 7.48. To compute it, you find the number that, when multiplied by itself, results in 56. In mathematical terms, finding the square root means identifying the number that, when raised to the power of 2, equals the original number. Visually, you can represent the square root of 56 as one side of a square with an area of 56 square units, where each side of the square is approximately 7.48 units in length. Understanding square roots is fundamental in various mathematical concepts and applications, such as geometry, algebra, and solving problems that involve areas or other quantities that are squared. In real-world scenarios, knowing the square root of 56 aids in calculations involving the measurement of areas or in any situation where you need to reverse a squaring operation to find an original quantity.
Square Root of 56: 7.483314774
Exponential Form: 56^1/2 or 56^0.5
Radical Form: √56
An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction or a precise decimal; it goes on infinitely without repeating. Since 56 is not a perfect square, its square root cannot be simplified into a fraction that perfectly represents a ratio of two integers, making it an irrational number.
Rational numbers can be written as a fraction with both the numerator and denominator as integers, where the denominator is not zero.
Examples:1/2, 3/4
Irrational numbers cannot be written as simple fractions and their decimal forms do not repeat or terminate.
Examples:π and √22
This method involves guessing a number that, when squared, comes close to 56. Start with numbers you know the squares of (e.g., 7² = 49 and 8² = 64) and estimate that √56 falls between 7 and 8.
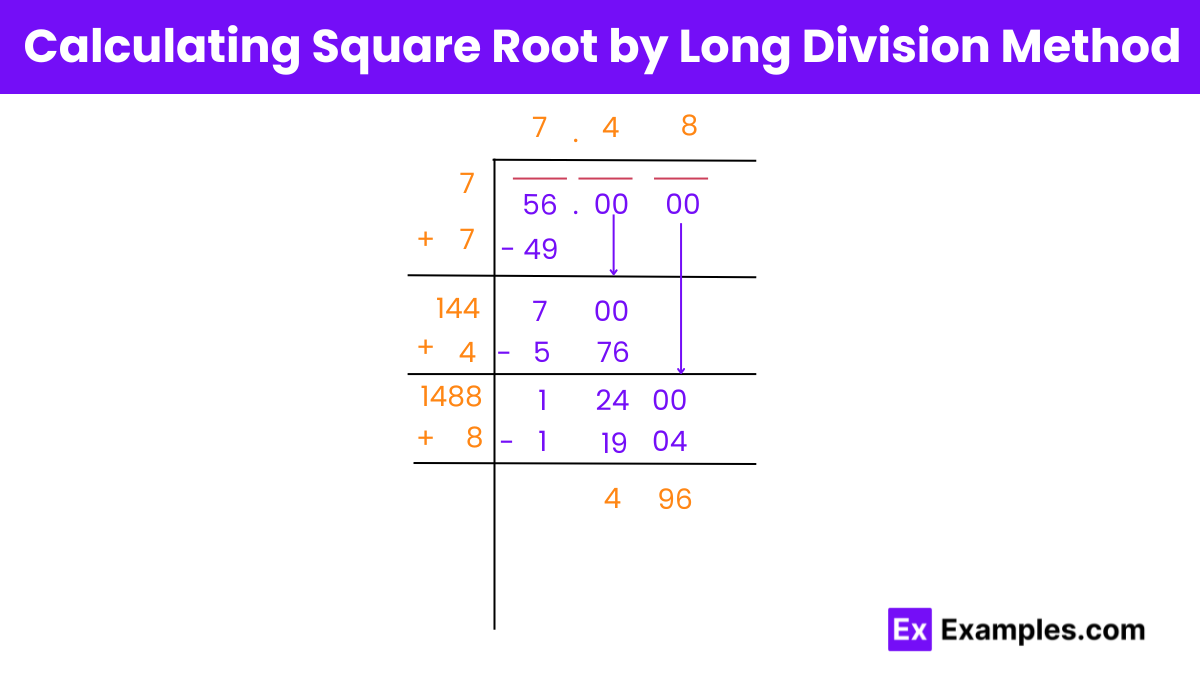
The long division method is a step-by-step procedure similar to traditional division, tailored for finding square roots. It involves dividing the number into pairs of digits from right to left, guessing the largest possible digits whose square is less than or equal to each segment, and subtracting to proceed to the next step. This method is precise but requires practice to master.
Prime factorization involves breaking down 56 into its prime factors (56 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 7) and then taking the square root of each factor. Since √56 = √(2² x 2 x 7), and knowing that the square root of a square is the number itself (i.e., √(2²) = 2), we simplify it to 2√14, acknowledging that √14 is irrational.
For most practical purposes, using a scientific calculator is the quickest and easiest way to find the square root of 56. It provides an approximate decimal value, which is sufficient for most applications.
Approximation techniques involve using known square roots of perfect squares close to 56 and then estimating or using a formula to get closer to the exact square root. For example, knowing that √49 = 7 and √64 = 8, one can estimate √56 to be closer to 7.5.
Newton’s Method, or the Newton-Raphson method, is a powerful technique for finding increasingly accurate approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. To find √56, you would start with an initial guess and iteratively apply Newton’s formula: xₙ₊₁ = xₙ – (f(xₙ)/f'(xₙ)), where f(x) = x² – 56. This method requires knowledge of calculus and is very effective for finding square roots to a high degree of accuracy.
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer. Since there is no whole number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 56, it is not considered a perfect square.
The square root of 56 simplified is √56 or approximately 7.48. It’s an irrational number, so it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
To work out 56 squared, multiply 56 by itself: 56 × 56 = 3136. This operation calculates the square of 56.
The number closest to √56 is 7, as √56 is approximately 7.48. Seven is just slightly less than the actual square root, making it the nearest whole number.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 56?
3136
3200
3225
3250
Estimate the square root of 56 to the nearest integer.
7
8
9
10
Calculate the square of 56 using the distributive property: (50 + 6)².
3000
3136
3160
3225
What is the approximate value of the square root of 56 using the average method between 7 and 8?
7.2
7.4
7.5
7.6
If x² = 3136, what is the value of x?
56
57
58
59
Verify the square of 56 by calculating (50 + 6) (50 + 6).
3100
3120
3136
3140
Using the approximation method, what is √56 rounded to two decimal places?
7.45
7.48
7.50
7.52
What is the difference between 57² and 56² ?
113
114
115
117
Express the square root of 56 as a product of its prime factors.
√2 × 28
√4 × 14
√7 × 8
√2³ × 7
Find the square root of 56 using the approximation method: √49 + 7.
7.48
7.5
7.6
7.8
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

