What is the square of 60?
3600
1200
6000
3000
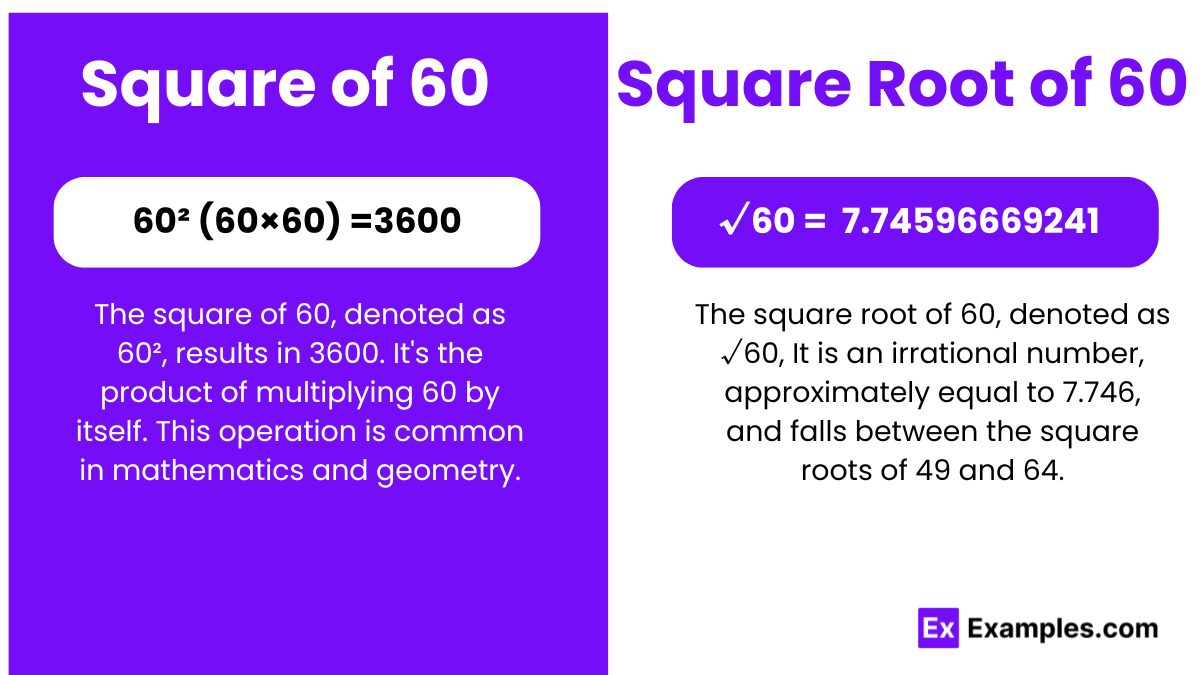
The square number of 60, denoted as 60², results in 3600. It’s the product of multiplying 60 by itself. This operation is common in mathematics and geometry.
√60 = 7.74596669241
Or
√60 = 7.745 up to three places of decimal
The square root of 60, denoted as √60, It is an irrational number, approximately equal to 7.746, and falls between the square roots of 49 and 64.
Square Root of 60: 7.74596669241
Exponential Form: 60^½
Radical Form: √60
The square root of 60, denoted as √60, does not result in a neat, simple fraction. To understand why, let’s break down the factors of 60. The prime factorization of 60 is2²×3×5.
For a square root to be rational, the exponents in its prime factorization need to be even, because a square root function essentially divides these exponents by 2. In the case of
√60, the prime factors 3 and 5 are raised to an odd power (1), which, when halved, results in non-integer exponents. Since a rational number is defined as one that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, and
√60 cannot be expressed in such a manner due to its prime factorization, it is deemed irrational. This property highlights a fundamental aspect of irrational numbers: their inability to be neatly expressed as fractions, making
√60 an endless, non-repeating decimal.
Rational numbers Rational numbers are fractions representing the quotient of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. They can be written as a/b, with both a and b being integers and b ≠ 0. Rational numbers include integers, proper fractions, improper fractions, and finite decimals.
Examples: 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8.
Irrational numbers Irrational numbers are real numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, meaning their decimal representation is infinite and non-repeating.
Examples: 2, π (pi), and e
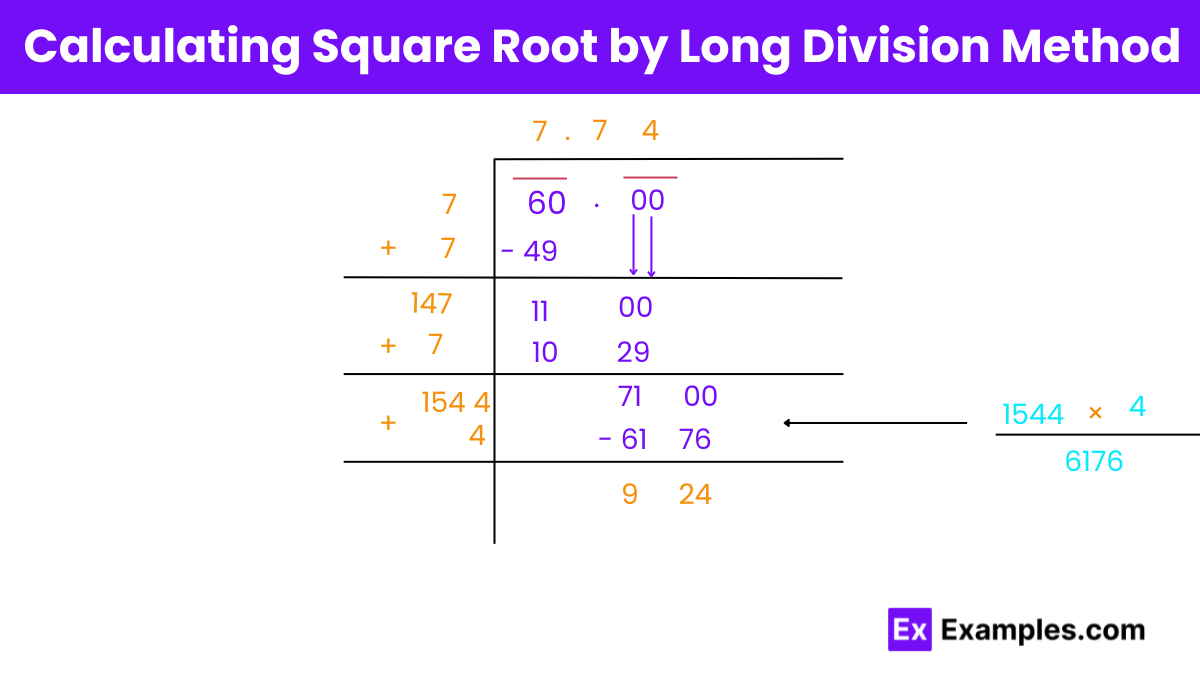
Step 1: Find the Largest Square
Identify the largest square number less than 60. Here,
7×7=49 is the largest square less than 60.
Step 2: Subtract and Find Remainder
Subtract 49 from 60 to get the remainder, 60−49=11.
Our initial quotient (which also serves as the divisor for this step) is 7.
Step 3: Update the Divisor
Double the current quotient (which is 7) to get 14. This will be the starting part of our new divisor.
Step 4: Extend the Dividend
Append two zeros to the remainder to get
1100 (as if we’re bringing down two zeros in traditional division).
Step 5: Find the New Divisor and Quotient Digit
Look for a digit X to place at the unit’s place of 14X such that 14X×X is less than 1100.
Here, 147×7=1029, fitting the condition. So, the new digit in the quotient is 7.
Step 6: Update Dividend and Divisor for the Next Step
Subtract 1029 from 1100 to get a new remainder, and then bring down two more zeros to form a new dividend.
Update the divisor by adding the last digit of the quotient to it, making 147+7=154.
Step 7: Repeat the Process
Repeat the process with the new dividend and divisor. Find a digit X for the divisor 154X such that 154X×X is less than the new dividend.
For example, 1544×4=6176, which is less than 7100, the new dividend after bringing down two zeros.
Add 4 to the quotient, following 7.7, to get 7.74.
The number 60 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. For example, 1 (1×1), 4 (2×2), 9 (3×3), 16 (4×4), and so on are perfect squares. To determine if 60 is a perfect square, one would typically look for an integer that, when multiplied by itself, equals 60. However, there is no integer that satisfies this condition for 60, making it not a perfect square.
The square root of 60 is not an integer, but it falls between the square roots of two perfect squares: 49 (7×7) and 64 (8×8). Since the square root of 49 is 7 and the square root of 64 is 8, the square root of 60 will be a decimal number between 7 and 8.
The factors of 60 are the integers that can be evenly divided into 60. These include:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, and 60.
The prime factors of 60 are 2, 3, and 5, with 2 appearing twice, because 60 equals 2 x 2 x 3 x 5. These are the smallest prime numbers that multiply together to give 60.
2 is a factor of 60 because 60 can be evenly divided by 2 with no remainder. This means 2 is a prime number that multiplies with others to result in 60.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 60?
3600
1200
6000
3000
What is the square root of 60 approximately?
7.8
8.0
7.5
8.2
If you square the number 60, what is the result?
3600
1200
600
6000
What is the approximate value of the square root of 60?
7.75
7.85
7.95
7.10
The square of which number gives 3600?
30
60
80
110
Which number is closest to the square root of 60?
7.7
8.0
7.9
8.3
What is the square of 60 expressed as a product?
60 × 60
30 × 120
50 × 72
40 × 90
The approximate square root of 60 is:
7.6
7.8
8.0
8.2
What is the value of the square root of 60 rounded to the nearest whole number?
7
8
9
10
If 60 is squared, what result is obtained?
3600
1200
2400
3000
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

