Find the square root of 13.
3.60
3.61
3.62
3.63
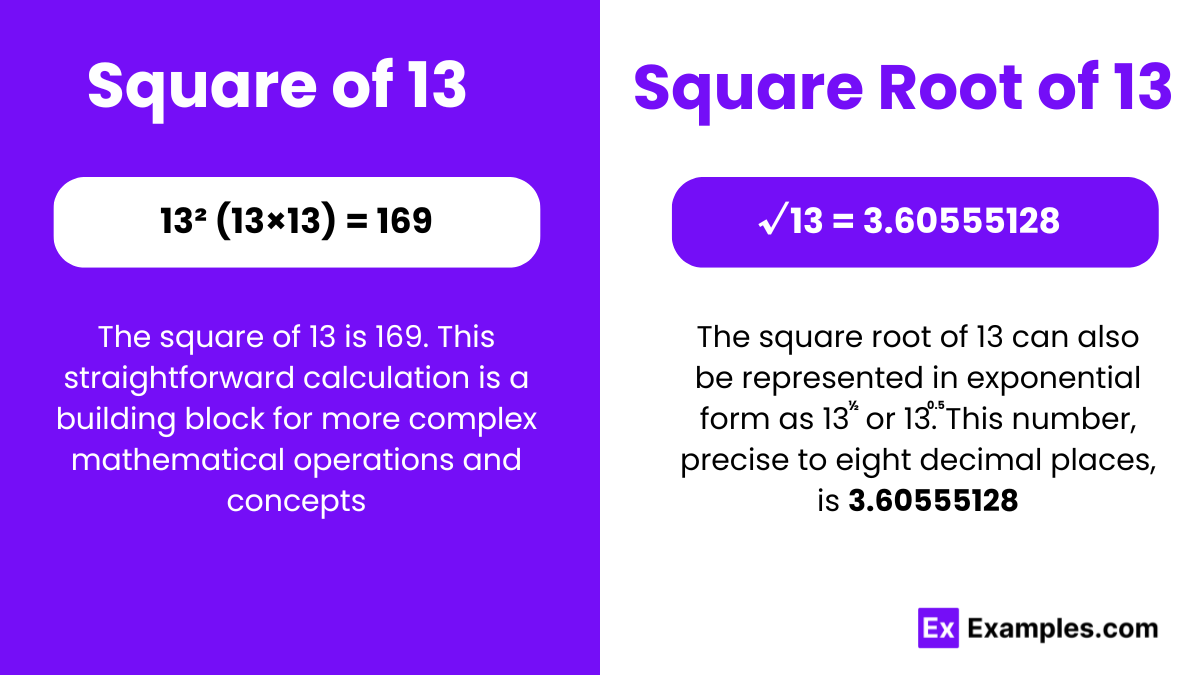
The square of 13 is 169. In mathematical terms, when you multiply 13 by itself, the result is 169. This fundamental arithmetic operation is important in various contexts, including geometry, algebra, and physics. Understanding squares and their properties is foundational in mathematical reasoning and problem-solving.
Or
√13= 3.605 up to three places of decimal.
The square root of 13 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 3.60555. This means that when you multiply this number by itself, the result is 13. Finding the square root of 13 involves using methods such as long division or approximation techniques. In practical terms, the square root of 13 may be used in mathematical calculations, engineering, and other scientific applications.
Exponential Form of 13:= (13)½ or (13)0.5
Radical Form of 13: √13
The square root of 13 is a irrational number.
The square root of 13, denoted as √13, is an irrational number.
To determine whether the square root of 13 is rational or irrational, we need to understand the definitions of these terms.
When we calculate the square root of 13, we find that it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Furthermore, its decimal expansion does not terminate or repeat. Therefore, by definition, the square root of 13 is an irrational number.
There are several methods to find the value of the square root of 13:
√13 cannot be simplified further into a simpler radical form because 13 is a prime number and has no perfect square factors other than 1. It remains as √13, representing an irrational number with a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion.
No, 13 is not a perfect number. A perfect number is an integer that is the sum of its positive divisors, excluding itself. For example, 6 is a perfect number because 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
No, 13 is not a squared number. A squared number, or perfect square, is the product of an integer multiplied by itself. Since there’s no integer whose square is 13, it is not considered a squared number.
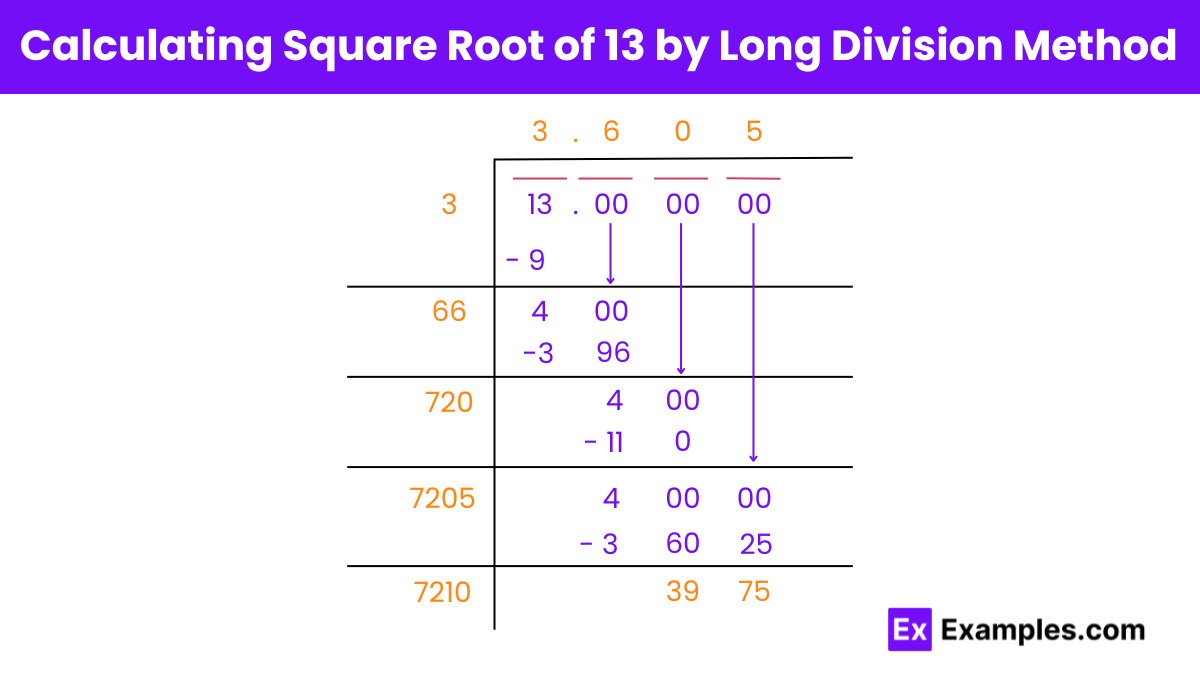
To find a square root, you can use methods like estimation, the long division method, or a calculator. The long division method involves a step-by-step process similar to division, allowing you to find the square root to several decimal places.
The first 13 perfect square numbers, starting from 1, are 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, and 169. These are the squares of the integers from 1 to 13, respectively.
In conclusion, the square of 13 is 169, a result of multiplying 13 by itself. On the other hand, the square root of 13, an irrational number, cannot be neatly expressed as a fraction, with an approximate value of 3.6055. These concepts underline the fascinating nature of numbers, bridging simple arithmetic and complex mathematical principles.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Find the square root of 13.
3.60
3.61
3.62
3.63
What is the square of 13?
169
156
144
130
What is the value of 13 squared?
156
158
161
169
If x² = 13, what is the approximate value of x?
3.60
3.61
3.62
3.63
What is the result of 13 raised to the power of 1/2?
3.60
3.61
3.62
3.63
What is the square of the square root of 13?
11
12
13
14
Find the number whose square is 13.
3.60
3.61
3.62
3.63
What is the square of 13 divided by the square root of 13?
13
14
15
16
What is the difference between 13 and the square of 3.60?
0
0.04
0.08
0.09
If 13 is a perfect square, what is its square root?
3.60
3.61
3.62
3.63
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

