What is the square of 74?
5476
5400
5625
4900


In the domain of mathematics, particularly within algebra, squares and square roots hold paramount importance. They serve as the cornerstone upon which our comprehension of rational and irrational numbers is built. By considering a number like 147 and squaring it, we unveil the fundamental essence of this operation, facilitating a deeper exploration of mathematical relationships and patterns.
A square number, such as 147, arises from multiplying an integer by itself. The square of 147 equals 21,609, showcasing algebraic principles and enriching our understanding of mathematical relationships and patterns within algebraic studies and beyond.
or
√147 ≈ 12.124 upto 3 decimals
The square root of 147, a perfect square number, is approximately 12.124. Mastering square roots involves identifying the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 147. This understanding is crucial for exploring algebraic relationships and patterns within mathematics.
Exponential Form: 147^1/2 or 147^0.5
Radical Form: √147
Rational Numbers : Rational numbers are expressible as fractions of two integers.
Irrational Numbers : Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions of integers.
Since the square root of 147 is not a perfect square, it is irrational. It cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
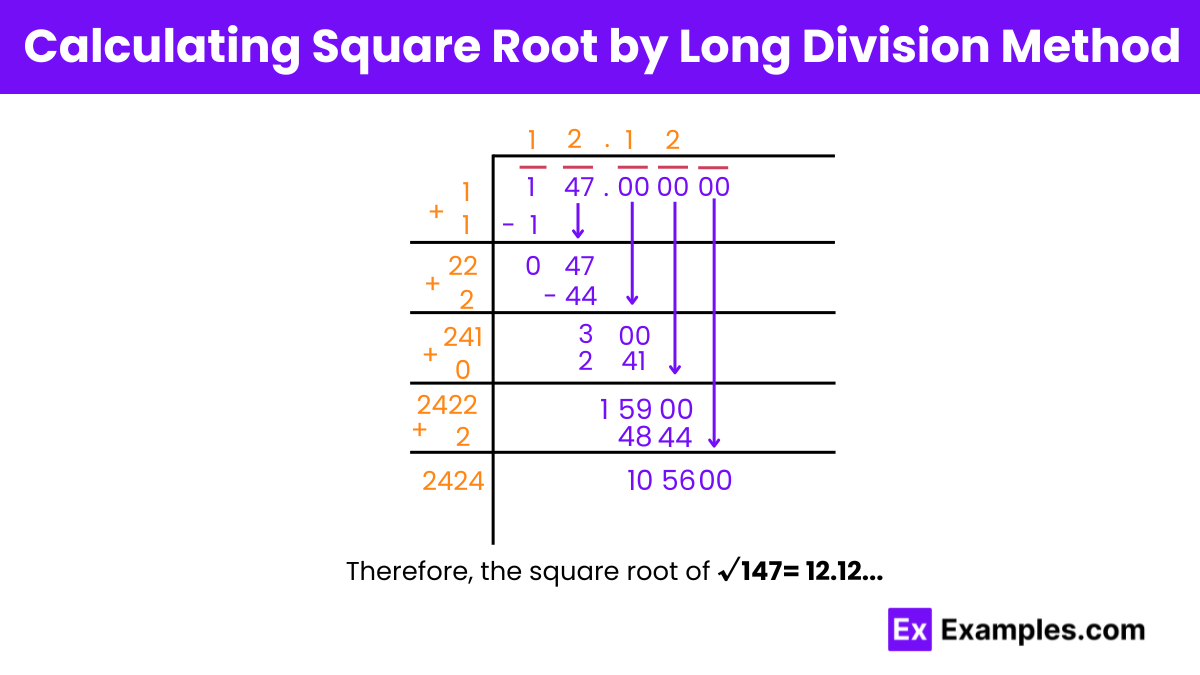
Step 1: Pairing Digits
Starting from the right, we’ll pair up the digits 147 by placing a bar above 47 and 1 separately. Additionally, we’ll pair the 0s in the decimal part in pairs of 2 from left to right.
Step 2: Finding Initial Quotient
Find a number that, when multiplied by itself, results in a product less than or equal to 1. Since this is 1, place 1 in the quotient and divisor’s place, resulting in a remainder of 0.
Step 3: Bringing Down
Drag down 47 beside the remainder 0. Also, add the divisor to itself and write it below (1 + 1 = 2).
Step 4: Continuing Division
Find a number ( X ) such that ( 2X × X ) results in a number less than or equal to 47. The number 2 fits here, so fill it next to 2 in the divisor as well as next to 1 in the quotient.
Step 5: Expanding the Divisor
Find the remainder and now drag down the pair of 0s from the decimal part of the number. By adding ( X ) to the divisor, the new divisor becomes 24.
Step 6: Repeat
Repeat this process iteratively to obtain additional decimal places as needed.
147 is not a perfect square because it cannot be expressed as the product of an integer multiplied by itself. In other words, there are no integers where the product of the integer with itself equals 147.
The product of (2) and (4 √147) is (8 √147).
The factors of 147 are 1, 3, 7, 21, 49, and 147.
The prime factorization of (√147) is (3 √147)
147 is divisible by 1, 3, 7, 21, 49, and 147.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 74?
5476
5400
5625
4900
What is the square root of 5476?
74
76
77
78
Which of the following numbers is closest to the square root of 74?
8.5
8.6
8.7
9
What is the approximate square root of 74 to the nearest whole number?
8
9
10
11
The square of which of the following is closest to 74?
8
9
10
11
What is the value of √74 in decimal form rounded to two decimal places?
8.60
8.62
8.65
8.70
If x² = 74, what is the value of x?
8.6
8.7
8.62
9
Which number squared is just above 74?
8
9
10
11
What is the square of 9?
81
72
90
100
The value of √74 falls between which two consecutive integers?
7 and 8
8 and 9
9 and 10
6 and 7
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

