What is the square of 43?
1849
1936
1764
2025

Within the domain of algebraic mathematics, squares and square roots hold significant importance. Squaring a number, such as 43, entails multiplying it by itself, yielding 1849. This foundational operation is vital for exploring rational and irrational numbers. A grasp of these fundamentals enriches understanding of mathematical relationships and patterns. Squares illuminate inherent number properties, while square roots unravel intricate numerical mysteries. These concepts serve as beacons, guiding mathematical explorations into fractional territories. Proficiency in squares and square roots equips mathematicians to navigate varied mathematical landscapes, unveiling the elegance and complexity inherent within algebraic frameworks.
The square of 43 equals 1849, obtained by multiplying 43 by itself, a fundamental operation in algebraic mathematics, uncovering inherent number properties.
The square root of 43 is approximately 6.557. This fundamental mathematical operation reveals the value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 43.
Exponential Form: 43^½ or 43^0.5
Radical Form: √43
Rational numbers are expressible as the quotient of two integers. Irrational numbers, however, cannot be represented as fractions of integers. Examples of irrational numbers include the square roots of non-perfect squares.
Step 1: Starting from the right, we will pair up the digits 43 by putting a bar above them. We also pair the 0s in decimals in pairs of 2 from left to right.
Step 2: Think of a number whose square is less than or equal to 43. In this case, that number would be 6.
Step 3: Dividing 43 by 6 with the quotient set as 6, we get a remainder of 7.
Step 4: Drag a pair of 0’s down and fill it next to 7 to make the dividend 700.
Step 5: The divisor, in this case 6 is doubled and written below. Now, we have 12X as the new divisor, and we need to find a value of X that makes the product of 12X × X less than or equal to 700. In this case, 125 is the required value.
Step 6: The number 5 is placed in the quotient after a decimal place. The new divisor for the next division will be 125 + 5 = 130.
A perfect square cannot be expressed as the square of an integer. Therefore, the square root of 43 is an irrational number.
The number closest to √43 is approximately 6.557, which can be rounded to 7 when considering whole numbers.
The prime factorization of 43 is 43 itself, as it is a prime number and cannot be factored further.
The nearest whole number to √43 is 7.
No, the square root of 43 cannot be expressed as a fraction because it is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be written as the quotient of two integers.

Within the domain of algebraic mathematics, squares and square roots hold significant importance. Squaring a number, such as 43, entails multiplying it by itself, yielding 1849. This foundational operation is vital for exploring rational and irrational numbers. A grasp of these fundamentals enriches understanding of mathematical relationships and patterns. Squares illuminate inherent number properties, while square roots unravel intricate numerical mysteries. These concepts serve as beacons, guiding mathematical explorations into fractional territories. Proficiency in squares and square roots equips mathematicians to navigate varied mathematical landscapes, unveiling the elegance and complexity inherent within algebraic frameworks.
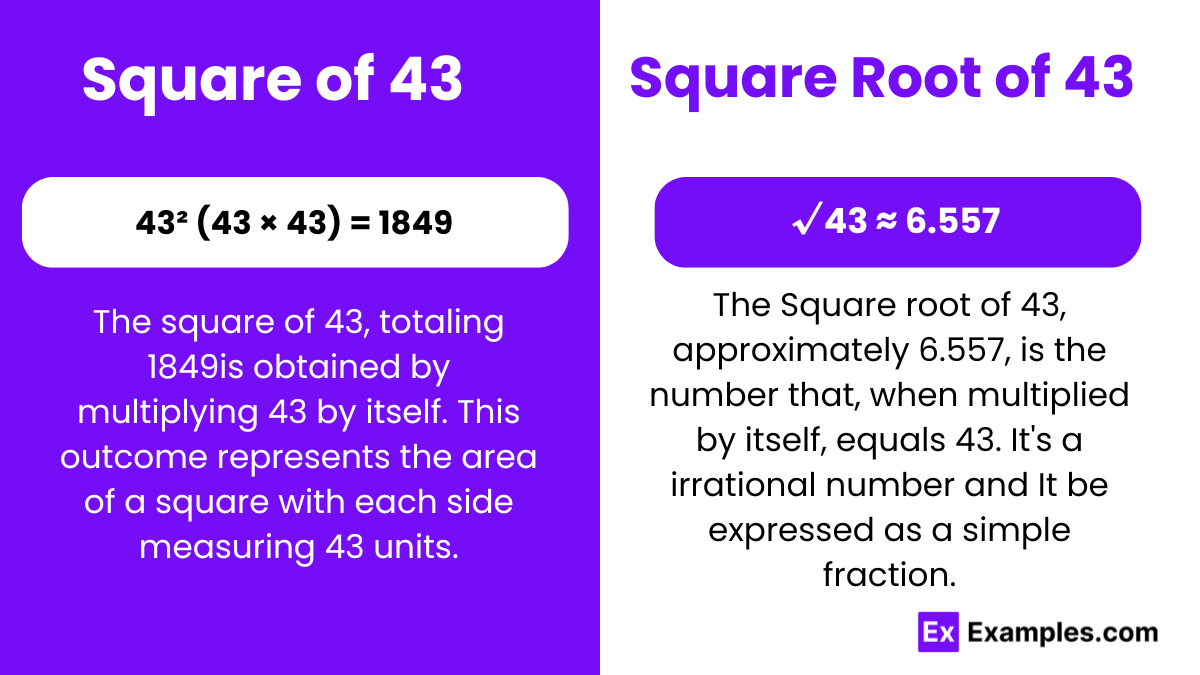
43² (43 × 43) = 1849
The square of 43 equals 1849, obtained by multiplying 43 by itself, a fundamental operation in algebraic mathematics, uncovering inherent number properties.
√43 ≈ 6.557
The square root of 43 is approximately 6.557. This fundamental mathematical operation reveals the value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 43.
Square Root of 43: ≈ 6.557
Exponential Form: 43^½ or 43^0.5
Radical Form: √43
The square root of 43 is irrational.
Rational numbers are expressible as the quotient of two integers. Irrational numbers, however, cannot be represented as fractions of integers. Examples of irrational numbers include the square roots of non-perfect squares.
Prime Factorization Method: Break down 43 into its prime factors. However, since 43 is not a perfect square, its prime factorization results in a mixture of prime factors.
Long Division Method: Utilize the long division algorithm to approximate the square root of 43 iteratively.
Using a Calculator: Most calculators are equipped with a square root function, enabling direct calculation of the square root of 43.
Estimation: As 43 falls between the perfect squares of 36 (6 × 6) and 49 (7 × 7), an estimate can be made that its square root is likely between 6 and 7, closer to 6.

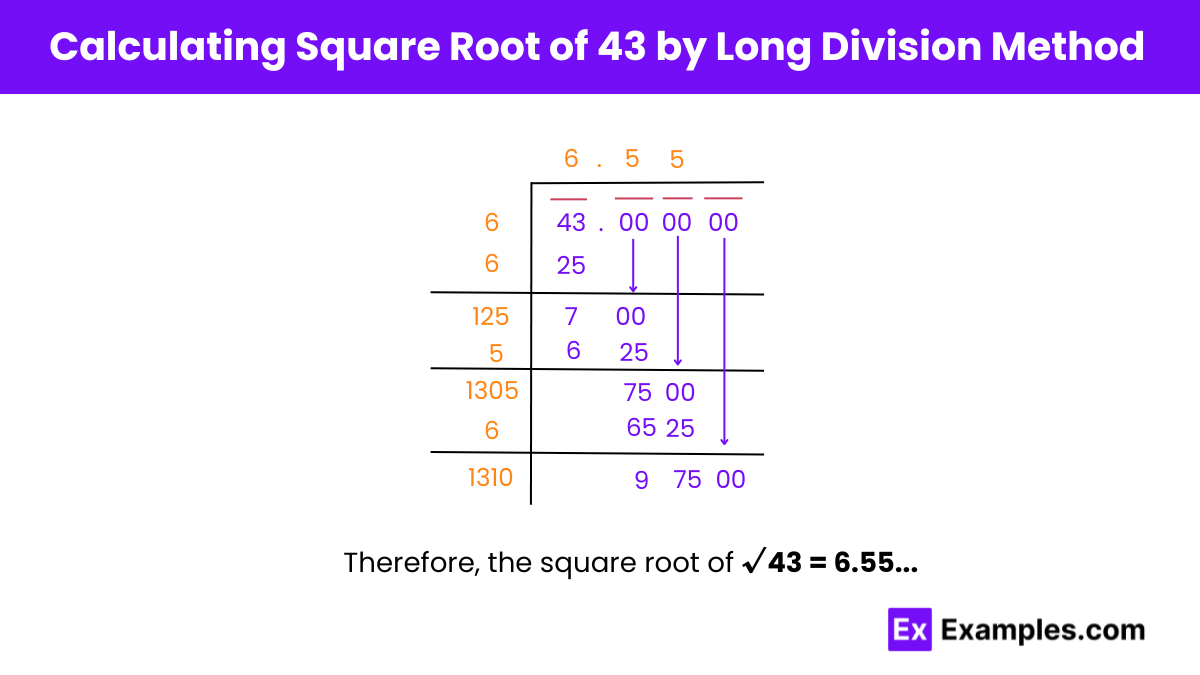
Step 1: Starting from the right, we will pair up the digits 43 by putting a bar above them. We also pair the 0s in decimals in pairs of 2 from left to right.
Step 2: Think of a number whose square is less than or equal to 43. In this case, that number would be 6.
Step 3: Dividing 43 by 6 with the quotient set as 6, we get a remainder of 7.
Step 4: Drag a pair of 0’s down and fill it next to 7 to make the dividend 700.
Step 5: The divisor, in this case 6 is doubled and written below. Now, we have 12X as the new divisor, and we need to find a value of X that makes the product of 12X × X less than or equal to 700. In this case, 125 is the required value.
Step 6: The number 5 is placed in the quotient after a decimal place. The new divisor for the next division will be 125 + 5 = 130.
No, 43 is not a perfect square.
A perfect square cannot be expressed as the square of an integer. Therefore, the square root of 43 is an irrational number.
The number closest to √43 is approximately 6.557, which can be rounded to 7 when considering whole numbers.
The prime factorization of 43 is 43 itself, as it is a prime number and cannot be factored further.
The nearest whole number to √43 is 7.
No, the square root of 43 cannot be expressed as a fraction because it is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be written as the quotient of two integers.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 43?
1849
1936
1764
2025
What is the square root of 1849?
42
43
44
45
If x² = 1849, what is x?
42
43
44
45
What is the value of 43 squared minus 1?
1848
1849
1850
1851
The square of which number is closest to 43?
6
7
8
9
Which of the following numbers is a perfect square close to 43?
36
44
49
52
What is the approximate square root of 43 to the nearest integer?
6
7
8
9
What is the value of 43⁰.⁵?
6.5
7
8
9
If you add 43 to its square, what is the result?
1889
1936
1849
1849
What is the result of subtracting 43 from its square?
1806
1849
1900
1850
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

