What is the square of 57?
324
3249
3225
3240

Within the domain of mathematics, particularly in algebraic studies, squares and square roots are fundamental. Squaring a number, such as 57 resulting in 3249, is pivotal. This operation unveils properties of rational (expressible as a fraction) and irrational numbers (defying neat fraction expression). Understanding these concepts enriches comprehension of mathematical patterns and relationships, crucial for navigating complexities in algebraic explorations. Mastery of these foundational principles fosters a deeper understanding of mathematical structures, enabling one to discern intricate connections within numerical systems. Thus, the study of squares and square roots transcends mere arithmetic, evolving into a profound exploration of algebraic concepts, essential for comprehending the underlying principles governing mathematical phenomena.
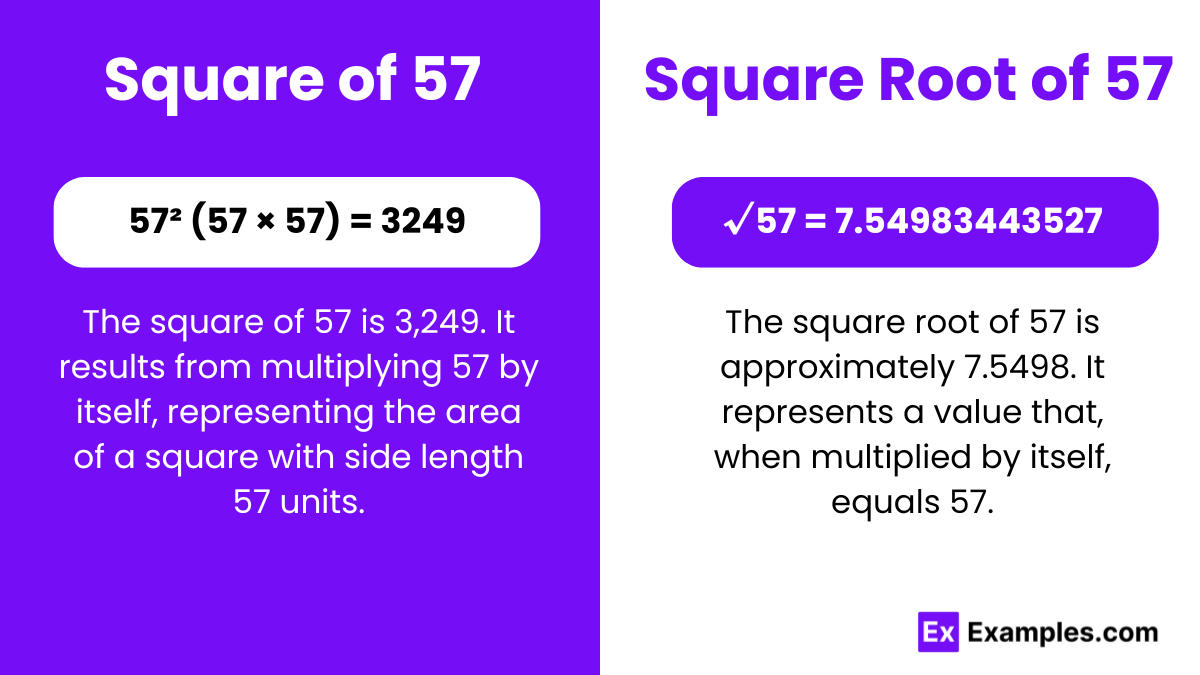
57² (57 × 57) = 3249
The square number of 57 is 3249. In mathematics, a square number arises when an integer is multiplied by itself. Understanding the properties and patterns of square numbers, like 57 squared, enriches comprehension of algebraic concepts, fostering a deeper insight into mathematical relationships and structures.
√57 = 7.54983443527
Or
√57 = 7.549 Upto 3 Decimals
The square root of 57 is approximately 7.55. In mathematics, the square root signifies the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 57. Exploring the square of 57 reveals fundamental principles, enriching comprehension of mathematical relationships and patterns embedded within numerical systems.
Square Root of 57: 7.54983443527
Exponential Form: 57^½ or 57^0.5
Radical Form: √57
The square root of 57 is an irrational number
The square root of 57 is irrational. It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. This classification distinguishes it from rational numbers, which can be represented in such a form, highlighting the complexity within mathematical systems.
Rational number : A rational number is one that can be written as a fraction of two integers.
For example, 3/4 or -5/2 are rational.
Irrational number : An irrational number cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, and its decimal expansion neither ends nor repeats.
For instance, √2 ≈ 1.41421356… is irrational.
To find the square root of 57, you can use various methods:
Prime Factorization: Break down 57 into its prime factors to simplify calculation.
Estimation: Use nearby perfect squares to approximate the root.
Newton’s Method: Iteratively refine guesses to converge on the precise value.
Calculator or Software: Utilize technology for accurate and rapid computation.
Long Division Method: Employ a step-by-step division process to manually extract the root.
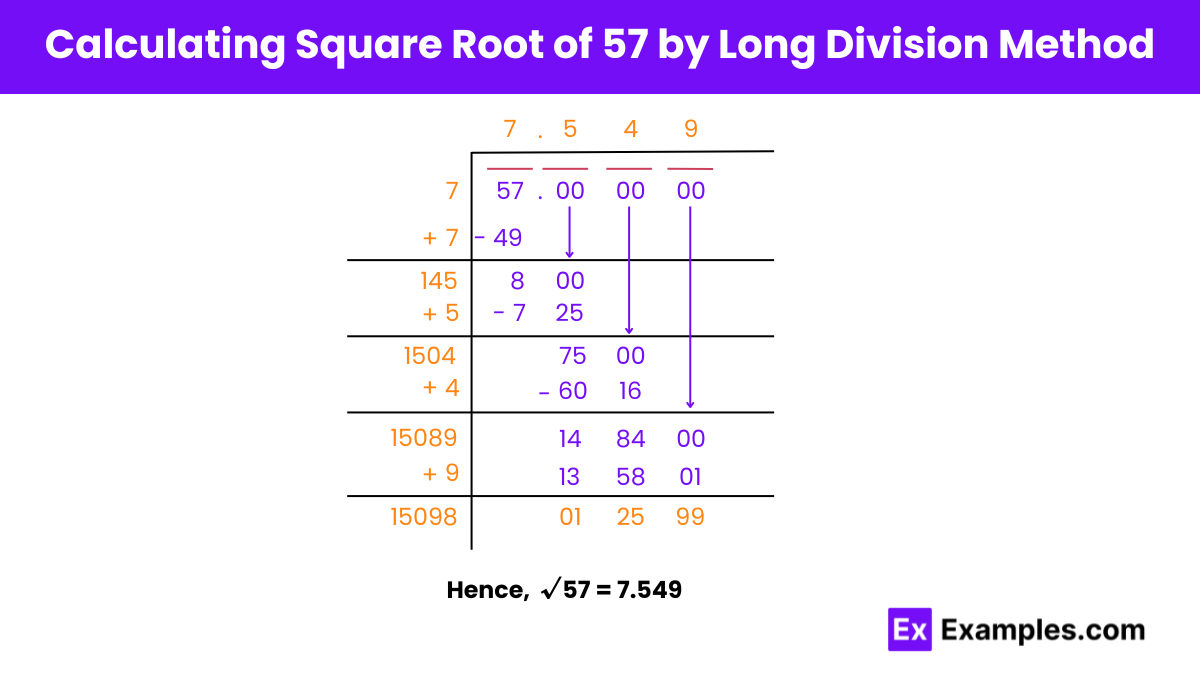
Step 1: Grouping Digits
Group digits from the unit’s place in pairs of two, yielding one pair (57).
Step 2: Finding Initial Guess
Find a number (t) where t × t ≤ 57. Thus, t = 7 (7 × 7 = 49).
Step 3: First Division
Divide 57 by 7, resulting in a quotient of 7 and a remainder of 8. Add the divisor (7) with itself to get the new divisor (14).
Step 4: Decimal Placement
Introduce a decimal in the dividend and quotient. Add three pairs of zero to the dividend (57. 00 00 00).
Step 5: Continuing Division
Bring down the pair of zero, yielding a new dividend of 800. Find a number (m) where 14m × m ≤ 800. Thus, m = 5 (145 × 5 = 725 ≤ 800).
Step 6: Repeat for Remaining Digits
Repeat the process for all pairs of zero.
Step 7: Conclusion
The square root of 57, calculated by the long division method, is approximately 7.549.
No, 57 is not a perfect square number
57 is not a perfect square because it cannot be expressed as the square of an integer. Its square root is approximately 7.549, which is not an integer, indicating that 57 is not a perfect square.
No, as 57 is not a perfect square, its square root cannot be simplified further.
The square root of 57 is used in geometric calculations, such as finding the diagonal of a rectangle with side lengths of 57 units.
The square root of 57 is involved in Pythagorean triples, such as (19, 20, 29), where 19² + 20² = 29².
Yes, the decimal expansion of the square root of 57 continues indefinitely without repeating, showcasing its irrationality.
Compared to perfect squares, such as 49 and 64, the square root of 57 falls between their respective square roots, highlighting its position within the number line.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 57?
324
3249
3225
3240
Which of the following values is closest to the square root of 57?
7.5
7.6
7.7
7.8
If x² = 57, what is x?
7.4
7.5
7.6
7.7
Simplify √57 to its decimal form.
7.52
7.53
7.54
7.55
What is (57)²?
3225
3249
3260
3276
Find the approximate value of √57 to two decimal places.
7.53
7.54
7.55
7.56
Which number is closest to 57 but is not a perfect square?
54
58
60
62
What is 57 raised to the power of 0.5?
7.5
7.55
7.6
7.65
Calculate 57 × 57.
3240
3249
3258
3267
What is the square root of 57 rounded to the nearest integer?
7
8
9
10
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

