What is 2 multiplied by 9?
16
18
20
22
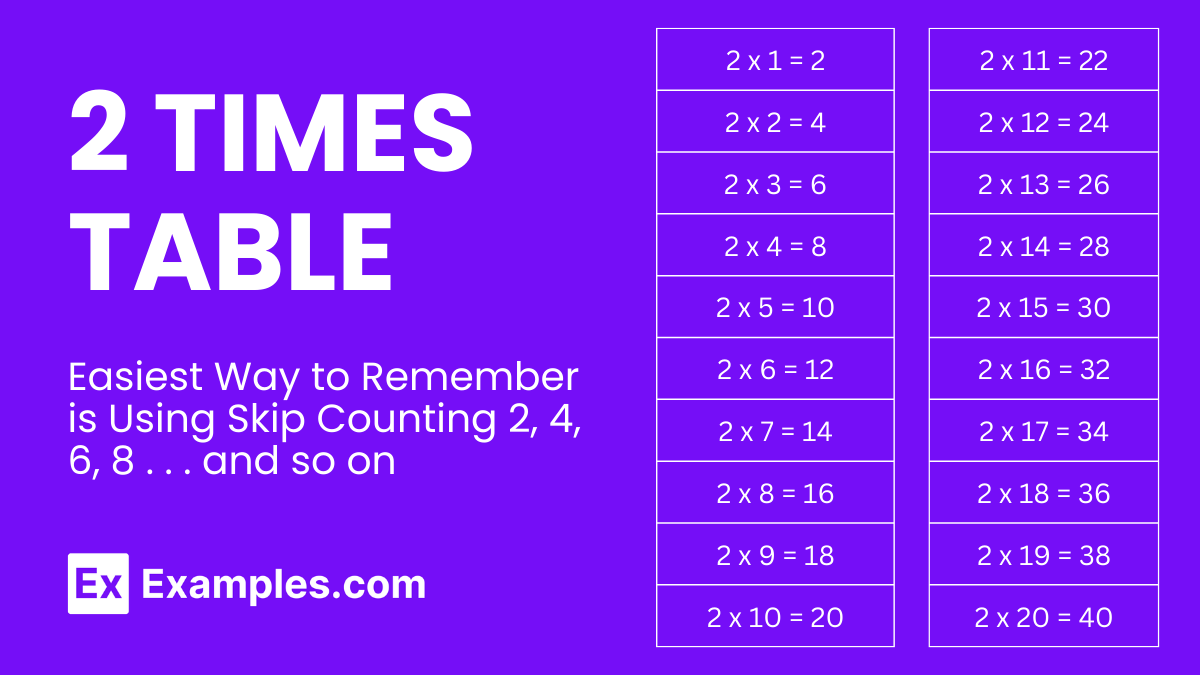
The 2 times multiplication table, often referred to as the table of 2, outlines the results of multiplying the number 2 by various whole numbers. It effectively demonstrates how adding the number 2 repeatedly, for a specific number of times, corresponds to multiplication. For instance, multiplying 2 by 3 (2 x 3) is equivalent to adding 2 to itself three times (2+2+2), resulting in 6. By applying this principle to different numbers, a variety of outcomes are generated. The multiplication table of 2, extending to multiplying by up to 20, is a crucial tool for quick calculations, significantly benefiting students in time-sensitive exams.
Providing the table of 2 in diverse formats aids in its memorization, offering an invaluable resource for students. Mastery of the 2 times table is fundamental, as it enhances mental math capabilities, deepens number sense, and lays the foundation for tackling more sophisticated mathematical challenges with ease. Understanding that the table of 2 represents sequential additions of the number 2 is key to grasping basic multiplication concepts, such as 2 + 2 + 2 equating to 2 x 3 = 6.
Multiplication Table of 2 Charts
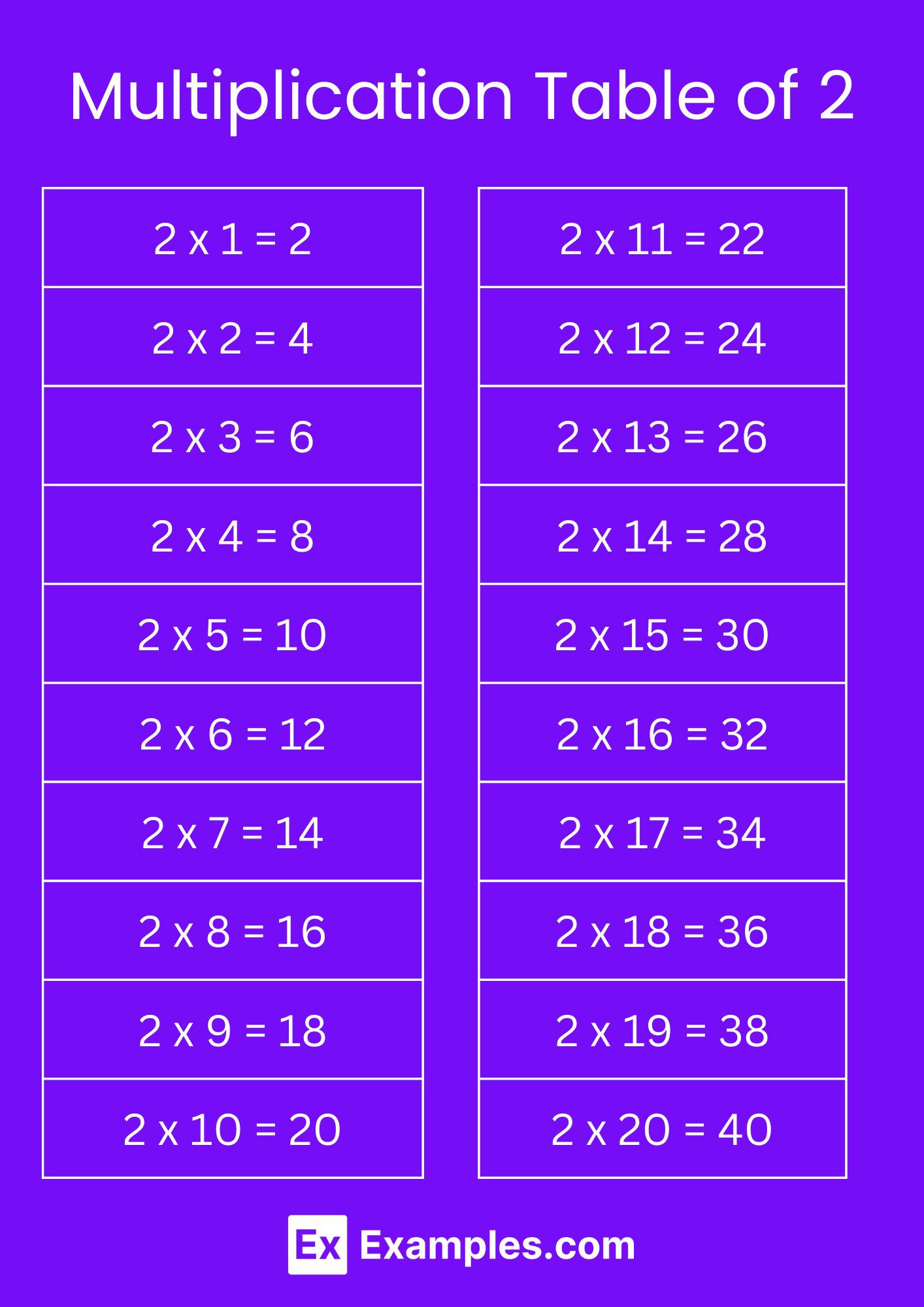
| Multiplication from ( 1-10 ) | Multiplication from ( 11 -20 ) |
|---|---|
| 2 x 1 = 2 | 2 x 11 = 22 |
| 2 x 2 = 4 | 2 x 12 = 24 |
| 2 x 3 = 6 | 2 x 13 = 26 |
| 2 x 4 = 8 | 2 x 14 = 28 |
| 2 x 5 = 10 | 2 x 15 = 30 |
| 2 x 6 = 12 | 2 x 16 = 32 |
| 2 x 7 = 14 | 2 x 17 = 34 |
| 2 x 8 = 16 | 2 x 18 = 36 |
| 2 x 9 = 18 | 2 x 19 = 38 |
| 2 x 10 = 20 | 2 x 20 = 40 |
The Multiplication Table of 2 lays the groundwork for understanding and applying one of the most basic yet crucial mathematical operations. It systematically lists the products of multiplying numbers by 2, providing a clear and concise reference for students. This table not only aids in memorization but also in the development of pattern recognition and algebraic thinking. As a vital component of mathematics education, the Multiplication Table of 2 equips students with the skills necessary to tackle more complex mathematical challenges, fostering a solid foundation in multiplication.
The 2 times table is a foundational element of mathematics, serving as the bedrock for understanding multiplication, division, and even more complex arithmetic operations. Mastering this table equips students with the skills necessary for quicker mental math, facilitating a smoother transition to advanced mathematical concepts. It’s not just about memorizing numbers; it’s about unlocking the door to mathematical fluency and confidence.
| Multiplication | Result |
|---|---|
| 2 x 1 | 2 |
| 2 x 2 | 4 |
| 2 x 3 | 6 |
| 2 x 4 | 8 |
| 2 x 5 | 10 |
| 2 x 6 | 12 |
| 2 x 7 | 14 |
| 2 x 8 | 16 |
| 2 x 9 | 18 |
| 2 x 10 | 20 |
Unlocking the 2 times table is more than rote learning; it’s about applying strategic tips and techniques to ensure students grasp and retain this essential math skill. Here are insights to make learning this table both effective and engaging:
By implementing these tips, educators can ensure that students not only learn the 2 times table but also understand the underlying principles, setting a solid foundation for future mathematical learning.
Dive into the multiplication journey with the table of 2 from 11 to 20, a fundamental building block for young learners mastering basic arithmetic. This table extends the concept of doubling, reinforcing numerical fluency and preparing students for more complex mathematical challenges. Essential for educators, this guide ensures students grasp multiplication’s core principles, enhancing their confidence and skills in mathematics.
| Number | Result |
|---|---|
| 2 x 11 | 22 |
| 2 x 12 | 24 |
| 2 x 13 | 26 |
| 2 x 14 | 28 |
| 2 x 15 | 30 |
| 2 x 16 | 32 |
| 2 x 17 | 34 |
| 2 x 18 | 36 |
| 2 x 19 | 38 |
| 2 x 20 | 40 |
Below is the table of 2 from 1 to 20, including three columns: Number (indicating the multiplier), Addition (showing the incremental addition of 2), and Result (the outcome of multiplying 2 by the number).
2 + 2 + 2 = 2×1 + 2×1 + 2×1
= 2(1 + 1+ 1) [using the distributive property of multiplication]
= 2(3)
2 + 2 + 2 = 2 × 3
| Number | Addition | Addition to Previous Result | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 x 1 | 2 + 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 x 2 | 2 + 2 | 2+2 | 4 |
| 2 x 3 | 2 + 2 + 2 | 4+2 | 6 |
| 2 x 4 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 6+2 | 8 |
| 2 x 5 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 8+2 | 10 |
| 2 x 6 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 10+2 | 12 |
| 2 x 7 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 12+2 | 14 |
| 2 x 8 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 +2 + 2 + 2 | 14+2 | 16 |
| 2 x 9 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 +2 + 2 + 2+ 2 | 16+2 | 18 |
| 2 x 10 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 +2 + 2 + 2+ 2 + 2 | 18+2 | 20 |
This table illustrates the pattern of adding 2 to the result of the previous multiplication to get the next result, providing a clear understanding of the progression within the 2 times table.
Mastering the 2 times table is a fundamental step in developing math fluency. This essential skill lays the groundwork for multiplication, a key concept in arithmetic. By understanding the 2 times table, students can easily double numbers, an ability that enhances mental math skills and prepares them for more complex multiplication tasks. Here are points to guide you through reading the 2 times table effectively:
By following these points, students can confidently navigate through the 2 times table, setting a solid foundation for mastering multiplication.
The table of 2 exclusively consists of even numbers, including 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, and so forth. It initiates with the number 2. To determine the subsequent term in the series, simply add 2 to the preceding number. Additionally, employing skip counting by one from 2—omitting the odd numbers in between—also yields the table of 2, such as 2, 4 (skipping 3), 6 (skipping 5), and continuing in this pattern.
Question: What is 2 times 3?
Solution: To find 2 times 3, you multiply 2 by 3.
Calculation: 2 x 3 = 6
Answer: 2 times 3 equals 6.
Question: How much is 2 added to itself 4 times?
Solution: Adding 2 to itself 4 times is the same as multiplying 2 by 4.
Calculation: 2 x 4 = 8
Answer: 2 added to itself 4 times equals 8.
Question: If a pair of socks costs $2, how much will 5 pairs cost?
Solution: Multiply the cost of one pair by the number of pairs.
Calculation: 2 x 5 = 10
Answer: 5 pairs of socks cost $10.
Question: What is the double of 6?
Solution: Doubling a number is the same as multiplying it by 2.
Calculation: 2 x 6 = 12
Answer: The double of 6 is 12.
Question: How do you find the 8th even number?
Solution: Multiply 2 by 8, since every multiple of 2 is an even number.
Calculation: 2 x 8 = 16
Answer: The 8th even number is 16.
Question: If one apple costs 2 dollars, how much do 9 apples cost?
Solution: Multiply the cost of one apple by the total number of apples.
Calculation: 2 x 9 = 18
Answer: 9 apples cost $18.
Question: How many groups of 2 can you form with 10 items?
Solution: Divide the total number of items by 2.
Calculation: 10 ÷ 2 = 5
Answer: You can form 5 groups of 2 with 10 items.
The 2 times table is a cornerstone of multiplication, offering a straightforward path to mastering basic arithmetic. By understanding and applying this table, learners can enhance their numerical fluency, laying a solid foundation for more complex mathematical concepts. Its simplicity and wide application make it an essential tool for students and educators alike.

The 2 times multiplication table, often referred to as the table of 2, outlines the results of multiplying the number 2 by various whole numbers. It effectively demonstrates how adding the number 2 repeatedly, for a specific number of times, corresponds to multiplication. For instance, multiplying 2 by 3 (2 x 3) is equivalent to adding 2 to itself three times (2+2+2), resulting in 6. By applying this principle to different numbers, a variety of outcomes are generated. The multiplication table of 2, extending to multiplying by up to 20, is a crucial tool for quick calculations, significantly benefiting students in time-sensitive exams.
Providing the table of 2 in diverse formats aids in its memorization, offering an invaluable resource for students. Mastery of the 2 times table is fundamental, as it enhances mental math capabilities, deepens number sense, and lays the foundation for tackling more sophisticated mathematical challenges with ease. Understanding that the table of 2 represents sequential additions of the number 2 is key to grasping basic multiplication concepts, such as 2 + 2 + 2 equating to 2 x 3 = 6.
Multiplication Table of 2 Charts

Multiplication from ( 1-10 ) | Multiplication from ( 11 -20 ) |
|---|---|
2 x 1 = 2 | 2 x 11 = 22 |
2 x 2 = 4 | 2 x 12 = 24 |
2 x 3 = 6 | 2 x 13 = 26 |
2 x 4 = 8 | 2 x 14 = 28 |
2 x 5 = 10 | 2 x 15 = 30 |
2 x 6 = 12 | 2 x 16 = 32 |
2 x 7 = 14 | 2 x 17 = 34 |
2 x 8 = 16 | 2 x 18 = 36 |
2 x 9 = 18 | 2 x 19 = 38 |
2 x 10 = 20 | 2 x 20 = 40 |
The Multiplication Table of 2 lays the groundwork for understanding and applying one of the most basic yet crucial mathematical operations. It systematically lists the products of multiplying numbers by 2, providing a clear and concise reference for students. This table not only aids in memorization but also in the development of pattern recognition and algebraic thinking. As a vital component of mathematics education, the Multiplication Table of 2 equips students with the skills necessary to tackle more complex mathematical challenges, fostering a solid foundation in multiplication.
The 2 times table is a foundational element of mathematics, serving as the bedrock for understanding multiplication, division, and even more complex arithmetic operations. Mastering this table equips students with the skills necessary for quicker mental math, facilitating a smoother transition to advanced mathematical concepts. It’s not just about memorizing numbers; it’s about unlocking the door to mathematical fluency and confidence.
Multiplication | Result |
|---|---|
2 x 1 | 2 |
2 x 2 | 4 |
2 x 3 | 6 |
2 x 4 | 8 |
2 x 5 | 10 |
2 x 6 | 12 |
2 x 7 | 14 |
2 x 8 | 16 |
2 x 9 | 18 |
2 x 10 | 20 |
Unlocking the 2 times table is more than rote learning; it’s about applying strategic tips and techniques to ensure students grasp and retain this essential math skill. Here are insights to make learning this table both effective and engaging:
Doubling Strategy: Emphasize that multiplying by 2 is the same as doubling the number, a concept familiar to students even from early addition.
Pattern Recognition: Highlight the pattern that results appear in even numbers, aiding in quicker identification and memorization.
Use Real-Life Examples: Incorporate examples like pairs of shoes or eyes to make the concept relatable and memorable.
Practice Regularly: Encourage daily practice with flashcards or timed quizzes to build speed and confidence.
Incorporate Games: Leverage educational games and activities that focus on the 2 times table to make learning fun and interactive.
By implementing these tips, educators can ensure that students not only learn the 2 times table but also understand the underlying principles, setting a solid foundation for future mathematical learning.
Dive into the multiplication journey with the table of 2 from 11 to 20, a fundamental building block for young learners mastering basic arithmetic. This table extends the concept of doubling, reinforcing numerical fluency and preparing students for more complex mathematical challenges. Essential for educators, this guide ensures students grasp multiplication’s core principles, enhancing their confidence and skills in mathematics.
Number | Result |
|---|---|
2 x 11 | 22 |
2 x 12 | 24 |
2 x 13 | 26 |
2 x 14 | 28 |
2 x 15 | 30 |
2 x 16 | 32 |
2 x 17 | 34 |
2 x 18 | 36 |
2 x 19 | 38 |
2 x 20 | 40 |
Below is the table of 2 from 1 to 20, including three columns: Number (indicating the multiplier), Addition (showing the incremental addition of 2), and Result (the outcome of multiplying 2 by the number).
2 + 2 + 2 = 2×1 + 2×1 + 2×1
= 2(1 + 1+ 1) [using the distributive property of multiplication]
= 2(3)
2 + 2 + 2 = 2 × 3
Number | Addition | Addition to Previous Result | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
2 x 1 | 2 + 0 | 2 | 2 |
2 x 2 | 2 + 2 | 2+2 | 4 |
2 x 3 | 2 + 2 + 2 | 4+2 | 6 |
2 x 4 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 6+2 | 8 |
2 x 5 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 8+2 | 10 |
2 x 6 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 10+2 | 12 |
2 x 7 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 12+2 | 14 |
2 x 8 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 +2 + 2 + 2 | 14+2 | 16 |
2 x 9 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 +2 + 2 + 2+ 2 | 16+2 | 18 |
2 x 10 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 +2 + 2 + 2+ 2 + 2 | 18+2 | 20 |
This table illustrates the pattern of adding 2 to the result of the previous multiplication to get the next result, providing a clear understanding of the progression within the 2 times table.
Mastering the 2 times table is a fundamental step in developing math fluency. This essential skill lays the groundwork for multiplication, a key concept in arithmetic. By understanding the 2 times table, students can easily double numbers, an ability that enhances mental math skills and prepares them for more complex multiplication tasks. Here are points to guide you through reading the 2 times table effectively:
One time 2 is 2
Two times 2 is 4
Three times 2 is 6
Four times 2 is 8
Five times 2 is 10
Six times 2 is 12
Seven times 2 is 14
Eight times 2 is 16
Nine times 2 is 18
Ten times 2 is 20
Start with Zero: Understand that any number times zero is zero. Thus, 2 x 0 = 0.
Increment by Two: Progress by adding 2 for each step. For example, 2 x 1 = 2, then 2 x 2 = 4.
Use Patterns: Recognize the pattern that results are even numbers, making it easier to anticipate subsequent values.
Memorization: Commit the table to memory for quicker recall. This helps in speeding up calculations in future math problems.
Practical Application: Apply your knowledge of the 2 times table in real-life scenarios, such as calculating double quantities or distributing items evenly.
By following these points, students can confidently navigate through the 2 times table, setting a solid foundation for mastering multiplication.
The table of 2 exclusively consists of even numbers, including 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, and so forth. It initiates with the number 2. To determine the subsequent term in the series, simply add 2 to the preceding number. Additionally, employing skip counting by one from 2—omitting the odd numbers in between—also yields the table of 2, such as 2, 4 (skipping 3), 6 (skipping 5), and continuing in this pattern.
Question: What is 2 times 3?
Solution: To find 2 times 3, you multiply 2 by 3.
Calculation: 2 x 3 = 6
Answer: 2 times 3 equals 6.
Question: How much is 2 added to itself 4 times?
Solution: Adding 2 to itself 4 times is the same as multiplying 2 by 4.
Calculation: 2 x 4 = 8
Answer: 2 added to itself 4 times equals 8.
Question: If a pair of socks costs $2, how much will 5 pairs cost?
Solution: Multiply the cost of one pair by the number of pairs.
Calculation: 2 x 5 = 10
Answer: 5 pairs of socks cost $10.
Question: What is the double of 6?
Solution: Doubling a number is the same as multiplying it by 2.
Calculation: 2 x 6 = 12
Answer: The double of 6 is 12.
Question: How do you find the 8th even number?
Solution: Multiply 2 by 8, since every multiple of 2 is an even number.
Calculation: 2 x 8 = 16
Answer: The 8th even number is 16.
Question: If one apple costs 2 dollars, how much do 9 apples cost?
Solution: Multiply the cost of one apple by the total number of apples.
Calculation: 2 x 9 = 18
Answer: 9 apples cost $18.
Question: How many groups of 2 can you form with 10 items?
Solution: Divide the total number of items by 2.
Calculation: 10 ÷ 2 = 5
Answer: You can form 5 groups of 2 with 10 items.
The 2 times table is a cornerstone of multiplication, offering a straightforward path to mastering basic arithmetic. By understanding and applying this table, learners can enhance their numerical fluency, laying a solid foundation for more complex mathematical concepts. Its simplicity and wide application make it an essential tool for students and educators alike.
Text prompt
Add Tone
Multiplication Table of 2
Tips for 2 Times Table
What is 2 multiplied by 9?
16
18
20
22
What is 2 times 14?
26
28
30
32
If you divide 24 by 2, what is the result?
10
12
14
16
What is 2 multiplied by 15?
28
30
32
34
What is 2 times 6?
10
11
12
13
What is the result of multiplying 2 by 11?
19
20
21
22
How much is 2 times 7?
12
14
16
18
What is 2 multiplied by 20?
38
39
40
41
If 2 is multiplied by 5, what do you get?
8
10
12
14
What is the product of 2 and 18?
34
36
38
40
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

