What is the value of sin 30 degrees?
0.5
0.6
0.7
1

Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships involving lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. It primarily deals with the sine, cosine, and tangent functions, which are ratios of sides of right triangles. These functions have profound applications in both theoretical and practical aspects, including physics, engineering, surveying, and computer graphics.
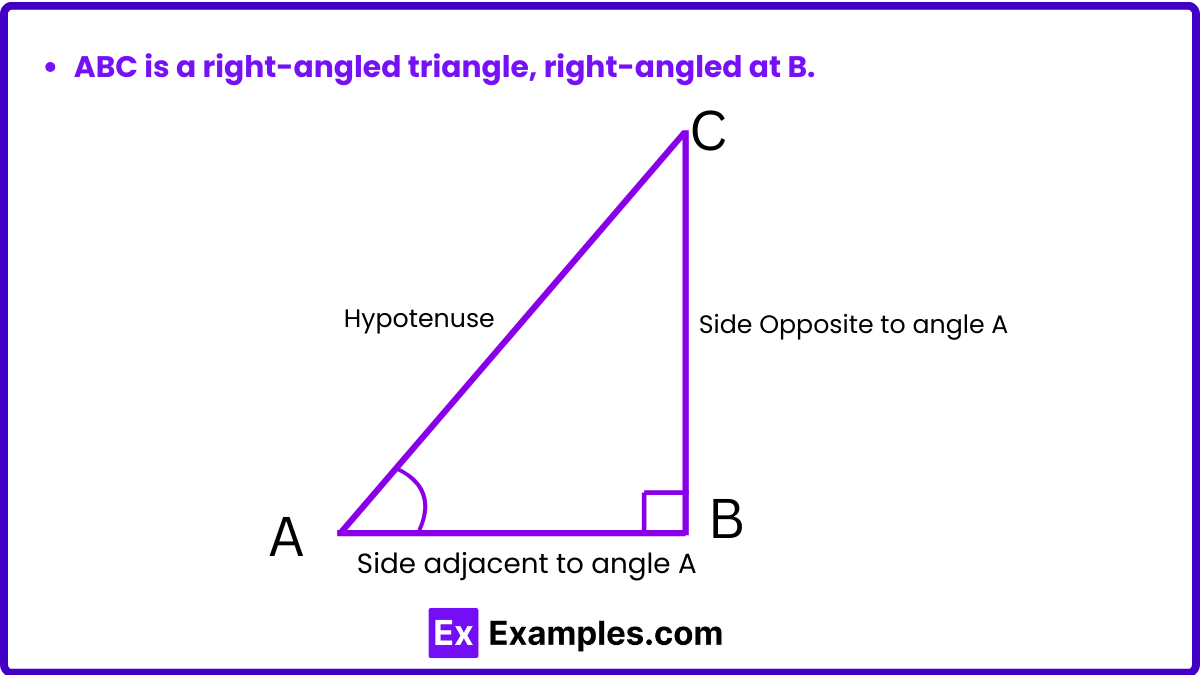
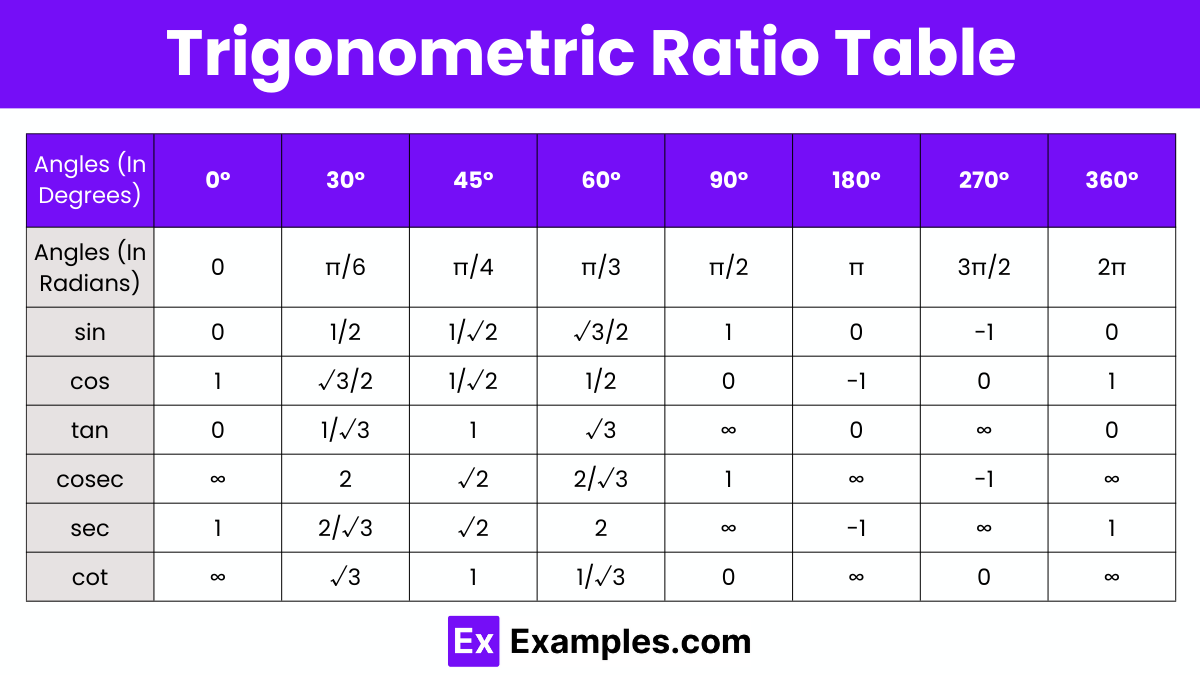
Trigonometric ratios are fundamental to the study of trigonometry and are used to relate the angles and sides of a right triangle. The three primary trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent, commonly abbreviated as sin, cos, and tan, respectively. Here’s a breakdown of each:
The sine of an angle in a right triangle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as: sin(θ)=opposite/hypotenuse
The cosine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is defined as: cos(θ)=adjacent/hypotenuse
The tangent of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side. It is defined as: tan(θ)=opposite/adjacent
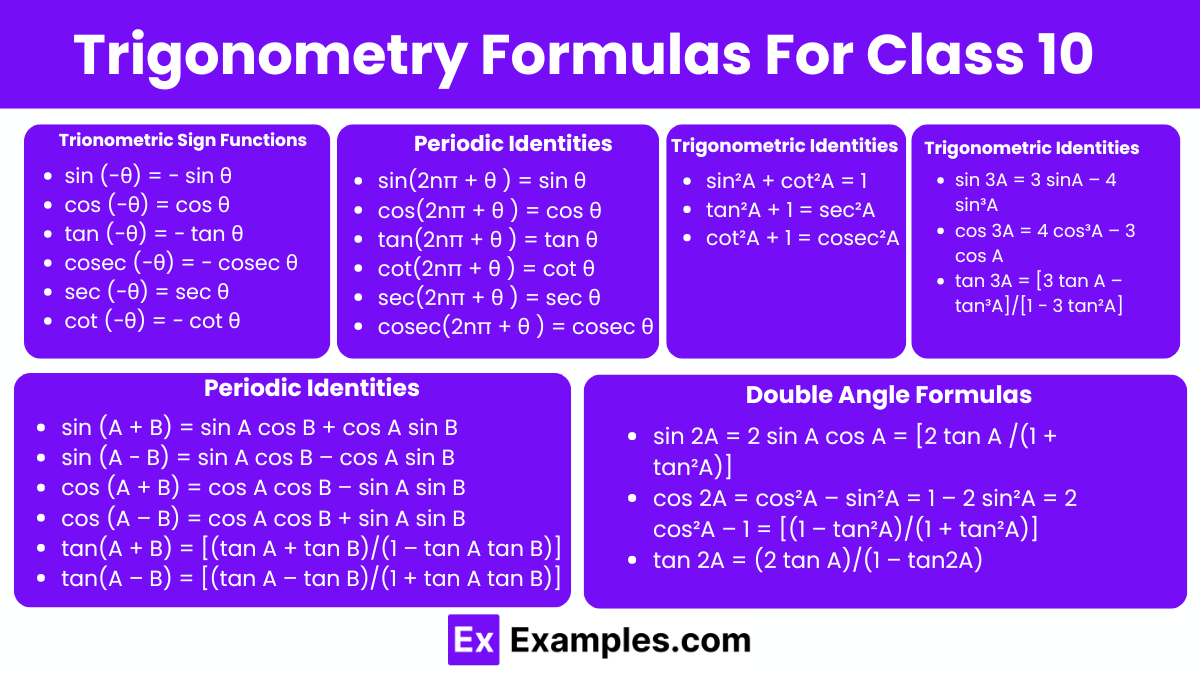
Odd Trigonometric Functions: A trigonometric function is classified as odd if it satisfies the condition f(−x)=−f(x) This implies that the function is symmetric with respect to the origin, meaning that reflecting the function across both axes results in the same graph.
Even Trigonometric Functions: A trigonometric function is classified as even if it satisfies the condition f(−x)=f(x). This indicates that the function is symmetric about the y-axis, meaning that reflecting the function across the y-axis results in the same graph.
| Function | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sine (sin) | (sin(-x) = -sin(x)) | Sine is an odd function. |
| Cosine (cos) | (cos(-x) = cos(x)) | Cosine is an even function. |
| Tangent (tan) | (tan(-x) = -tan(x)) | Tangent is an odd function. |
| Cosecant (csc) | (csc(-x) = -csc(x)) | Cosecant is an odd function. |
| Secant (sec) | (sec(-x) = sec(x)) | Secant is an even function. |
| Cotangent (cot) | (cot(-x) = -cot(x)) | Cotangent is an odd function. |
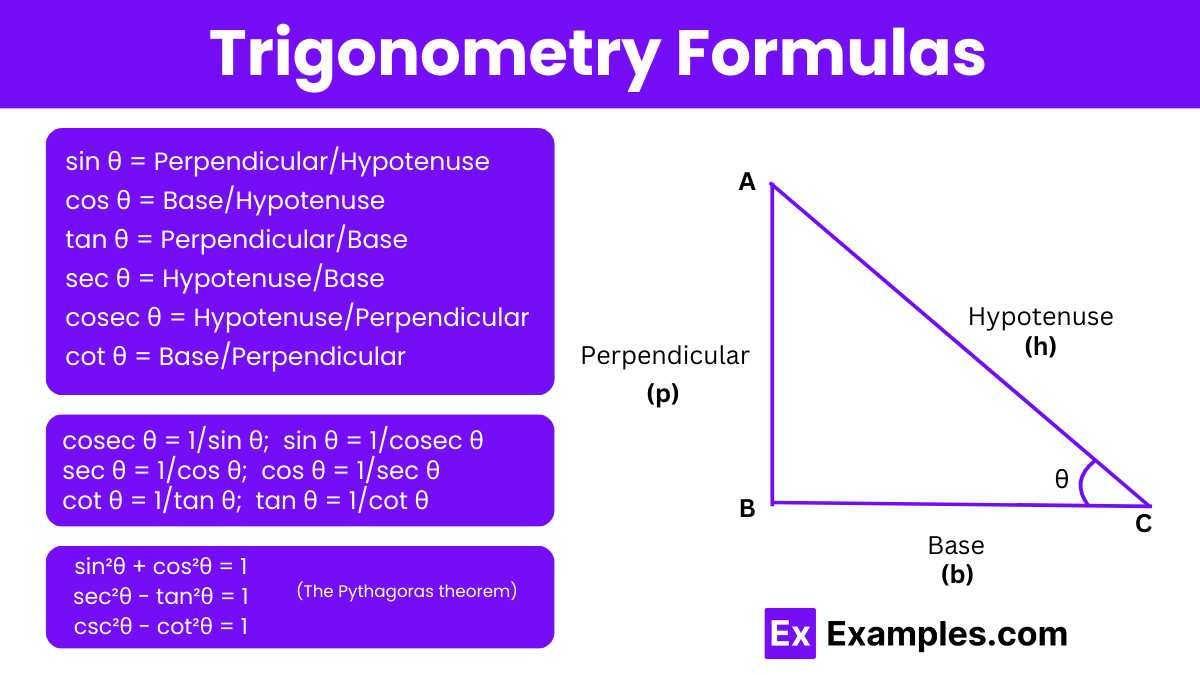
Cosecant, secant, and cotangent are the reciprocals of the basic trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, and tangent, respectively. These reciprocal identities are derived from the properties of a right-angled triangle and play a crucial role in trigonometry. They are often used to simplify and solve trigonometric problems. The formulas for these reciprocal trigonometric identities, which are essential for various calculations and transformations in trigonometry, are:
The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (ccc) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (aaa and bbb). Mathematically, this is expressed as: c² = a² + b² ,Using this theorem, we can derive Pythagorean identities in trigonometry, which allow us to convert one trigonometric ratio into another. These identities are fundamental in simplifying and solving trigonometric equations.
These formulas are used to shift the angles by π/2, π, 2π, etc. They are also called co-function identities.
Quadrant I
Quadrant II
Quadrant III
Quadrant IV
Trigonometry is typically taught in high school, usually in the 10th or 11th grade, depending on the school curriculum and the student’s track in mathematics.
Basic knowledge of trigonometry includes understanding angles, trigonometric ratios like sine, cosine, and tangent, and how to apply these to calculate distances and angles in triangles.
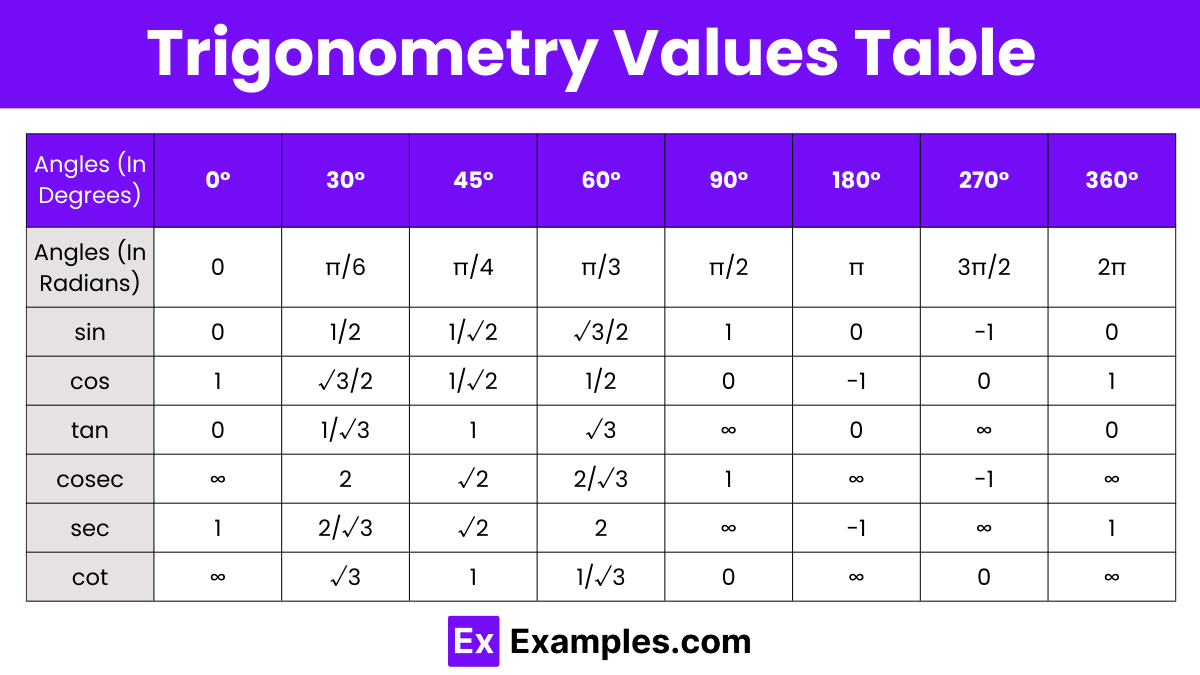
To do trigonometry easily, familiarize yourself with the unit circle, common angle values, and trigonometric identities. Practice solving problems step-by-step and use visual aids to help understand concepts better.
Trigonometry can be challenging for some students due to its abstract concepts and the need to understand both geometric and algebraic representations of problems.
Trigonometry focuses on the relationships within triangles, particularly right triangles, using angles and ratio functions. Geometry is broader, dealing with properties and relations of points, lines, surfaces, and solids.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the value of sin 30 degrees?
0.5
0.6
0.7
1
What is the value of cos 90 degrees?
0
0.5
1
-1
What is the tangent of 45 degrees?
0
0.5
1
2
Which of the following is the Pythagorean identity?
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
sin²θ + tan²θ = 1
cos²θ - sin²θ = 1
tan²θ + 1 = sin²θ
What is the value of tan 30 degrees?
√3
1
√3/3
2
Which function represents the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side in a right triangle?
Cosine
Sine
Tangent
Secant
What is the value of sin(30°)?
0
0.5
0.7
1
What is cos(90°)?
0
0.5
1
-1
What is the value of sin(90°)?
0
0.5
1
2
What is the value of sin(45°)?
0.5
0.707
0.866
1
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

