Demographics is the study of statistical data related to populations, including variables such as age, gender, race, income, education, and migration. It helps identify patterns and trends that influence societal dynamics and healthcare needs. Understanding demographics is essential for analyzing public health issues, forecasting resource demands, and addressing health disparities. The MCAT emphasizes concepts like fertility, mortality, population growth, and aging to evaluate how these factors shape health outcomes and healthcare access, preparing students to address population-level health challenges effectively.
Learning Objectives
In studying "Demographics" for the MCAT, you should learn to understand key population variables, including age, gender, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. Analyze how demographic factors impact healthcare access, public health policies, and health disparities. Evaluate models like the demographic transition and explore concepts such as fertility, mortality, migration, and population aging. Additionally, examine how shifts in demographics influence healthcare demand and resource distribution. Apply your understanding to interpret real-world public health data, predict trends in population health, and analyze demographic-related scenarios in MCAT practice passages, emphasizing the role of social determinants in health outcomes.
Demographics provide a statistical framework for analyzing populations, which helps in understanding trends related to birth rates, mortality, migration, and aging. These insights are essential for healthcare professionals to grasp public health challenges, plan interventions, and anticipate healthcare needs. The MCAT includes demographic concepts to assess your understanding of population dynamics and how they influence health outcomes.
1. Key Concepts in Demographics
Demographic Variables:
Demographics refer to measurable characteristics of populations, such as:Age
Gender
Race and Ethnicity
Education Level
Income and Occupation
Geographic Location
Population Size:
The total number of people within a defined geographic region. It determines the resources needed, including healthcare infrastructure, and helps predict trends like overpopulation or population decline.Population Density:
The number of people per unit area. Higher density can stress healthcare systems (e.g., in urban centers), while lower density may lead to limited access to healthcare (e.g., in rural areas).
2. Demographic Transition Model
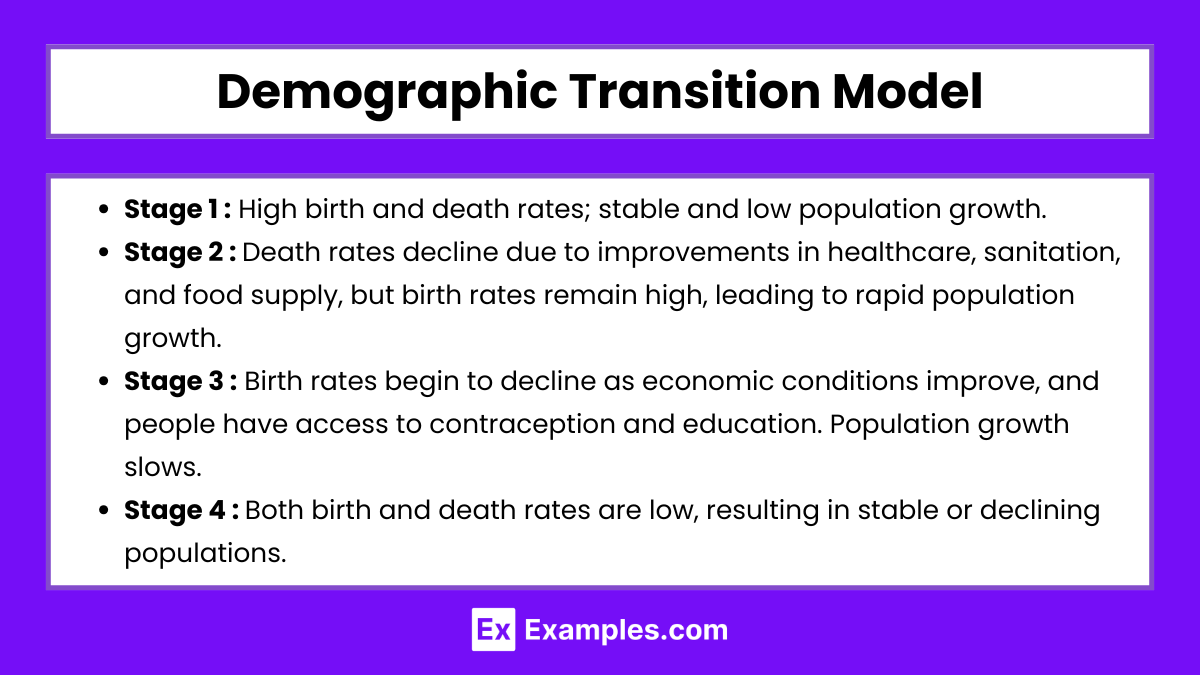
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM) describes the shift in birth and death rates as a country develops, often broken into four stages:
Stage 1: High birth and death rates; stable and low population growth.
Example: Pre-industrial societies with high infant mortality rates.Stage 2: Death rates decline due to improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and food supply, but birth rates remain high, leading to rapid population growth.
Example: Early industrial societies.Stage 3: Birth rates begin to decline as economic conditions improve, and people have access to contraception and education. Population growth slows.
Example: Developing countries experiencing urbanization.Stage 4: Both birth and death rates are low, resulting in stable or declining populations.
Example: Highly industrialized nations like Japan.
3. Fertility, Mortality, and Migration
Fertility Rate:
The average number of children a woman is expected to have over her lifetime. High fertility rates can lead to population growth, increasing demand for healthcare services like maternal and child care.Mortality Rate:
The number of deaths in a population over a specific period. High mortality rates indicate poor health conditions, often prompting public health interventions.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) measures the number of infants dying before one year of age per 1,000 live births. It is a crucial indicator of healthcare quality.Migration:
Refers to the movement of people between regions or countries. Migration affects population size and structure and can impact healthcare services.Immigration: Inflow of people, increasing population size.
Emigration: Outflow of people, reducing population size.
Migrants often face healthcare challenges, such as access to services, cultural barriers, and language differences.
4. Aging Population and Its Impact on Healthcare
Aging Population:
An increase in the proportion of older adults due to higher life expectancy and declining birth rates. Aging populations strain healthcare systems by increasing the demand for chronic disease management and long-term care services.Dependency Ratio:
The ratio of non-working individuals (children and elderly) to working-age individuals. A high dependency ratio indicates a greater economic burden on the workforce and challenges in funding healthcare services.Elderly Care:
As populations age, the need for specialized services such as geriatric care, nursing homes, and end-of-life care increases.
5. Demographic Shifts and Global Trends
Urbanization:
The movement of people from rural to urban areas. Urbanization can improve access to healthcare facilities but also leads to challenges like overcrowding, pollution, and increased mental health issues.Globalization:
The growing interconnection between nations impacts healthcare through the spread of diseases (e.g., COVID-19), medical innovations, and public health strategies.Overpopulation vs. Population Decline:
Overpopulation creates resource scarcity, leading to environmental degradation and healthcare system overload.
Population decline affects economies and healthcare systems, as fewer young people are available to support the elderly.
Examples
Example 1: Age Distribution
Age is a crucial demographic variable that affects healthcare needs and public policy. Different age groups face distinct health challenges—for example, infants may require immunization programs, while older adults often need chronic disease management and long-term care. An aging population increases the demand for geriatric care and impacts economic productivity, as fewer working-age individuals support a growing number of elderly people. The MCAT might test your understanding of how age distribution affects public health strategies and healthcare resource allocation.
Example 2: Gender and Sex
Gender and sex demographics help identify patterns in health outcomes, behaviors, and risks. For example, women may have higher rates of osteoporosis and require specialized maternal care, while men may experience higher incidences of cardiovascular disease. In addition, understanding the unique health challenges of transgender and non-binary individuals is increasingly important. The MCAT may assess your ability to recognize how gender roles and healthcare disparities affect the accessibility and quality of care for different populations.
Example 3: Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity are key demographic categories influencing healthcare disparities and public health outcomes. Racial minorities often face systemic barriers to healthcare, including limited access to preventive care and higher rates of chronic illnesses. For example, African American populations have higher risks of hypertension and diabetes, while certain genetic conditions, such as sickle cell anemia, are more prevalent in specific racial groups. The MCAT may present case studies that require you to analyze health disparities based on race and ethnicity.
Example 4: Socioeconomic Status (SES)
SES includes income, education, and occupation, all of which are significant predictors of health outcomes. Individuals with higher SES generally have better access to healthcare services, nutritious food, and healthy living environments. On the other hand, lower SES is associated with increased exposure to environmental hazards and limited access to preventive care. The MCAT may ask questions about how SES impacts health behaviors and outcomes, such as the relationship between education levels and health literacy.
Example 5: Migration Patterns
Migration impacts both the population size and health needs of regions. Immigration introduces diversity into the population, but it can also create challenges related to cultural competence, language barriers, and access to healthcare. For example, migrant populations may face higher risks of infectious diseases or mental health issues due to stress and displacement. The MCAT may assess your understanding of how migration patterns affect public health planning and how healthcare providers can address the unique needs of migrant communities.
Practice Questions
Question 1
Which demographic factor is most likely to influence the increased demand for geriatric healthcare services in a society?
A) High fertility rates
B) High birth rates
C) Increasing life expectancy
D) Declining population density
Recommended Answer: C) Increasing life expectancy
Explanation:
Increasing life expectancy leads to a larger elderly population, which creates a growing demand for geriatric healthcare services, such as chronic disease management, nursing homes, and end-of-life care.
High fertility rates (A) and high birth rates (B) lead to population growth, but they primarily increase the proportion of children and young adults rather than the elderly population.
Declining population density (D) affects access to healthcare in rural areas but does not directly correlate with the need for geriatric services.
Question 2
How does urbanization typically impact healthcare access in a country?
A) Improves healthcare access in rural areas
B) Reduces healthcare disparities between urban and rural populations
C) Increases access to healthcare facilities in urban areas
D) Eliminates the need for healthcare services in urban centers
Recommended Answer: C) Increases access to healthcare facilities in urban areas
Explanation:
Urbanization involves the movement of people from rural areas to cities, where healthcare facilities, such as hospitals and clinics, are more concentrated and accessible. This process generally increases access to healthcare for urban populations.
Option A is incorrect because urbanization can lead to a decline in healthcare availability in rural areas as resources and medical professionals concentrate in urban centers.
Option B is incorrect as disparities often widen between urban and rural populations due to uneven resource distribution.
Option D is incorrect because urban areas still require healthcare services to address the needs of growing populations, including emergency care and public health measures.
Question 3
Which of the following is a consequence of a high dependency ratio in a population?
A) Reduced need for healthcare services
B) Increased economic burden on the working population
C) Decrease in healthcare costs due to fewer elderly individuals
D) Higher levels of migration to reduce the dependent population
Recommended Answer: B) Increased economic burden on the working population
Explanation:
A high dependency ratio means that a large proportion of the population is not in the workforce (e.g., children and elderly), placing financial and social pressure on the working-age population to support them.
Option A is incorrect because healthcare needs typically increase with a high dependency ratio, especially if there are more elderly individuals who require medical care.
Option C is inaccurate because healthcare costs tend to rise when the elderly population increases.
Option D is not a direct consequence of a high dependency ratio, although migration can impact the workforce size indirectly.