Foundations of behavior passages: Practice Passages: Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior

- Notes
The MCAT’s “Foundations of Behavior” section tests your understanding of psychological, social, and biological factors that influence behavior. Mastering this section requires a solid grasp of key topics like neurotransmitters, learning theories, and sociocultural influences. By focusing on these areas and practicing passage-based questions, you can enhance your critical thinking skills and boost your exam performance.
Learning Objectives
The MCAT‘s “Foundations of Behavior” section tests your understanding of psychological, social, and biological factors that influence behavior. Mastering this section requires a solid grasp of key topics like neurotransmitters, learning theories, and sociocultural influences. By focusing on these areas and practicing passage-based questions, you can enhance your critical thinking skills and boost your exam performance.
Understanding the Biological Basis of Behavior
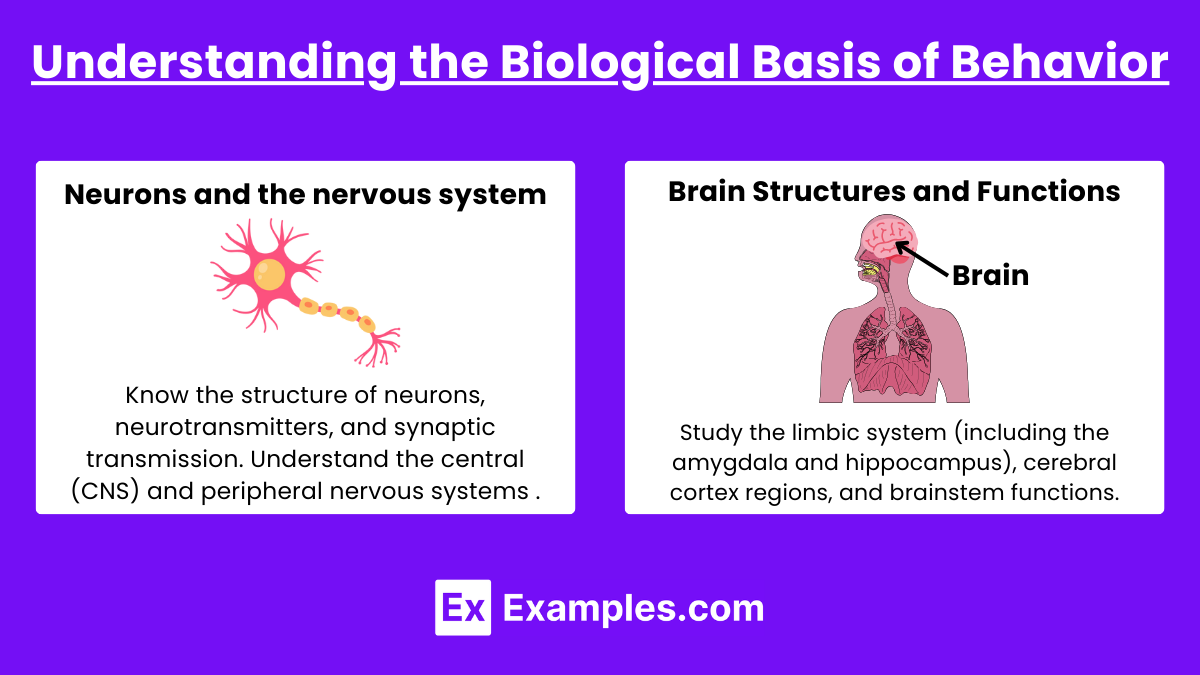
- Neurons and the Nervous System: Know the structure of neurons, neurotransmitters, and synaptic transmission. Understand the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS), with particular attention to the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
- Brain Structures and Functions: Study the limbic system (including the amygdala and hippocampus), cerebral cortex regions, and brainstem functions. Know how these structures are linked to behavior, emotion, and memory.
Theories of Psychological Development
- Cognitive Development: Familiarize yourself with Piaget’s stages and how they relate to cognitive abilities. Understand Vygotsky’s social learning theory and the concept of scaffolding.
- Social Development: Review Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development, focusing on identity, role confusion, and intimacy. Be able to relate these stages to real-life scenarios often found in passages.
Understanding Behavior and Mental Processes

Understanding Behavior and Mental Processes involves studying how humans think, feel, and act. Key areas include cognition, perception, learning, emotion, and motivation, along with the influence of biological, psychological, and social factors on behavior, providing insights into mental health and human interaction.
- Theories of Personality: Familiarize yourself with Freudian theory, the Big Five personality traits, and behaviorist perspectives.
- Motivation and Attitudes: Learn about intrinsic vs. extrinsic motivation, theories like Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, and how attitudes form and change.
- Emotion and Stress: Know the theories of emotion (James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Schachter-Singer) and understand how stress affects the body and behavior.
Sociocultural Influences on Behavior
Sociocultural Influences on Behavior explore how cultural norms, values, and social interactions shape individual actions, thoughts, and attitudes.
- Socialization and Norms: Study how socialization influences behavior and the impact of norms, values, and roles in society.
- Group Dynamics and Social Influence: Learn about conformity, obedience, groupthink, and how groups affect individual behavior.
- Culture and Identity: Understand cultural dimensions, social identity theory, and how culture influences perception and behavior.
Psychological Disorders and Treatments

Psychological Disorders and Treatments examine various mental health conditions, their symptoms, and effective therapeutic approaches, including psychotherapy and medication options.
- Classification and Diagnosis: Familiarize yourself with the DSM-5 and common disorders, such as anxiety disorders, mood disorders, and schizophrenia.
- Theories and Models of Psychological Disorders: Review biological, psychological, and sociocultural models of mental illness.
- Therapies and Treatment Approaches: Know different therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychoanalysis, and biomedical treatments.
Examples
Example 1: Social Influence on Health Behaviors
A passage describes how peer pressure and social norms impact smoking habits among adolescents. It explores concepts like conformity, social learning, and the role of group dynamics in influencing behavior, highlighting the significance of understanding social factors when designing health interventions.
Example 2: The Role of Neurotransmitters in Mood Disorders
A passage discusses how imbalances in serotonin and dopamine contribute to depression. It explains the biological basis of mood disorders and emphasizes the importance of neurotransmitters in regulating mood, illustrating how pharmacological treatments target these neurotransmitters to alleviate symptoms.
Example 3: Memory and Cognitive Decline in Aging
This passage examines how aging affects memory retention and cognitive function. It covers topics such as the role of the hippocampus, age-related neural changes, and factors that mitigate cognitive decline, emphasizing the interplay between biology and environmental factors in maintaining cognitive health.
Example 4: Impact of Culture on Perception of Time
A passage explores cultural differences in time perception, contrasting societies that prioritize punctuality versus those with a more relaxed attitude toward time. It delves into how cultural norms influence daily behavior and interpersonal relationships, illustrating the role of sociocultural factors in shaping individual perceptions.
Example 5: Effects of Operant Conditioning in Classroom Settings
The passage explains how positive and negative reinforcement shape student behavior in a classroom. It outlines principles of operant conditioning, such as reward schedules and punishment, and discusses their effectiveness in promoting learning and managing classroom behavior.
Practice Questions
Question 1:
Which of the following neurotransmitters is most directly associated with mood regulation and is commonly targeted by antidepressant medications?
A) Dopamine
B) Serotonin
C) Acetylcholine
D) Glutamate
Answer: B) Serotonin
Explanation: Serotonin is a neurotransmitter primarily involved in mood regulation, as well as in controlling sleep, appetite, and other bodily functions. Many antidepressants, particularly SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors), work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain to improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression. Dopamine is more associated with reward and motivation, while acetylcholine and glutamate are involved in memory and learning processes.
Question 2:
In a study, researchers observe that students are more likely to engage in academic dishonesty if they believe that their peers are also cheating. This scenario best exemplifies which psychological concept?
A) Cognitive dissonance
B) Social facilitation
C) Conformity
D) Operant conditioning
Answer: C) Conformity
Explanation: Conformity refers to the tendency of individuals to align their behaviors, beliefs, or attitudes with those of a group. In this scenario, students are influenced by the perceived actions of their peers, leading them to conform to the behavior of academic dishonesty. Cognitive dissonance involves the discomfort felt when holding conflicting beliefs, social facilitation refers to improved performance in the presence of others, and operant conditioning involves learning behaviors through rewards and punishments.
Question 3:
A researcher studying memory processes finds that older adults have more difficulty recalling new information than younger adults, which is thought to be due to decreased activity in which part of the brain?
A) Amygdala
B) Prefrontal cortex
C) Hippocampus
D) Cerebellum
Answer: C) Hippocampus
Explanation: The hippocampus plays a critical role in forming new memories and is one of the first areas of the brain to show decline with age, which can impact memory recall. The amygdala is primarily associated with emotions, the prefrontal cortex with decision-making and executive functions, and the cerebellum with balance and coordination. Therefore, the hippocampus is the area most directly associated with the challenges older adults face in recalling new information.
The MCAT's "Foundations of Behavior" section tests your understanding of psychological, social, and biological factors that influence behavior. Mastering this section requires a solid grasp of key topics like neurotransmitters, learning theories, and sociocultural influences. By focusing on these areas and practicing passage-based questions, you can enhance your critical thinking skills and boost your exam performance.
Learning Objectives
The MCAT's "Foundations of Behavior" section tests your understanding of psychological, social, and biological factors that influence behavior. Mastering this section requires a solid grasp of key topics like neurotransmitters, learning theories, and sociocultural influences. By focusing on these areas and practicing passage-based questions, you can enhance your critical thinking skills and boost your exam performance.
Understanding the Biological Basis of Behavior
Neurons and the Nervous System: Know the structure of neurons, neurotransmitters, and synaptic transmission. Understand the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS), with particular attention to the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
Brain Structures and Functions: Study the limbic system (including the amygdala and hippocampus), cerebral cortex regions, and brainstem functions. Know how these structures are linked to behavior, emotion, and memory.
Theories of Psychological Development
Cognitive Development: Familiarize yourself with Piaget’s stages and how they relate to cognitive abilities. Understand Vygotsky’s social learning theory and the concept of scaffolding.
Social Development: Review Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development, focusing on identity, role confusion, and intimacy. Be able to relate these stages to real-life scenarios often found in passages.
Understanding Behavior and Mental Processes
Understanding Behavior and Mental Processes involves studying how humans think, feel, and act. Key areas include cognition, perception, learning, emotion, and motivation, along with the influence of biological, psychological, and social factors on behavior, providing insights into mental health and human interaction.
Theories of Personality: Familiarize yourself with Freudian theory, the Big Five personality traits, and behaviorist perspectives.
Motivation and Attitudes: Learn about intrinsic vs. extrinsic motivation, theories like Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, and how attitudes form and change.
Emotion and Stress: Know the theories of emotion (James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Schachter-Singer) and understand how stress affects the body and behavior.
Sociocultural Influences on Behavior
Sociocultural Influences on Behavior explore how cultural norms, values, and social interactions shape individual actions, thoughts, and attitudes.
Socialization and Norms: Study how socialization influences behavior and the impact of norms, values, and roles in society.
Group Dynamics and Social Influence: Learn about conformity, obedience, groupthink, and how groups affect individual behavior.
Culture and Identity: Understand cultural dimensions, social identity theory, and how culture influences perception and behavior.
Psychological Disorders and Treatments
Psychological Disorders and Treatments examine various mental health conditions, their symptoms, and effective therapeutic approaches, including psychotherapy and medication options.
Classification and Diagnosis: Familiarize yourself with the DSM-5 and common disorders, such as anxiety disorders, mood disorders, and schizophrenia.
Theories and Models of Psychological Disorders: Review biological, psychological, and sociocultural models of mental illness.
Therapies and Treatment Approaches: Know different therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychoanalysis, and biomedical treatments.
Examples
Example 1: Social Influence on Health Behaviors
A passage describes how peer pressure and social norms impact smoking habits among adolescents. It explores concepts like conformity, social learning, and the role of group dynamics in influencing behavior, highlighting the significance of understanding social factors when designing health interventions.
Example 2: The Role of Neurotransmitters in Mood Disorders
A passage discusses how imbalances in serotonin and dopamine contribute to depression. It explains the biological basis of mood disorders and emphasizes the importance of neurotransmitters in regulating mood, illustrating how pharmacological treatments target these neurotransmitters to alleviate symptoms.
Example 3: Memory and Cognitive Decline in Aging
This passage examines how aging affects memory retention and cognitive function. It covers topics such as the role of the hippocampus, age-related neural changes, and factors that mitigate cognitive decline, emphasizing the interplay between biology and environmental factors in maintaining cognitive health.
Example 4: Impact of Culture on Perception of Time
A passage explores cultural differences in time perception, contrasting societies that prioritize punctuality versus those with a more relaxed attitude toward time. It delves into how cultural norms influence daily behavior and interpersonal relationships, illustrating the role of sociocultural factors in shaping individual perceptions.
Example 5: Effects of Operant Conditioning in Classroom Settings
The passage explains how positive and negative reinforcement shape student behavior in a classroom. It outlines principles of operant conditioning, such as reward schedules and punishment, and discusses their effectiveness in promoting learning and managing classroom behavior.
Practice Questions
Question 1:
Which of the following neurotransmitters is most directly associated with mood regulation and is commonly targeted by antidepressant medications?
A) Dopamine
B) Serotonin
C) Acetylcholine
D) Glutamate
Answer: B) Serotonin
Explanation: Serotonin is a neurotransmitter primarily involved in mood regulation, as well as in controlling sleep, appetite, and other bodily functions. Many antidepressants, particularly SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors), work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain to improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression. Dopamine is more associated with reward and motivation, while acetylcholine and glutamate are involved in memory and learning processes.
Question 2:
In a study, researchers observe that students are more likely to engage in academic dishonesty if they believe that their peers are also cheating. This scenario best exemplifies which psychological concept?
A) Cognitive dissonance
B) Social facilitation
C) Conformity
D) Operant conditioning
Answer: C) Conformity
Explanation: Conformity refers to the tendency of individuals to align their behaviors, beliefs, or attitudes with those of a group. In this scenario, students are influenced by the perceived actions of their peers, leading them to conform to the behavior of academic dishonesty. Cognitive dissonance involves the discomfort felt when holding conflicting beliefs, social facilitation refers to improved performance in the presence of others, and operant conditioning involves learning behaviors through rewards and punishments.
Question 3:
A researcher studying memory processes finds that older adults have more difficulty recalling new information than younger adults, which is thought to be due to decreased activity in which part of the brain?
A) Amygdala
B) Prefrontal cortex
C) Hippocampus
D) Cerebellum
Answer: C) Hippocampus
Explanation: The hippocampus plays a critical role in forming new memories and is one of the first areas of the brain to show decline with age, which can impact memory recall. The amygdala is primarily associated with emotions, the prefrontal cortex with decision-making and executive functions, and the cerebellum with balance and coordination. Therefore, the hippocampus is the area most directly associated with the challenges older adults face in recalling new information.

