Self-identity refers to how individuals perceive themselves in relation to their social environment. Key theories include Erikson's stages of psychosocial development, which track identity formation across life stages, and Mead's social self theory, emphasizing social interaction in self-concept development. Identity formation involves personal identity (individual beliefs) and social identity (group roles). Social identity theory explores how group membership affects behavior. Concepts like self-concept, self-esteem, and self-efficacy explain how individuals evaluate their abilities and worth, all contributing to overall self-identity.
Learning Objectives
In studying "Self-identity" for the MCAT, you should aim to understand how psychological theories and concepts related to self-identity explain individual and social behavior. Key objectives include analyzing Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development, focusing on identity formation, and understanding Mead’s theory of the social self. You should also explore how social identity theory explains group dynamics, and how personal identity differs from social identity. Additionally, examine how self-concept, self-esteem, and self-efficacy influence individual perceptions and actions, and how these concepts relate to behavioral outcomes in various contexts.
Self-identity refers to how individuals perceive themselves in terms of personal attributes, beliefs, values, and roles. It is a key concept in psychology and sociology, impacting behavior, motivation, and social interactions. Understanding self-identity is essential for the MCAT, especially within the context of behavioral sciences.
Key Theories of Self-identity
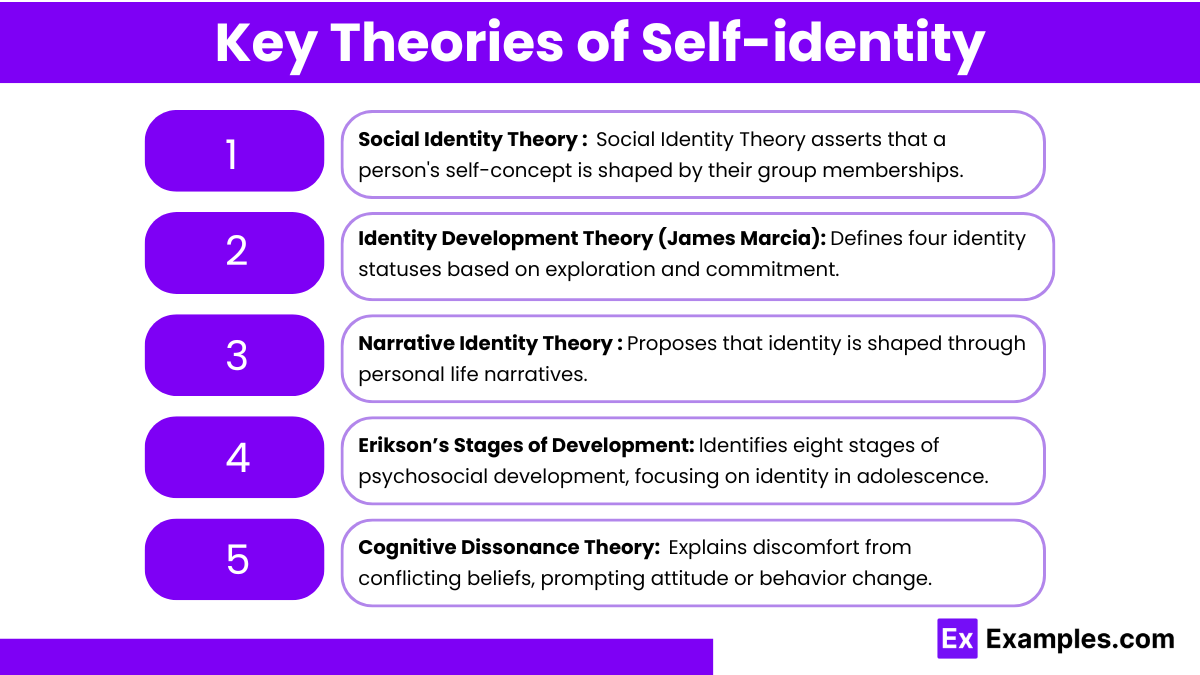
Social Identity Theory
Developed by Henri Tajfel and John Turner.
Proposes that a person’s self-concept is derived from their group memberships (e.g., ethnicity, religion, gender).
Emphasizes in-group favoritism and out-group discrimination, influencing social behaviors and attitudes.
Erikson’s Stages of Development
Proposed by Erik Erikson, focusing on psychosocial development across the lifespan.
Key stage: Identity vs. Role Confusion during adolescence, where individuals explore their personal and social identities.
Successful resolution leads to a strong sense of self, while failure results in confusion about one’s identity.
Identity Development Theory (James Marcia)
Expands on Erikson’s work, identifying four identity statuses:
Identity Diffusion: Lack of commitment and exploration.
Identity Foreclosure: Commitment without exploration (e.g., adopting parental beliefs).
Identity Moratorium: Active exploration without commitment.
Identity Achievement: Commitment after exploration.
Narrative Identity Theory
Suggests that individuals create personal narratives to make sense of their lives and identities.
These narratives are shaped by experiences, cultural influences, and personal reflections.
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Proposed by Leon Festinger, it describes the mental discomfort experienced when holding contradictory beliefs or values.
Individuals may change their beliefs or behaviors to reduce dissonance, which can affect self-identity.
Key Concepts of Self-identity
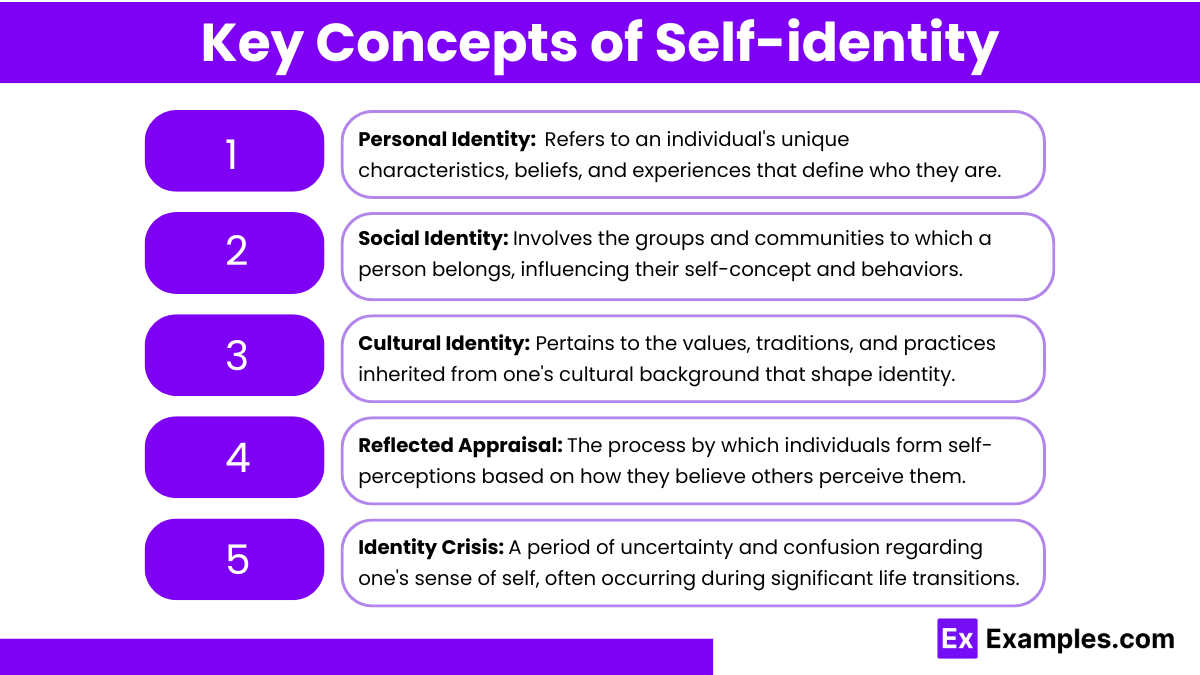
Personal Identity
Refers to individual characteristics, beliefs, and experiences that define a person.
Influences self-esteem and personal development.
Social Identity
Comprises the groups and communities to which a person belongs.
Affects behavior and attitudes towards others, impacting social interactions.
Cultural Identity
Involves the cultural background, traditions, and values that shape one’s worldview.
Influences how individuals relate to others from different cultural contexts.
Reflected Appraisal
The process by which individuals form self-perceptions based on how they believe others view them.
Plays a crucial role in developing self-esteem and self-concept.
Identity Crisis
A period of uncertainty and confusion in which an individual questions their sense of self.
Often occurs during adolescence but can happen at any stage of life due to significant changes.
The practice of recognizing and asserting one’s self-worth and values.
Can enhance resilience and improve mental health.
Applications of Self-Identity
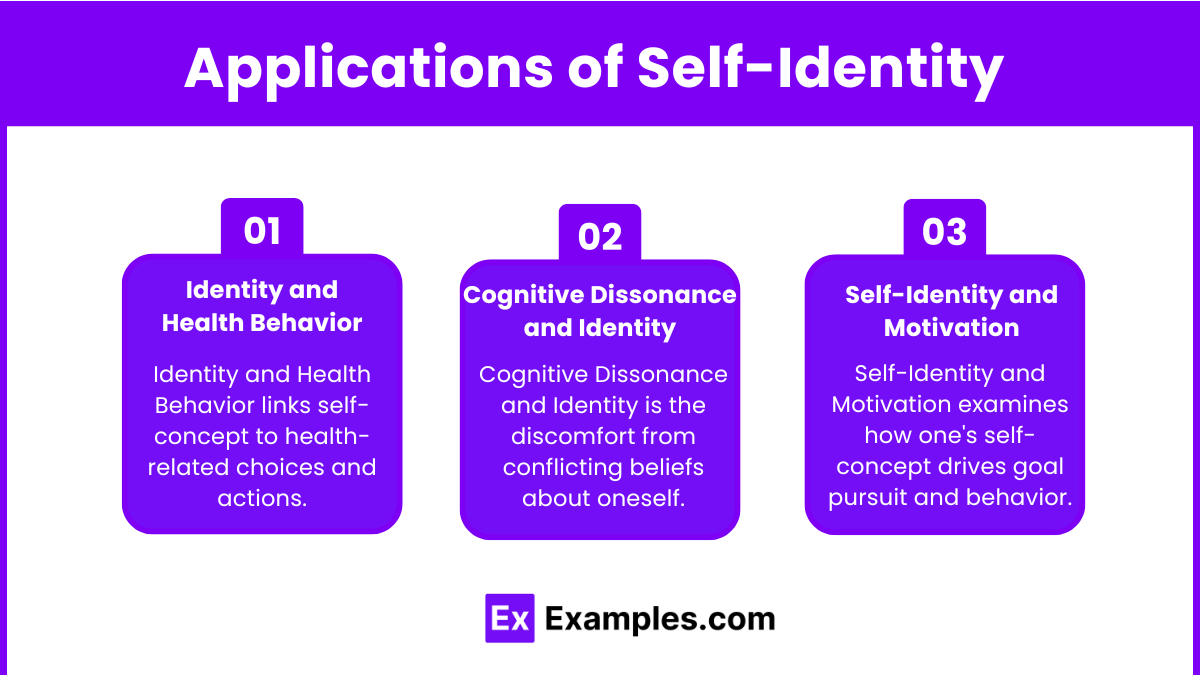
Identity and Health Behavior:
A person’s self-identity can impact health-related behaviors. For example, individuals who identify strongly with being healthy are more likely to engage in activities that promote well-being (e.g., exercising, avoiding smoking).
MCAT questions may ask you to analyze how changes in self-identity influence lifestyle choices and adherence to medical advice.
Cognitive Dissonance and Identity:
Cognitive dissonance occurs when there is a conflict between one’s behavior and self-identity.
For instance, someone who identifies as an environmentalist might feel discomfort if they engage in environmentally harmful activities, leading them to change their behavior or justify it to reduce dissonance.
Expect MCAT questions that assess how individuals resolve identity conflicts and dissonance.
Self-Identity and Motivation:
Self-identity is a powerful motivator of behavior. People strive to act in ways that align with their identity to maintain consistency.
For example, someone who identifies as a compassionate person might be motivated to volunteer or help others.
Understanding the link between self-identity and motivation will be critical in answering MCAT questions on behavioral patterns.
Examples
Example 1 : A student identifying as an academic achiever:
A student who sees themselves as a high achiever academically may adopt study habits and a rigorous work ethic to maintain that identity. They might prioritize completing assignments early, engaging in extra study sessions, or seeking out challenging coursework because doing so aligns with their self-concept of being a dedicated student.
Example 2 : A healthcare professional identifying as compassionate:
A nurse who identifies as a compassionate caregiver may go the extra mile to provide emotional support to their patients. Their self-identity as someone who cares deeply about others drives them to spend additional time comforting patients, advocating for their needs, or offering reassurance, even in challenging situations.
Example 3 :An individual identifying as environmentally conscious:
A person who identifies as an environmentalist may make lifestyle choices that reflect this self-concept, such as reducing plastic use, recycling, or choosing sustainable products. Even in situations where it is inconvenient, they adhere to eco-friendly practices because it aligns with their identity and values.
Example 4 : A professional identifying as a leader:
Someone who sees themselves as a leader in their workplace may take on additional responsibilities or guide team members to achieve collective goals. Their leadership identity encourages them to mentor others, make decisive decisions, and manage conflicts, reinforcing their role as a key figure in organizational success.
Example 5 : An athlete identifying as resilient:
An athlete who identifies as resilient may push through setbacks, such as injuries or losses, without giving up. Their self-identity as a resilient individual motivates them to stay focused on recovery and improvement, often leading them to adopt positive coping strategies and perseverance in the face of adversity.
Multiple Choice Practice Questions
Question 1
Which of the following best describes self-concept?
A. How one views their physical appearance
B. The roles and expectations society imposes on individuals
C. A person's understanding of who they are, including personal attributes, beliefs, and values
D. A temporary state of mind influenced by emotions
Answer: C. A person's understanding of who they are, including personal attributes, beliefs, and values
Explanation:
Self-concept refers to the comprehensive understanding an individual has of themselves, including their traits, beliefs, values, and roles. This concept encompasses various aspects of a person's identity, such as self-image, self-esteem, and the ideal self. Option A refers only to physical appearance, which is a narrow aspect of self-concept. Option B describes social roles and expectations, which may influence identity but do not fully capture self-concept. Option D refers to a temporary state of mind, which is unrelated to the more stable and lasting concept of self-identity. Therefore, the correct answer is C, as it best encapsulates self-concept as a broad and enduring understanding of oneself.
Question 2
According to social identity theory, how do individuals form their identity?
A. By reflecting on their own personal attributes independently of social groups
B. By aligning their identity based on group memberships such as ethnicity, gender, or profession
C. By comparing their self-image to others’ successes and failures
D. By observing role models and imitating their behavior
Answer: B. By aligning their identity based on group memberships such as ethnicity, gender, or profession
Explanation:
Social identity theory, developed by Henri Tajfel, states that individuals define themselves through their group memberships, such as those based on gender, ethnicity, religion, or professional affiliations. This theory emphasizes how belonging to in-groups (groups one identifies with) and distinguishing from out-groups (groups one does not belong to) helps shape self-identity. Option A suggests a more individualistic approach to identity formation, which doesn't align with social identity theory. Option C refers to social comparison theory, which is not the focus of this question. Option D refers to observational learning, a concept from social learning theory. Thus, the correct answer is B, as it directly refers to the influence of group memberships on identity formation.
Question 3
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates role identity?
A. A person feeling happy because they have met their ideal self-image
B. A student actively participating in extracurricular activities because they see themselves as a leader
C. A person experiencing anxiety due to a mismatch between their actual self and their ought self
D. An individual who avoids social interaction to maintain their self-esteem
Answer: B. A student actively participating in extracurricular activities because they see themselves as a leader
Explanation:
Role identity refers to how individuals define themselves based on the specific roles they occupy, such as being a student, leader, parent, or employee. In this case, the student who sees themselves as a leader takes on responsibilities and behaviors that align with this role, such as engaging in extracurricular activities to reinforce their identity as a leader. Option A describes self-image, not role identity. Option C refers to self-discrepancy theory, which involves mismatches between different aspects of the self but is not specifically related to roles. Option D addresses self-esteem maintenance but does not reflect the concept of role identity. Therefore, the correct answer is B, as it demonstrates how a person’s role influences their actions and behaviors.


