Instantly transform nanometer to inch and vice versa on Examples.com. Simply enter your value for quick conversion outcomes.
nm to inch
Formula: Length in inches (inch) = Length in nanometers (nm) ÷ 25400000
Nanometer:
Inch:
| Nanometers | Inches | Exponential Form (inch) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00000003937000000000 | 3.9370e-8 |
inch to nm
Formula: Length in nanometers (nm) = Length in inches (inch) × 25400000
Inch :
Nanometer :
| Inches | Nanometers |
|---|---|
| 1 | 25400000 |
Length Converters to Nanometer (nm)
| Mile to Nanometer | Feet to Nanometer | Inch to Nanometer |
| Nautical Mile to Nanometer | Kilometer to Nanometer | Centimeter to Nanometer |
| Millimeter to Nanometer | Micrometer to Nanometer |
Length Converters to Inch (in)
| Kilometer to Inch | Meter to Inch | Centimeter to Inch |
| Millimeter to Inch | Micrometer to Inch | Nanometer to Inch |
| Mile to Inch | Yard to Inch | Feet to Inch |
| Nautical Mile to Inch |
Conversion Factors:
- Nanometers to Inches: 1 inch = 25,400,000 nanometers
- Inches to Nanometers: 1 nanometer = 1/25,400,000 inches
How to Convert Nanometers to Inches:
To convert nanometers to inches, divide the number of nanometers by 25,400,000.
Inches=Nanometers/25,400,000
Example: Convert 50,000,000 nanometers to inches.Inches=50,000,000/25,400,000≈1.9685 inches
How to Convert Inches to Nanometers:
To convert inches to nanometers, multiply the number of inches by 25,400,000.
Nanometers=Inches×25,400,000
Example: Convert 2 inches to nanometers. Nanometers=2×25,400,000=50,800,000 nanometers
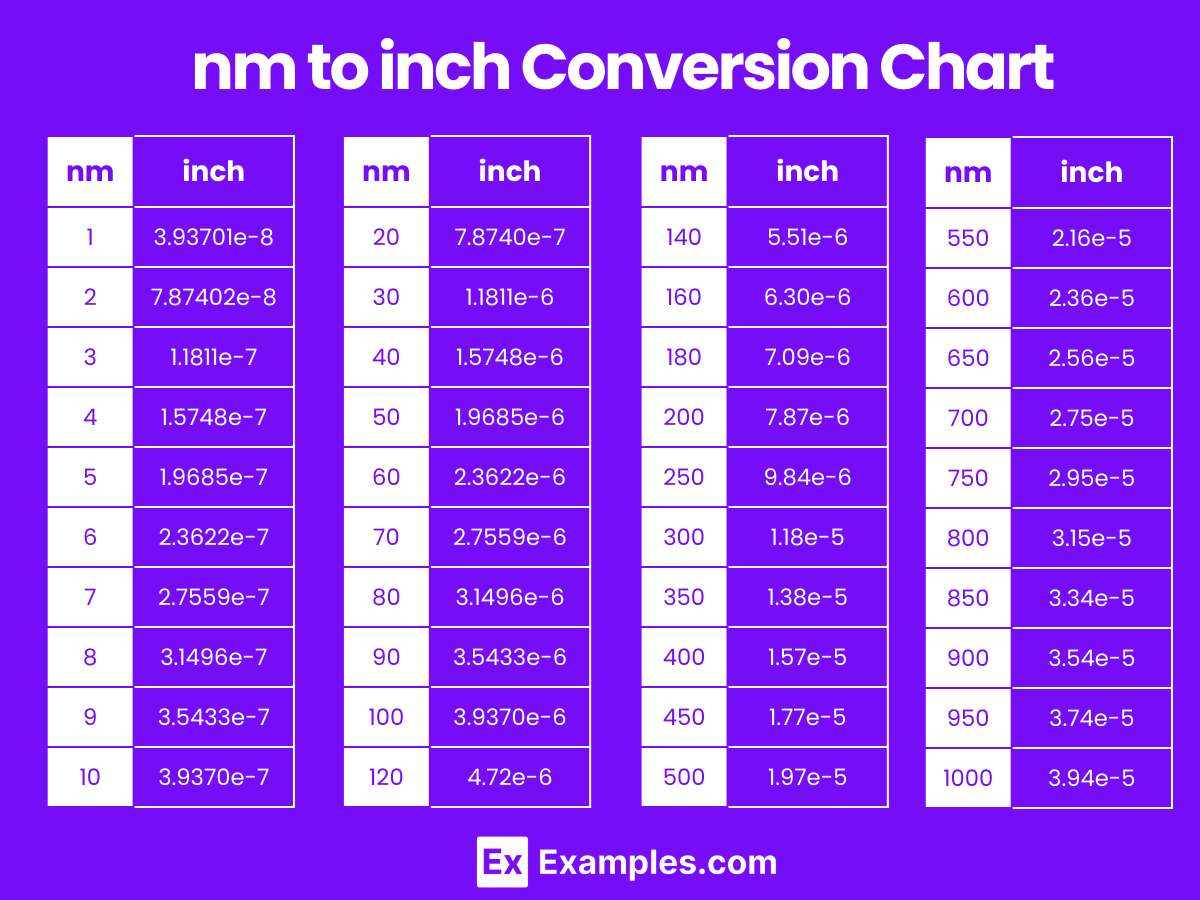
Nanometers to Inches Conversion Table
| Nanometers (nm) | Inches (in) (approximate) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.93701e-8 |
| 2 | 7.87402e-8 |
| 3 | 1.1811e-7 |
| 4 | 1.5748e-7 |
| 5 | 1.9685e-7 |
| 6 | 2.3622e-7 |
| 7 | 2.7559e-7 |
| 8 | 3.1496e-7 |
| 9 | 3.5433e-7 |
| 10 | 3.9370e-7 |
| 20 | 7.8740e-7 |
| 30 | 1.1811e-6 |
| 40 | 1.5748e-6 |
| 50 | 1.9685e-6 |
| 60 | 2.3622e-6 |
| 70 | 2.7559e-6 |
| 80 | 3.1496e-6 |
| 90 | 3.5433e-6 |
| 100 | 3.9370e-6 |
nm to inch Conversion Chart
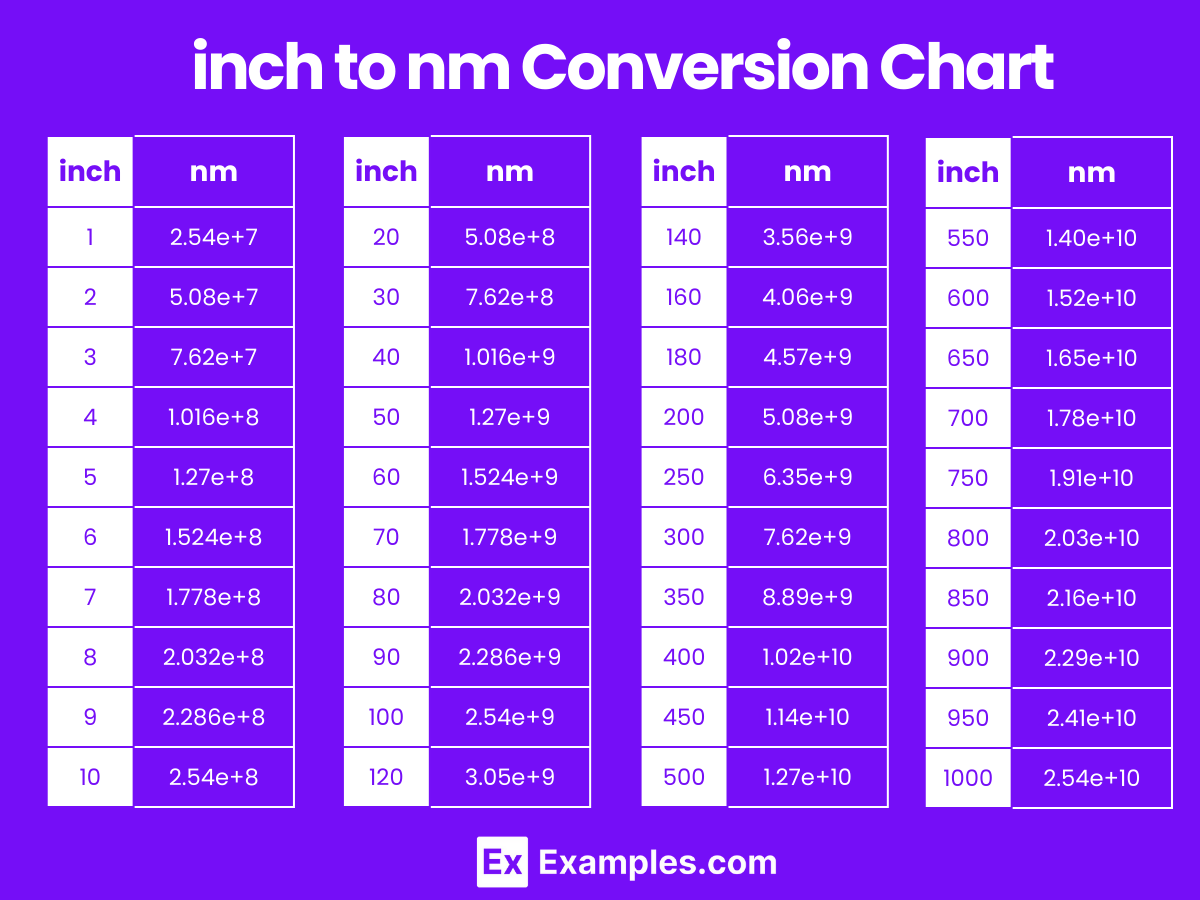
Inches to Nanometers Conversion Table
| Inches (in) | Nanometers (nm) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2.54e+7 |
| 2 | 5.08e+7 |
| 3 | 7.62e+7 |
| 4 | 1.016e+8 |
| 5 | 1.27e+8 |
| 6 | 1.524e+8 |
| 7 | 1.778e+8 |
| 8 | 2.032e+8 |
| 9 | 2.286e+8 |
| 10 | 2.54e+8 |
| 20 | 5.08e+8 |
| 30 | 7.62e+8 |
| 40 | 1.016e+9 |
| 50 | 1.27e+9 |
| 60 | 1.524e+9 |
| 70 | 1.778e+9 |
| 80 | 2.032e+9 |
| 90 | 2.286e+9 |
| 100 | 2.54e+9 |
inch to nm Conversion Chart
Difference Between Nanometers to Inches
| Aspect | Description of Nanometers | Description of Inches |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Definition | A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter, used for very small measurements. | An inch is defined as exactly 25.4 millimeters; widely used in the United States for everyday measurements. |
| Scale | Extremely small, typically used to measure wavelengths of light, thickness of films, or size of cells. | Larger scale, commonly used to measure length in construction, textiles, and more. |
| Typical Use | Predominantly used in science and engineering to describe microscopic entities. | Frequently used in everyday situations, DIY projects, and commercial construction. |
| Measurement Tools | Measured using specialized instruments like atomic force microscopes or electron microscopes. | Measured with rulers, tape measures, calipers, and laser measuring tools. |
| Precision | Requires high precision for accurate measurement due to the tiny scale of the unit. | Less precision required compared to nanometers; tools with standard accuracy are sufficient for most uses. |
| Units Conversion | Nanometers are converted from or to other metric units using powers of ten. | Inches are often converted to or from other imperial units (feet, yards) using multiples of 12 or 36. |
| Visualization | Cannot be visualized without electronic or optical magnification. | Easily visualized and marked in most measuring tools like measuring tapes. |
| Examples of Measurement | The diameter of a virus might be around 100 nanometers. | The width of a standard smartphone is typically about 3 inches. |
| Interdisciplinary Importance | Important in fields like nanotechnology, materials science, and microfabrication. | Critical in architecture, manufacturing, carpentry, and interior design. |
| Cultural Relevance | Mainly significant in scientific communities and advanced technology sectors. | Part of everyday life in countries using the imperial system; fundamental in education and commerce. |
1. Solved Examples on Converting Nanometers to Inches
Example 1: Convert 50,000,000 nanometers to inches.
Inches=50,000,000/25,400,000≈1.9685 inches
Example 2: Convert 10,000,000 nanometers to inches.
Inches=10,000,00025,400,000≈0.3937 inches
Example 3: Convert 100,000,000 nanometers to inches.
Inches=100,000,00025,400,000≈3.9370 inches
Example 4: Convert 1,000,000 nanometers to inches.
Inches=1,000,00025,400,000≈0.03937 inches
Example 5: Convert 250,000,000 nanometers to inches.
Inches=250,000,00025,400,000≈9.8425 inches
2. Solved Examples on Converting Inches to Nanometers
Example 1: Convert 1 inch to nanometers.
Nanometers=1×25,400,000=25,400,000 nm
Example 2: Convert 0.5 inches to nanometers.
Nanometers=0.5×25,400,000=12,700,000 nm
Example 3: Convert 2 inches to nanometers.
Nanometers=2×25,400,000=50,800,000 nm
Example 4: Convert 0.1 inches to nanometers.
Nanometers=0.1×25,400,000=2,540,000 nm
Example 5: Convert 3 inches to nanometers.
Nanometers=3×25,400,000=76,200,000 nm
1. How accurate is the conversion from nanometers to inches?
The accuracy depends on the precision of the initial measurements and the quality of the calculation tools used.
2. How can technology help with converting nanometers to inches?
Advanced calculators and software that handle scientific notation and large numbers can automate and error-check these conversions, making them quicker and more reliable.
3. Why is it important to convert nanometers to inches in scientific publications?
Converting to inches can make the data more accessible to a broader audience, including those familiar with the imperial system, thereby enhancing understanding and communication.
4. What are the potential errors in manually converting nanometers to inches?
Human errors could include miscalculations due to overlooking decimal places, incorrect placement of commas, or rounding off errors, which are significant at such scale differences.
5. Can converting nanometers to inches help in understanding better the scale of certain products?
Yes, converting to a more familiar measurement system can help non-specialists understand and appreciate the scale of tiny objects.
6. How do scientists measure nanometers?
Scientists measure nanometers using highly specialized instruments designed for viewing and measuring at the molecular or atomic scale. Key tools include electron microscopes, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEM) and transmission electron microscopes (TEM), and atomic force microscopes (AFM). These devices can visualize surfaces and structures down to the nanometer level, enabling precise measurements of extremely small dimensions.

