Which symbol represents ampere?
V
Ω
A
W

In physics, the ampere is defined as the unit of electric current. It represents the constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length and negligible circular cross-section, and placed one meter apart in a vacuum, would produce a force between these conductors of 2×10⁻⁷ newtons per meter of length.
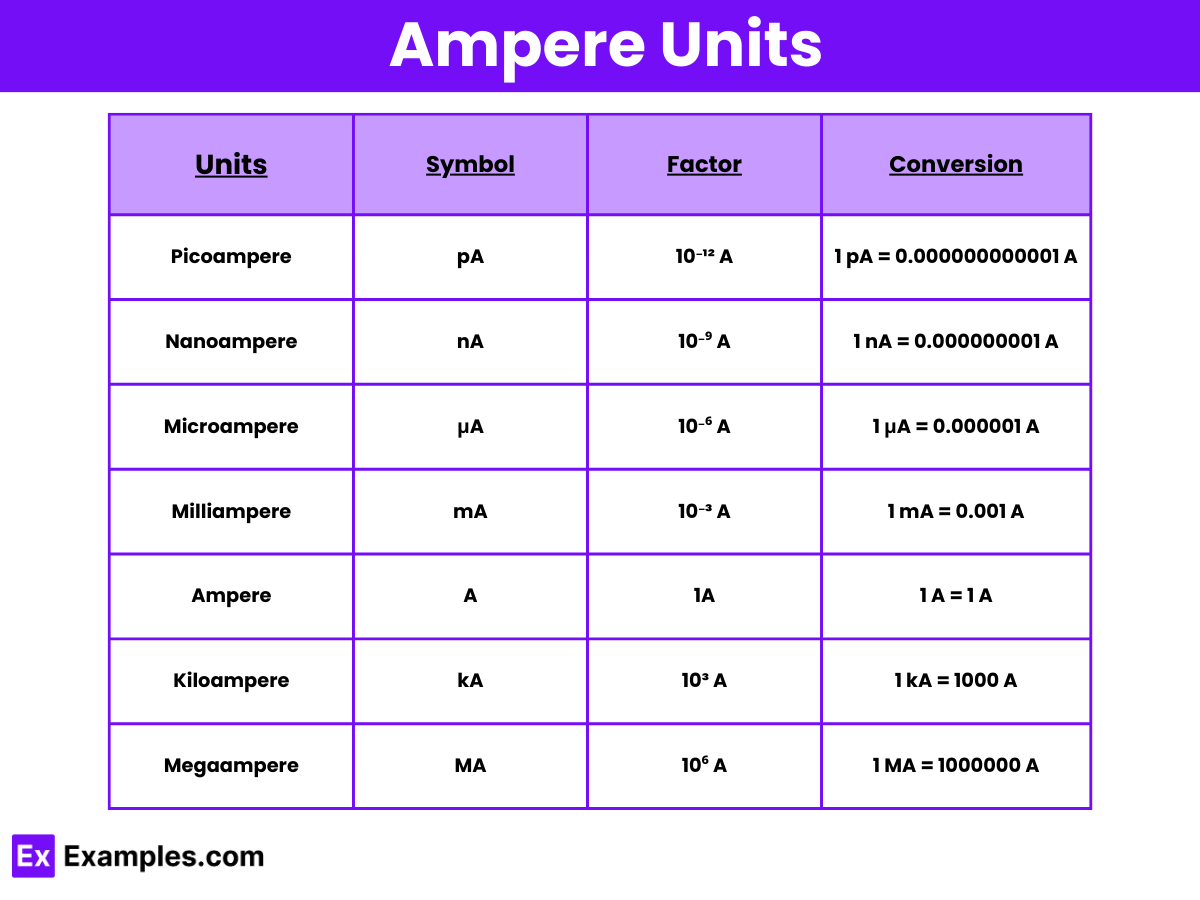
The table below outlines the common prefixes for the ampere unit, a fundamental measure of electric current. These prefixes help express the vast range of current levels encountered in various electrical and electronic applications, from the extremely small currents used in medical and semiconductor technologies to the large currents found in industrial electrical systems. Each entry includes the symbol and a conversion to the base unit of ampere, facilitating precise calculations and conversions in scientific and engineering contexts.
| Units | Symbol | Factor | Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Picoampere | pA | 10⁻¹² A | 1 pA = 0.000000000001 A |
| Nanoampere | nA | 10⁻⁹ A | 1 nA = 0.000000001 A |
| Microampere | μA | 10⁻⁶ A | 1 μA = 0.000001 A |
| Milliampere | mA | 10⁻³ A | 1 mA = 0.001 A |
| Ampere | A | 1A | 1 A = 1 A |
| Kiloampere | kA | 10³ A | 1 kA = 1000 A |
| Megaampere | MA | 10⁶ A | 1 MA = 1000000 A |
Here is the format for converting amperes to other units of electrical measurement, mirroring your request:
An ampere meter, more commonly known as an ammeter. It is an instrument used to measure the electric current in a circuit. The current is measured in amperes, and the device is connected in series with the circuit so it can measure the flow of electrical charge through it. Ammeters are designed to have very low resistance, which minimizes any potential voltage drop across the meter that could affect the circuit operation.
Connecting an ammeter (ampere meter) in parallel to a load can lead to severe consequences. Initially, because ammeters have very low internal resistance, this configuration exposes the meter to the full circuit voltage. Consequently, the meter can draw excessive current, potentially leading to its immediate damage or destruction. Moreover, this error risks short-circuiting, damaging the load or other circuit components, and could even pose safety hazards such as fires or electrical shocks. In essence, ammeters must always be connected in series with the load to avoid these risks and ensure accurate current measurement.
When discussing different types of current measured in amperes, it’s important to differentiate between the various forms based on how they behave over time:
Firstly, the Direct Current (DC), measured in amperes, flows in one direction and maintains a constant value, making it ideal for devices like batteries and solar panels that require a stable and unidirectional flow of electricity.
Secondly, there is Alternating Current (AC), also measured in amperes, which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude over time. This type of current is commonly used in household and industrial power because it is more efficient for transporting electricity over long distances.
Additionally, we consider Pulsating Current, which, similar to direct current, generally moves in one direction but varies in intensity. This type of current is often seen in applications involving rectifiers where AC is converted to DC, but not perfectly, resulting in a fluctuating DC output.
These distinctions in amplitude types are crucial for designing and implementing electrical systems appropriately, ensuring that each application operates efficiently and safely under the correct current type.
In physics, “amp” stands for ampere, the unit of electric current that measures the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
The ampere is not a unit of energy; it measures electric current. The related energy unit would involve amps combined with voltage (joules), as in watts.
In electromagnetism, the ampere defines the measurement of electric current, representing the flow of charges influenced by electromagnetic forces within electrical circuits.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which symbol represents ampere?
V
Ω
A
W
What is the unit of electric current?
Volt
Ohm
Ampere
Watt
If 5 coulombs of charge pass through a wire in 1 second, what is the current?
1 A
5 A
10 A
15 A
How much charge passes through a conductor in 4 seconds if the current is 3 amperes?
3 C
7 C
12 C
15 C
Which device measures electric current?
Voltmeter
Ohmmeter
Ammeter
Wattmeter
If 8 A of current flows for 3 seconds, how much charge has passed?
11 C
24 C
8 C
16 C
What is the current in a circuit with a voltage of 12 V and a resistance of 4 Ω?
3 A
4 A
5 A
6 A
Which of the following represents the flow of electric current?
Voltage
Charge
Resistance
Power
What is the current if 15 coulombs pass through a wire in 5 seconds?
1 A
2 A
3 A
4 A
Which of the following is true about ampere?
It measures voltage
It measures resistance
It measures electric current
It measures power
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

