What is the Band Theory of Solids primarily used to explain?
Thermal conductivity of metals
Electrical conductivity of solids
Magnetic properties of materials
Optical properties of gases

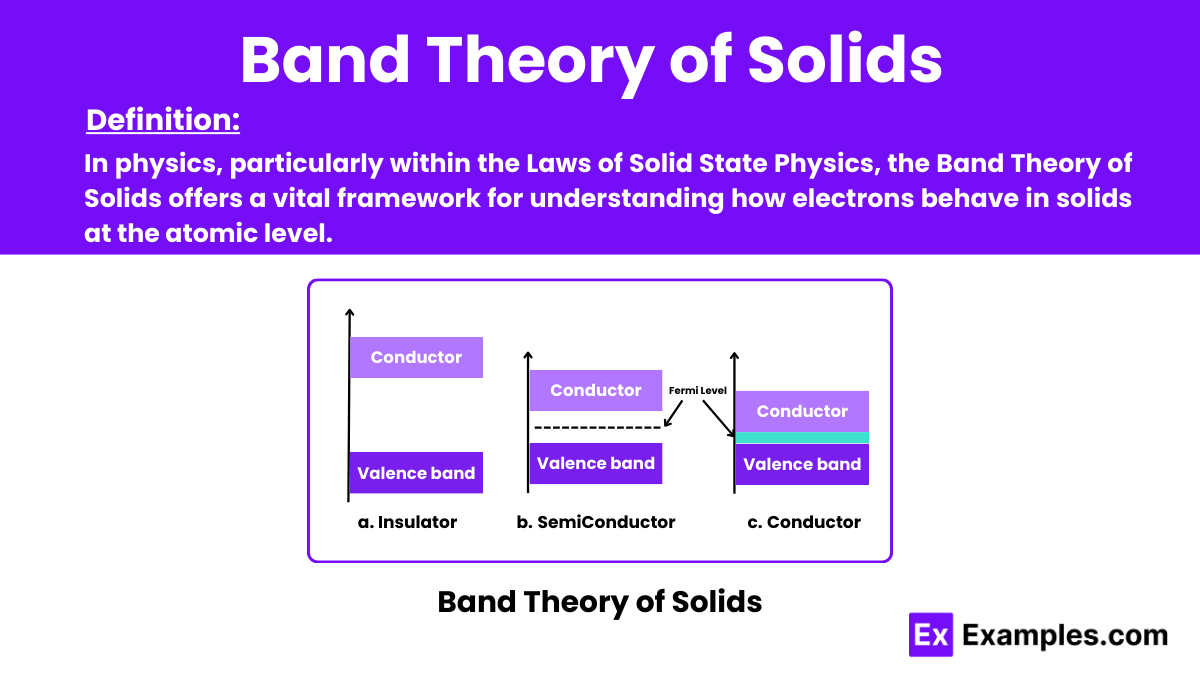
In physics, particularly within the Laws of Solid State Physics, the Band Theory of Solids is a fundamental framework that explains the behavior of electrons in solids at the atomic level. This theory is essential for understanding how electrical conductivity works in different materials.
Energy bands in solids refer to the range of allowed energy levels that electrons can occupy within a material. These bands result from the arrangement of atoms in the solid, particularly in crystalline structures. The concept is fundamental in understanding the electronic properties of materials. As it determines how electrons can move and interact within the solid. Depending on the material’s structure and properties, energy bands can be either filled with electrons (valence bands) or empty (conduction bands). With a forbidden energy gap between them known as the bandgap. The arrangement and characteristics of these energy bands play a crucial role in determining a material’s conductivity, optical properties, and electronic behavior.
When considering the energy levels within a solid composed of Avogadro’s number of atoms, it’s important to recognize the sheer magnitude of possibilities. With each atom contributing its own set of energy levels, the cumulative effect results in an immense number of available states for electrons. Consequently, this abundance of energy levels leads to the formation of continuous energy bands within the material. Unlike discrete energy levels found in isolated atoms. These bands offer a spectrum of permissible energy states for electrons to occupy. Moreover, the density of these energy levels increases significantly. Due to the large number of atoms, resulting in a densely populated energy landscape.
When examining the energy levels within a solid composed of a large number of atoms (represented here as “n”), we’re delving into the intricate electronic structure of the material. With each atom contributing its own set of energy levels, the cumulative effect is a complex network of permissible energy states for electrons. This abundance of energy levels forms continuous energy bands throughout the material. Providing a wide range of potential states for electrons to occupy. Unlike discrete energy levels observed in isolated atoms, these bands offer a continuous spectrum of energy states. Facilitating electron movement and interactions within the solid. The density of these energy levels increases with the number of atoms. Resulting in a densely populated energy landscape.

The band theory of solids is utilized in various fields due to its profound implications for understanding and manipulating the electronic properties of materials. Some key uses include:
Bands in solids originate from the collisions of atomic orbitals, resulting in the formation of molecular orbitals and energy bands. This phenomenon arises due to constructive interference between electron wavefunctions.
The band theory of solids in semiconductors explains electronic behavior. Electrons occupy energy bands, including valence and conduction bands, separated by a bandgap. This determines semiconductor conductivity and electronic properties.
Energy bands in solids form through the interaction of atoms, creating a continuum of electron energy levels. Transitioning from discrete atomic energy levels, bands emerge, influenced by crystal structure and atomic interactions.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the Band Theory of Solids primarily used to explain?
Thermal conductivity of metals
Electrical conductivity of solids
Magnetic properties of materials
Optical properties of gases
What is the energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band called?
Conduction gap
Valence gap
Energy band gap
Forbidden gap
In a metal, where do the electrons primarily exist?
In the forbidden gap
In the conduction band
In the valence band
In the core band
How is the band gap of a semiconductor compared to that of an insulator?
Larger
Smaller
Equal
Variable
What determines the electrical conductivity of a solid according to Band Theory?
Number of free electrons
Size of the atoms
Type of crystal structure
Width of the energy bands
Which of the following is a characteristic of conductors in terms of band theory?
Wide forbidden gap
Overlapping valence and conduction bands
Full valence band
Empty conduction band
In semiconductors, what happens to the conductivity as temperature increases?
Decreases
Remains constant
Increases
Varies unpredictably
Which material typically has the largest band gap?
Conductor
Semiconductor
Insulator
Superconductor
How is the band structure of an insulator different from that of a semiconductor?
Insulators have a larger band gap
Insulators have a smaller band gap
Insulators have no band gap
Insulators have overlapping bands
What role do impurities play in the conductivity of semiconductors?
Decrease conductivity
Increase conductivity
Have no effect
Change the band gap size
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

