What is the primary function of a bar in a mechanical context?
To provide decoration
To support loads
To conduct electricity
To insulate heat

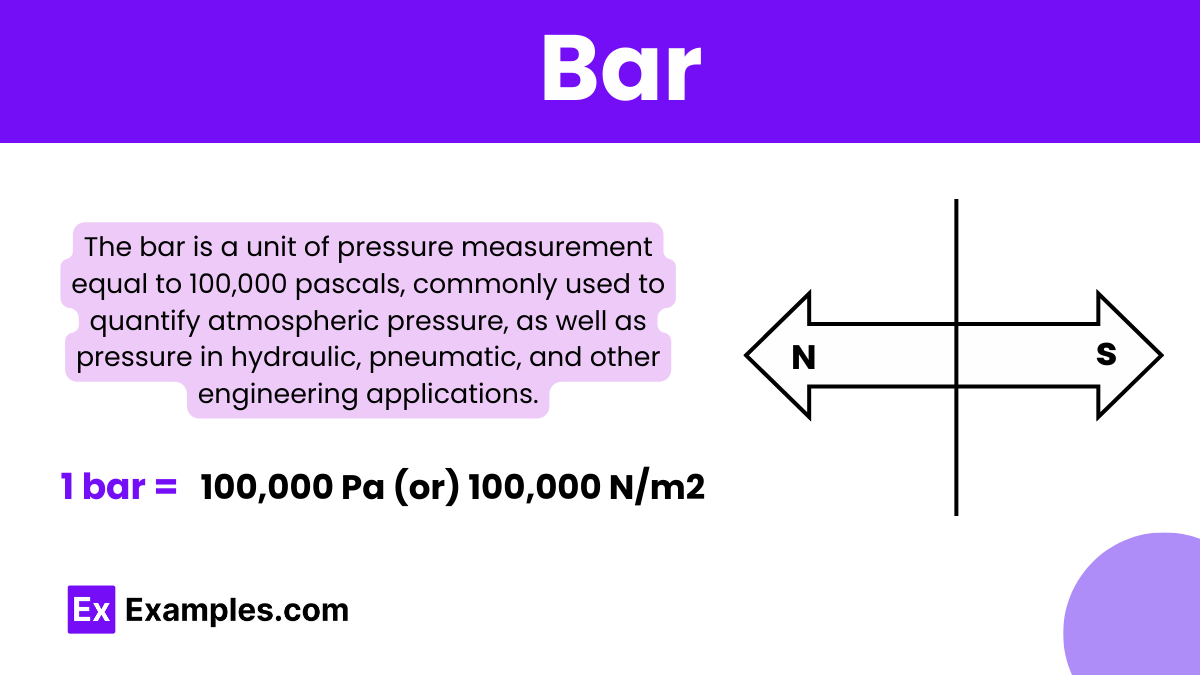
Where:
| Prefix | Symbol | Factor | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decibar | dbar | 10⁻¹ | 0.1 bar |
| Centibar | cbar | 10⁻² | 0.01 bar |
| Millibar | mbar | 10⁻³ | 0.001 bar |
| Microbar | μbar | 10⁻⁶ | 0.000001 bar |
| Nanobar | nbar | 10⁻⁹ | 0.000000001 bar |
| Picobar | pbar | 10⁻¹² | 0.000000000001 bar |
| Femtobar | fbar | 10⁻¹⁵ | 0.000000000000001 bar |
| Attobar | abar | 10⁻¹⁸ | 0.000000000000000001 bar |
| Zeptobar | zbar | 10⁻²¹ | 0.000000000000000000001 bar |
| Yoctobar | ybar | 10⁻²⁴ | 0.000000000000000000000001 bar |
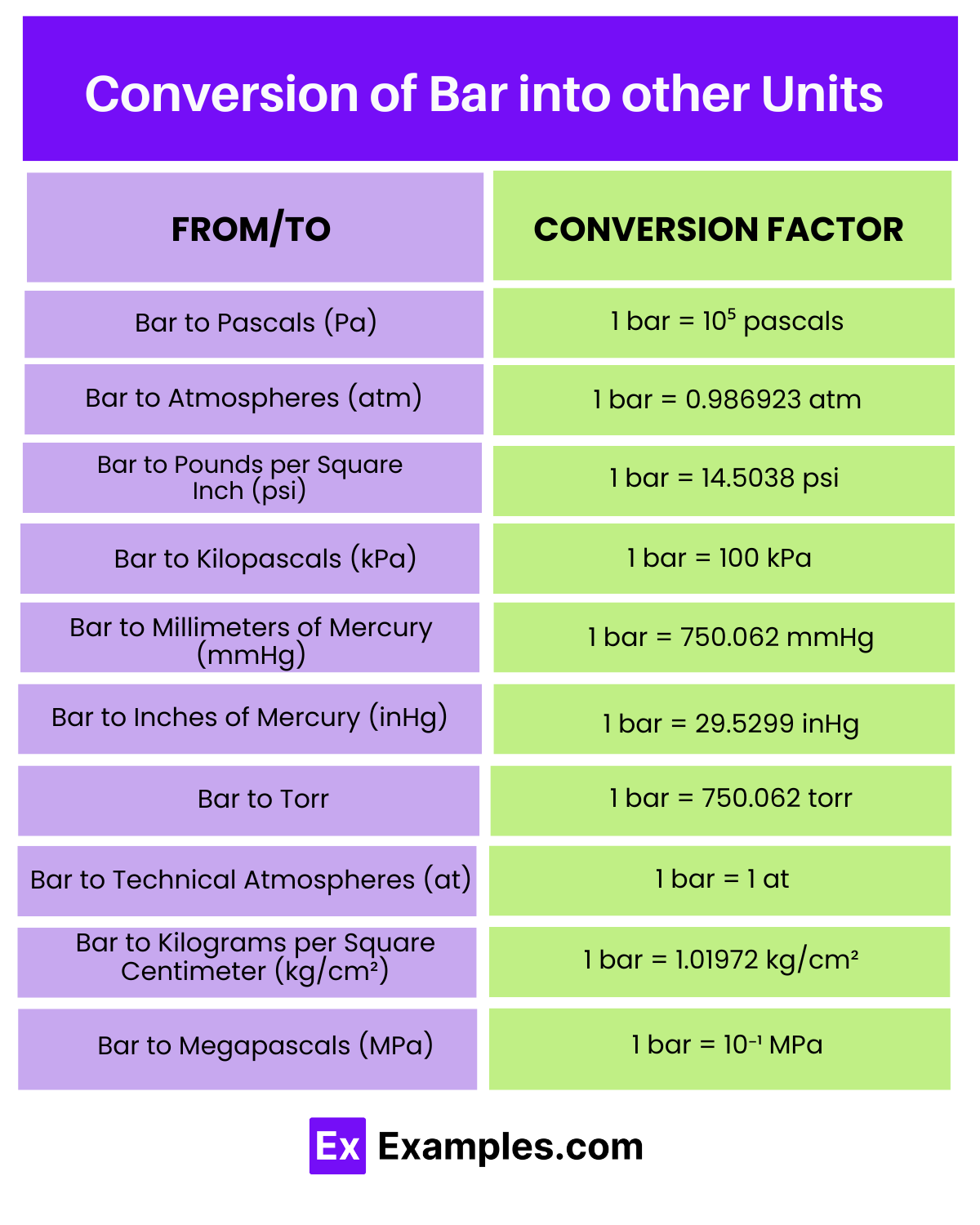
| From/To | Conversion Factor | Example Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Bar to Pascals (Pa) | 1 bar = 10⁵ pascals | 10 bars = 1,000,000 Pa |
| Bar to Atmospheres (atm) | 1 bar = 0.986923 atm | 10 bars ≈ 9.86923 atm |
| Bar to Pounds per Square Inch (psi) | 1 bar = 14.5038 psi | 10 bars ≈ 145.038 psi |
| Bar to Kilopascals (kPa) | 1 bar = 100 kPa | 10 bars = 1,000 kPa |
| Bar to Millimeters of Mercury (mmHg) | 1 bar = 750.062 mmHg | 10 bars ≈ 7500.62 mmHg |
| Bar to Inches of Mercury (inHg) | 1 bar = 29.5299 inHg | 10 bars ≈ 295.299 inHg |
| Bar to Torr | 1 bar = 750.062 torr | 10 bars ≈ 7500.62 torr |
| Bar to Technical Atmospheres (at) | 1 bar = 1 at | 10 bars = 10 at |
| Bar to Kilograms per Square Centimeter (kg/cm²) | 1 bar = 1.01972 kg/cm² | 10 bars = 10.1972 kg/cm² |
| Bar to Megapascals (MPa) | 1 bar = 10⁻¹ MPa | 10 bars = 1 MPa |
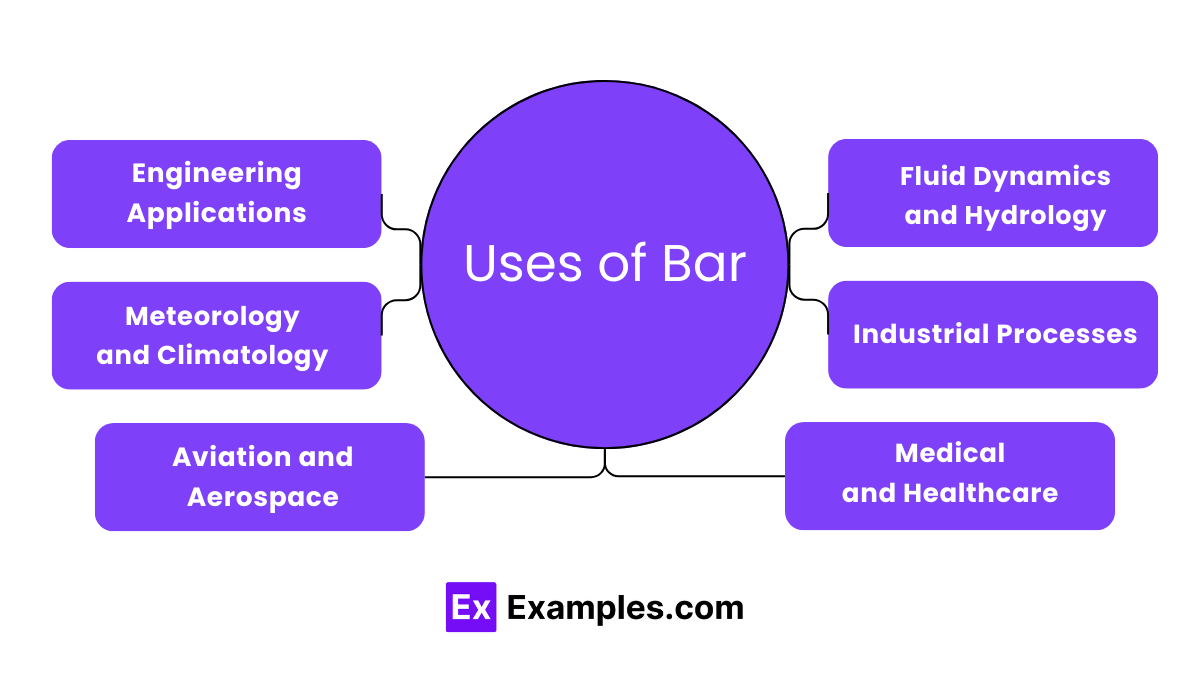
The bar is a commonly used unit for measuring pressure in various applications, ranging from weather forecasting to industrial processes.
Atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 bar, serving as a reference point for pressure measurements in meteorology and aviation.
In engineering, pressure expressed in bars is crucial for assessing the performance and safety of hydraulic systems, pneumatic machinery, and structural components.
Fluid dynamics studies often use bars to quantify pressure gradients, fluid flow rates, and hydraulic forces within pipelines, channels, and vessels.
While the bar is widely recognized and used internationally, countries like the United States primarily employ pounds per square inch (psi) for pressure measurements.
The bar allows for easy conversion into other pressure units such as pascals (Pa), atmospheres (atm), and torr, facilitating seamless communication and analysis across diverse disciplines.
In industrial settings, monitoring pressure in bars ensures the safe operation of equipment and processes, helping to prevent overpressurization and potential hazards.
Barometric pressure, measured in bars, plays a crucial role in aviation for determining aircraft altitude, setting altimeter settings, and assessing atmospheric conditions during flight.
Hydrologists and oceanographers use barometric pressure data to study weather patterns, ocean currents, and tidal variations, providing insights into Earth’s dynamic systems.
Bar-based pressure measurements are essential in research and development, facilitating the design and testing of innovative technologies in fields like renewable energy, materials science, and biotechnology.
Bar pressure can be converted to other units such as atmospheres, pascals, pounds per square inch (psi), and millimeters of mercury (mmHg) for various applications.
High bar pressure may indicate overinflated tires, while low bar pressure can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and compromised vehicle safety.
Changes in barometric pressure often precede weather changes, with decreasing pressure typically indicating the approach of low-pressure systems and potentially stormy weather.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of a bar in a mechanical context?
To provide decoration
To support loads
To conduct electricity
To insulate heat
What is the unit of measurement for the force applied to a bar?
Joule
Pascal
Newton
Watt
What is the term for the maximum stress a bar can withstand without permanent deformation?
Yield strength
Ultimate strength
Elastic limit
Breaking point
In engineering, what does the term \"bar\" typically refer to?
A unit of pressure
A solid cylindrical object
A measurement of distance
A type of lever
What is the common material used for making bars in construction?
Plastic
Wood
Steel
Glass
How is the cross-sectional area of a cylindrical bar calculated?
2πr
πd
πd²
πr²
What is the term for the internal resistance of a bar to an external force?
Strain
Stress
Displacement
Deformation
What does the term \"elastic modulus\" refer to in the context of bars?
The amount of elongation under load
The ratio of stress to strain
The ultimate tensile strength
The density of the material
Which property of a bar is indicated by its ability to return to its original shape after being deformed?
Plasticity
Toughness
Hardness
Elasticity
What is the significance of the neutral axis in a bending bar?
It is where maximum stress occurs
It is where no stress occurs
It is the axis of rotation
It is the outermost layer of the bar
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

