Which planet is known as the Red Planet?
Earth
Venus
Mars
Jupiter

Celestial bodies are natural objects located outside Earth’s atmosphere, including stars, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. These objects are significant in the study of astronomy as they make up the universe and provide insight into the formation, structure, and evolution of cosmic phenomena. Celestial bodies vary greatly in size, composition, and distance from Earth, playing key roles in the dynamics of space and influencing various cosmic events and processes.
Celestial bodies are natural objects located outside Earth’s atmosphere. These include planets, stars, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, and galaxies. Each type of celestial body has unique characteristics and behaviors. For example, stars are massive, luminous spheres of plasma, while planets are large objects that orbit stars.
Celestial bodies are natural objects located outside Earth’s atmosphere. The Solar System, our local cosmic neighborhood, contains various celestial bodies, each with unique characteristics and importance. Below are examples of different types of celestial bodies within our Solar System:
Hypothetical Cloud of Icy Bodies . The Oort Cloud is a theoretical cloud of icy objects that is believed to surround the Solar System at a vast distance, potentially up to 100,000 AU (astronomical units) from the Sun. It is considered a source of long-period comets, which have orbits lasting thousands of years.
Region of Icy Bodies The Kuiper Belt is a region of the Solar System beyond the orbit of Neptune, extending from about 30 to 55 AU from the Sun. It is populated with a variety of icy bodies, including dwarf planets like Pluto, Haumea, and Makemake. The Kuiper Belt is significant for understanding the formation and evolution of the Solar System, as it contains remnants from its early history.
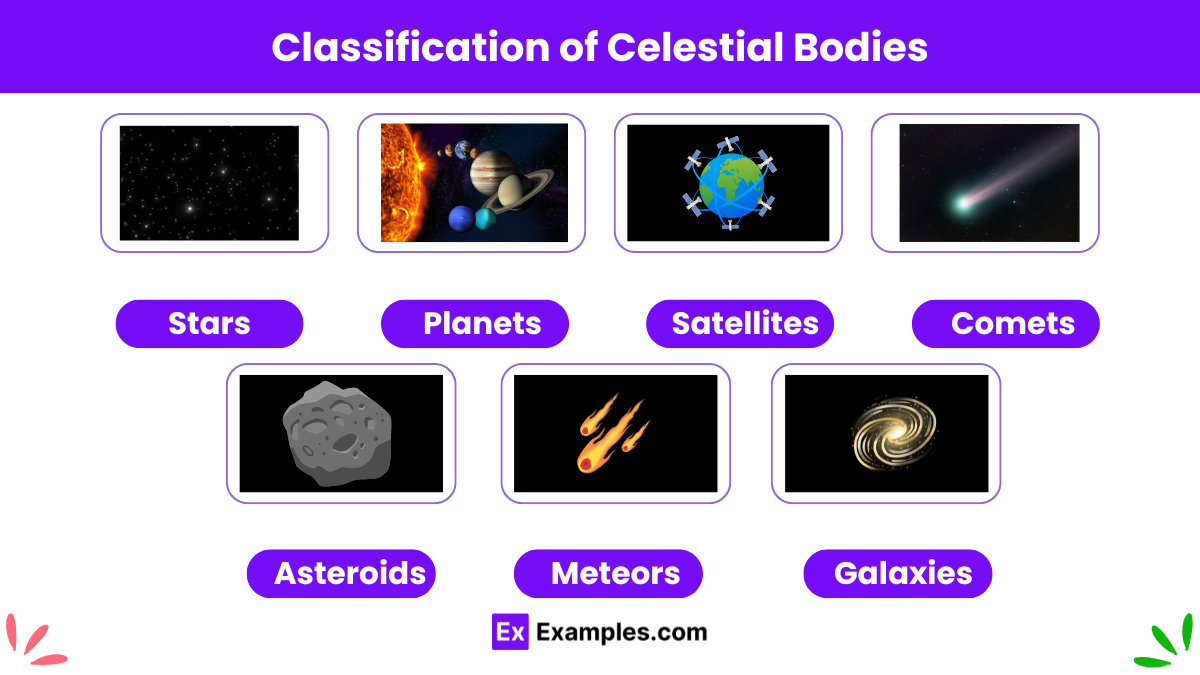
Celestial bodies are naturally occurring physical entities found in the universe. They come in various forms and sizes, each possessing unique characteristics. The classification of celestial bodies helps astronomers understand their formation, structure, and behavior.
Stars are luminous spheres of plasma held together by gravity, generating light and heat through nuclear fusion reactions in their cores. They form the basic building blocks of galaxies and vary in size, temperature, and brightness. Our Sun is a medium-sized star, essential for life on Earth, while other well-known stars include Betelgeuse and Rigel.
Planets are large celestial bodies that orbit stars. They do not emit their own light but reflect the light of their star. The eight recognized planets in our Solar System are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Each planet has unique features, such as Earth’s ability to support life or Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
Satellites, or moons, are natural objects that orbit planets. They vary significantly in size, composition, and number. Earth’s Moon is the most familiar satellite, influencing phenomena like tides and eclipses. Other planets, such as Jupiter and Saturn, have multiple moons, with some, like Ganymede and Titan, being larger than Mercury.
Comets are icy bodies that travel around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits. When they approach the Sun, the heat causes their ice to vaporize, forming a glowing coma and often a tail that can stretch for millions of kilometers. Famous comets include Halley’s Comet, visible from Earth approximately every 76 years, and Comet Hale-Bopp.
Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun, primarily located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. They are remnants from the early Solar System that never formed into planets. Examples of notable asteroids include Ceres, the largest in the asteroid belt, and Vesta.
Meteors are meteoroids that enter Earth’s atmosphere and vaporize, creating a streak of light commonly known as a shooting star. Meteorites are meteoroids that survive their journey through the atmosphere and land on Earth’s surface. These celestial fragments can vary from tiny grains to large masses, providing valuable scientific information about the early Solar System.
Galaxies are vast systems containing billions of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter, all bound together by gravity. The Milky Way is our home galaxy, hosting our Solar System and billions of other stars. Other notable galaxies include Andromeda, the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, and the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Stars form from collapsing clouds of gas and dust in space, undergoing nuclear fusion to emit light and heat.
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star, large enough to be rounded by its gravity and clear its orbit of debris.
A moon is a natural satellite that orbits a planet or dwarf planet, varying in size and composition.
Asteroids are rocky objects, mostly in the asteroid belt, while comets are icy bodies that develop tails when near the sun.
A dwarf planet orbits the sun and is spherical but hasn’t cleared its orbit of other debris, unlike a planet.
Meteoroids are space rocks, meteors are meteoroids burning in Earth’s atmosphere, and meteorites are fragments that reach the ground.
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, with a mass more than twice that of all other planets combined.
Black holes form from the collapse of massive stars after a supernova, creating a region with gravity so strong that not even light can escape.
The moon affects Earth through its gravitational pull, causing ocean tides and stabilizing the planet’s axial tilt.
A galaxy is a massive system of stars, stellar remnants, gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which planet is known as the Red Planet?
Earth
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
What is the largest planet in our solar system?
Earth
Saturn
Jupiter
Neptune
Which celestial body is the closest to the Sun?
Earth
Mercury
Venus
Mars
What do we call a moon that orbits a planet?
Satellite
Comet
Asteroid
Star
Which planet has the most extensive ring system?
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
What type of celestial body is the Sun classified as?
Planet
Comet
Star
Moon
Which celestial object is known for having a long, visible tail when it approaches the Sun?
Asteroid
Comet
Planet
Star
Which planet is famous for its Great Red Spot?
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
What is a celestial body that orbits a star and is not a planet called?
Meteor
Asteroid
Exoplanet
Dwarf planet
What celestial body has a core composed mostly of iron and is known for its strong magnetic field?
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

