What is the freezing point of water in Celsius?
100°C
32°C
0°C
-273°C
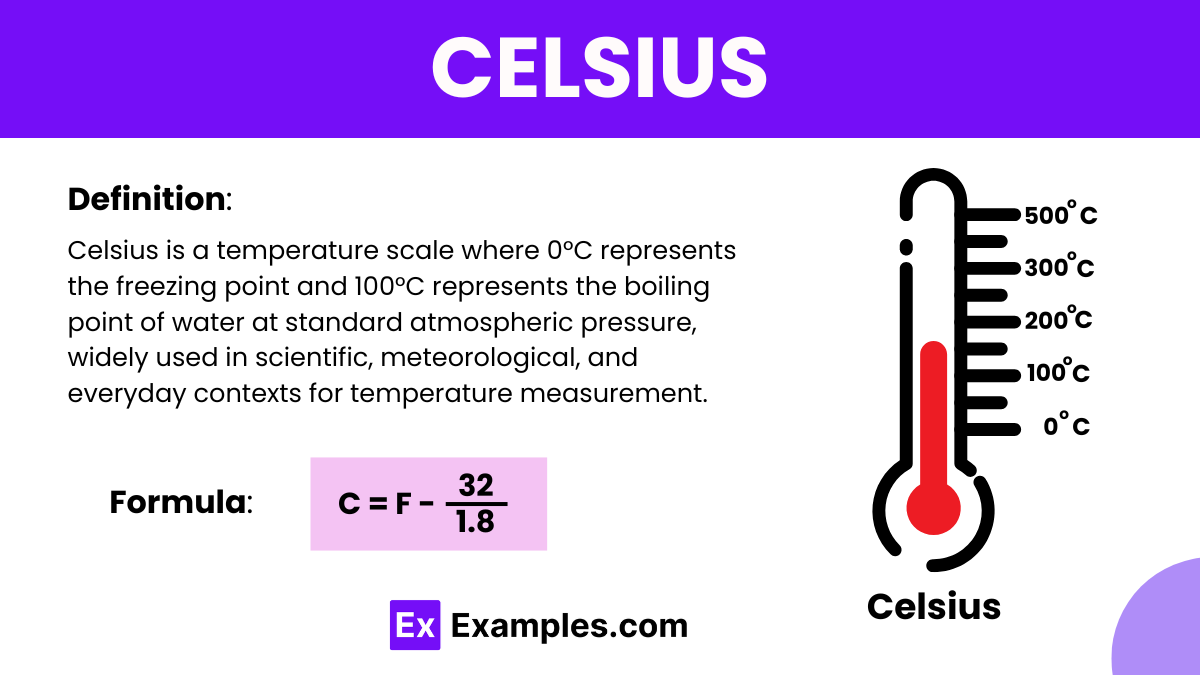
Celsius, a unit of temperature measurement in the International System of Units (SI), is widely used in scientific and everyday contexts. It is based on the properties of materials and their responses to heat, a fundamental concept in physics. Celsius scale measures temperature through the degree Celsius (°C), where water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. Temperature, a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance, affects various processes including conduction and radiation, which are modes of heat transfer crucial in understanding thermal dynamics.
Where:
Absolute zero in Celsius is the lowest possible temperature that can theoretically be reached, where all molecular motion ceases. It is defined as 0 Kelvin (0 K), which is equivalent to approximately -273.15 degrees Celsius (°C). At this temperature, atoms and molecules have minimal energy and do not move, resulting in a complete absence of thermal energy. Absolute zero serves as the basis for the Kelvin temperature scale and is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics and physics.
To convert Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C), you can use the following formula:
C = 1.8(F−32)
Where:
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Let’s illustrate this with an example:
Suppose you have a temperature of 68 degrees Fahrenheit (°F), and you want to convert it to Celsius (°C).
C = 1.8(68−32)
C = 1.836
C = 20
So, 68°F is equivalent to 20°C.
| Temperature Scale | Freezing Point of Water | Boiling Point of Water | Absolute Zero |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fahrenheit (°F) | 32°F | 212°F | -459.67°F |
| Celsius (°C) | 0°C | 100°C | -273.15°C |
Negative temperatures on the Celsius scale indicate temperatures below freezing, which are common in colder climates and during winter months.
0°C represents the freezing point of water, and 100°C represents the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure. These reference points make the Celsius scale easy to understand and use.
Celsius is more commonly used in scientific and international contexts, while Fahrenheit is still prevalent in some regions, particularly the United States
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the freezing point of water in Celsius?
100°C
32°C
0°C
-273°C
What is the boiling point of water in Celsius?
50°C
212°C
100°C
0°C
Which temperature is the same on both the Celsius and Kelvin scales?
-273.15°C
0°C
273.15°C
100°C
What is absolute zero in Celsius?
0°C
-100°C
-273.15°C
-459.67°C
How do you convert Celsius to Kelvin?
Subtract 273.15
Add 273.15
Multiply by 1.8
Divide by 1.8
What is room temperature approximately in Celsius?
0°C
100°C
20-25°C
50°C
Which of the following is a characteristic of the Celsius scale?
It is an absolute temperature scale
It is used primarily in the United States
It is based on the freezing and boiling points of water
It is not used in scientific measurements
What is the normal human body temperature in Celsius?
100°C
37°C
32°C
0°C
How do you convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
(°C × 1.8) + 32
(°C - 32) × 1.8
(°C × 1.8) - 32
(°C + 32) / 1.8
What is the equivalent of 25°C in Fahrenheit?
77°F
32°F
50°F
100°F
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

