A uniformly charged rod has a length of 2 meters and a total charge of 10 C. What is the linear charge density?
5C/m
10C/m
15C/m
8

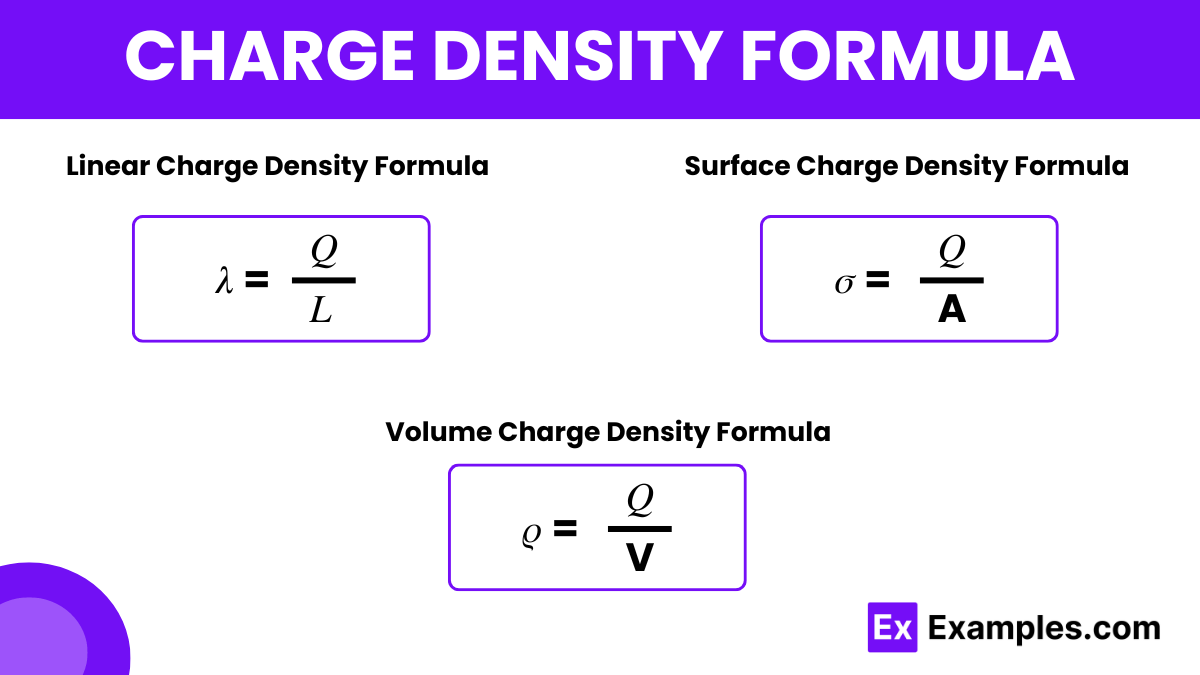
The charge density formula is essential in physics, quantifying electric charge distribution within a specific area or volume. It’s differentiated into three types: linear charge density (λ), surface charge density (σ), and volume charge density (ρ). Linear charge density is applied to charges along with a line. It is represented as
Surface charge density is applied for charges over a surface. we can represent it as;
volume charge density is applied for charges within a volume. It is represented as :
These formulas are fundamental for understanding electric fields and forces in various electrical systems. Developed based on the work of early physicists like Charles-Augustin de Coulomb and Michael Faraday, these principles help predict electrical interactions and are crucial in designing electronic components.
Problem: A wire that is 2 meters long carries a total charge of 10 coulombs. What is its linear charge density?Solution:
Use the formula for linear charge density: 𝜆 = 𝑄 \ 𝐿.
Given 𝑄=10 coulombs and 𝐿=2 meters.
Calculate 𝜆=10 / 2 = 5 coulombs per meter.
Answer: The linear charge density is 5 coulombs per meter.
Problem: A square sheet of metal with an area of 4 square meters has a uniform charge of 8 coulombs. Calculate the surface charge density.
Solution:
Apply the formula for surface charge density: 𝜎 = 𝑄 / 𝐴.
Given 𝑄=8 coulombs and 𝐴=4 square meters.
Calculate 𝜎 = 8 / 4 = 2 coulombs per square meter.
Answer: The surface charge density is 2 coulombs per square meter.
Problem: A spherical balloon with a volume of 500 cubic centimeters is uniformly charged with a charge of 5 coulombs. What is the volume charge density?
Solution:
Use the volume charge density formula: 𝜌 = 𝑄 / 𝑉.
Given 𝑄=5 coulombs and 𝑉 = 500 cubic centimeters.
Convert cubic centimeters to cubic meters if necessary (1 cubic meter = 1,000,000 cubic centimeters), so 𝑉=0.0005 cubic meters.
Calculate 𝜌 = 5 / 0.0005 = 10,000 coulombs per cubic meter.
Answer: The volume charge density is 10,000 coulombs per cubic meter.
The current formula for charge density varies: 𝜆 = 𝑄 / 𝐿, 𝜎 = 𝑄 / 𝐴, 𝜌 = 𝑄 / 𝑉 for linear, surface, and volume densities.
“Charge per density” isn’t a standard term; it may refer to the charge distributed per unit length, area, or volume in various contexts.
Calculate charge (Q) by rearranging the charge density formula, e.g., 𝑄 = 𝜆 × 𝐿, 𝑄 = 𝜎 × 𝐴, 𝑄 = 𝜌 × 𝑉, depending on context.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
A uniformly charged rod has a length of 2 meters and a total charge of 10 C. What is the linear charge density?
5C/m
10C/m
15C/m
8
A spherical shell has a surface charge density of σ = 8 C/m² and a radius of 0.5 m. What is the total charge on the shell?
4πC
6πC
8πC
16πC
A cylindrical rod with length 3 m and radius 0.1 m has a volume charge density of ρ = 2 C/m³. What is the total charge?
1.8πC
6πC
0.6πC
1.8C
A thin ring of radius 0.4 m carries a total charge of 2 C. What is the linear charge density?
\frac{5}{\pi} \, \text{C/m}
\frac{5}{4\pi} \, \text{C/m}
\frac{5}{8\pi} \, \text{C/m}
\frac{10}{\pi} \, \text{C/m}
A sheet of dimensions 1 m by 2 m has a uniform surface charge density of σ = 4 C/m². Find the total charge.
4C
8C
12C
16C
A rod of length L has a uniform linear charge density λ. What is the total charge Q on the rod?
λ²L
λL²
λ/L
λL
A hollow sphere of radius R has a surface charge density σ\sigmaσ. If the radius is doubled, how does the total charge Q on the sphere change?
It doubles.
It quadruples.
It halves.
It remains the same.
If a cylinder has a volume charge density ρ and a total charge Q, what is the volume V of the cylinder?
Q+ρ
ρ/Q
Qρ
Q/ρ
If a spherical shell of radius R carries a surface charge density σ, what is the total charge Q on the shell?
4πR²σ
4πRσ
4πR²/σ
σ/4πR²
What is the linear charge densityλ of a wire if the total charge Q on the wire is 12 C and the length of the wire is 3 m?
3 C/m
6 C/m
4 C/m
12 C/m
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

