What is the formula for the diffraction grating?
d sinθ = nλ
d cosθ = nλ
d tanθ = nλd
d sinθ = λ

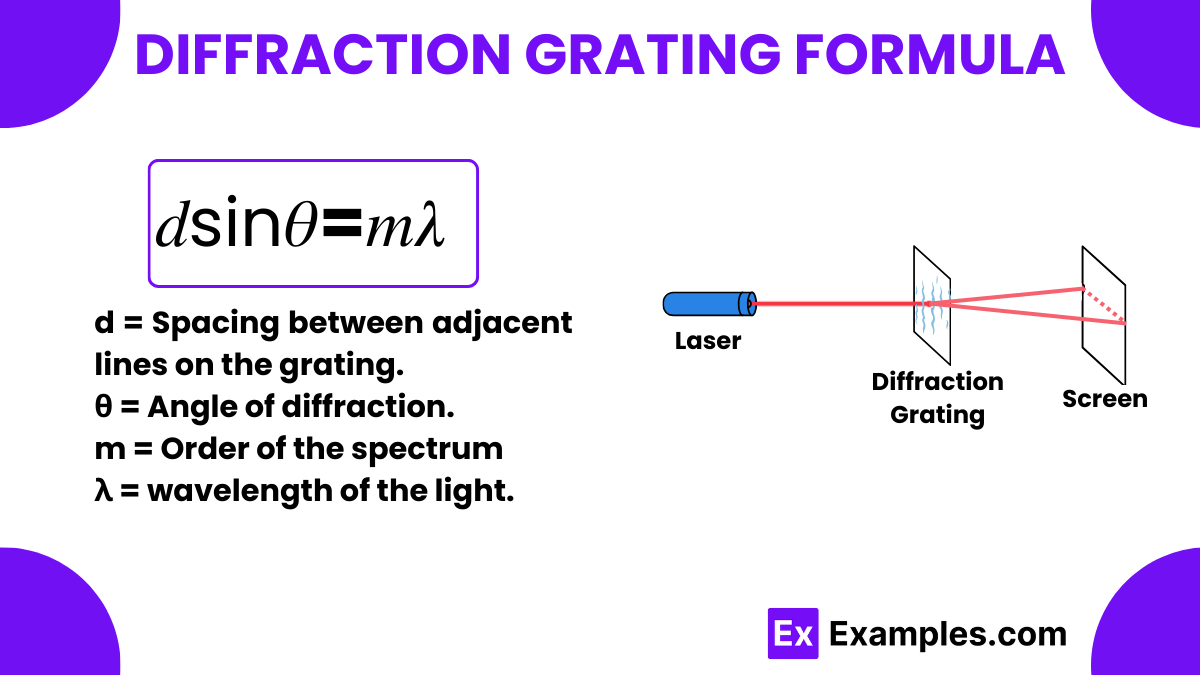
A diffraction grating is an optical component with a regular pattern of closely spaced lines or slits, which diffracts light into several beams traveling in different directions. The fundamental physics governing the behavior of light as it passes through a diffraction grating is encapsulated in the diffraction grating formula. This formula calculates the angles at which light rays spread out after passing through the grating. It can represent as
The concept and mathematical description of diffraction gratings were developed by the American physicist David Rittenhouse in 1785. His early experiments, which involved looking at the spectra created by light diffraction through bird feathers, paved the way for later, more refined techniques. This formula helps scientists and engineers design grating to precisely control light dispersion in spectrometers, telescopes, and other optical devices, making it a cornerstone in the field of optics within physics.
Question: A diffraction grating has 5000 lines per centimeter. Find the angle at which the first-order maximum (m = 1) will occur for light with a wavelength of 600 nm.
Solution:
Step 1: Calculate the line spacing 𝑑d. Since there are 5000 lines/cm, convert cm to meters for consistency:
𝑑=1 cm / 5000 lines = 0.01 m / 5000 = 2×10⁻⁶ m=2000 nm;
Step 2: Use the diffraction grating formula 𝑑sin𝜃 = 𝑚𝜆
2000 nm × sin𝜃 = 1×600 nm
Step 3: Solve for θ:
sin𝜃=600 nm / 2000 nm=0.3
𝜃=sin−1(0.3)≈17.5.
Conclusion: The First-order maximum for 600 nm light occurs at approximately 17.5 degrees.
Question: If the same grating is used, at what angle will the second-order maximum (m = 2) occur for the same wavelength of light?
Solution:
Step 1: Use the same line spacing 𝑑=2000 nm and apply the Diffraction grating formula:
2000 nm × sin𝜃 = 2×600 nm=1200 nm.
Step 2: Solve for θ:
sin𝜃=1200 nm / 2000 nm=0.6
𝜃=sin−1(0.6)≈36.9.
Conclusion: The Second-order maximum for 600 nm light occurs at approximately 36.9 degrees.
In the double slit formula, D represents the distance between the two slits, crucial for calculating the interference pattern.
The main idea of a diffraction grating is to separate light into its component wavelengths by interference, providing detailed spectral analysis.
To calculate D in a diffraction grating, divide the length of the grating by the total number of slits to get the spacing between them.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for the diffraction grating?
d sinθ = nλ
d cosθ = nλ
d tanθ = nλd
d sinθ = λ
In the diffraction grating formula, what does d represent?
Wavelength of light
Distance between slits
Angle of diffraction
Order of maximum
How is the order of maximum represented in the diffraction grating formula?
θ
d
n
λ
What happens to the angle of diffraction (θ) if the wavelength (λ) is increased?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
If the number of slits per unit length increases, what happens to the distance ddd between slits?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
For a given order nnn, if the angle of diffraction θ is 0°, what is the wavelength λ?
Zero
Infinite
Equal to d
Cannot be determined
What does the grating spacing d depend on?
Number of slits
Wavelength of light
Angle of diffraction
Number of slits per unit length
If the wavelength of light used in a diffraction grating experiment is doubled, what happens to the angle of diffraction for the first-order maximum?
It is halved
It doubles
It remains the same
It becomes zero
For a grating with 600 lines per mm, what is the grating spacing ddd?
600 nm
1/600 m
1/600 mm
600 mm
How is the angle of diffraction affected when the order of maximum n is increased?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

