What is the formula for calculating electrical energy consumption?
E = P×t
E = V×I
E = I×R
E = V×Q

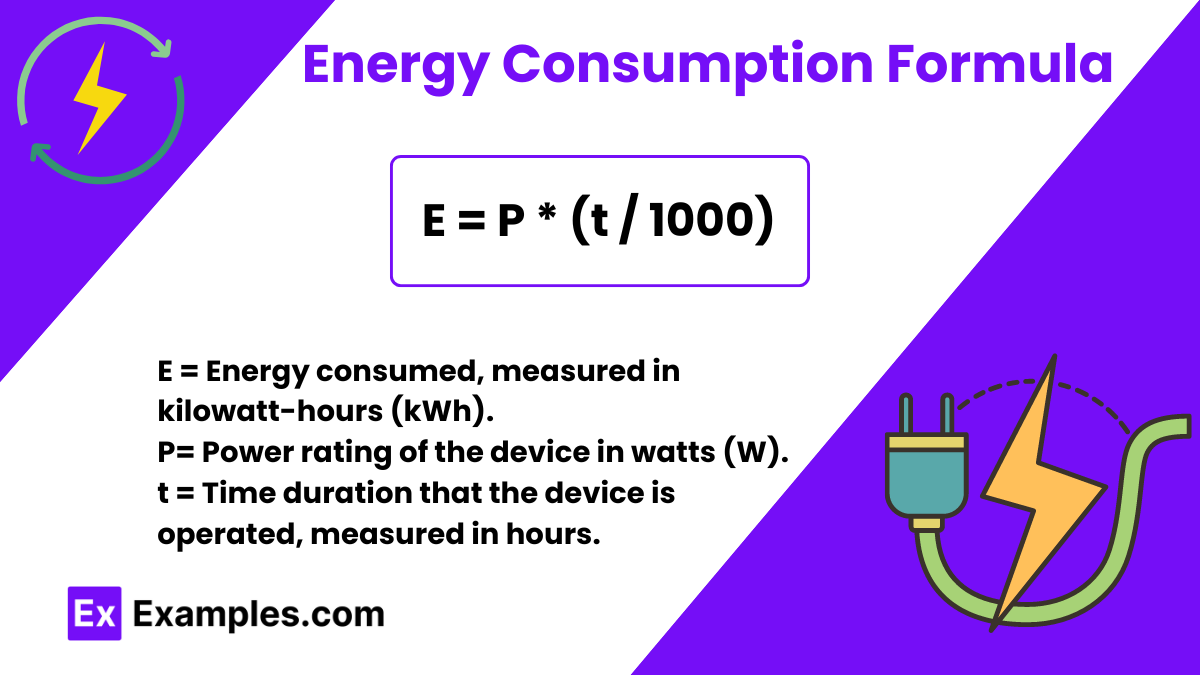
The formula represents the energy consumption as:
is a crucial tool in physics for calculating the energy used by an electrical device over a specific period.
The division by 1000 is necessary to convert the power from watts to kilowatts, as the standard unit for energy consumption is kilowatt-hours.
This formula was developed from the basic principles of power and energy in physics. Power is defined as the rate at which energy is used, and by integrating this rate over time, we obtain the total energy consumed. The formula itself is an application of these principles, formulated to provide a practical tool for measuring energy usage in electrical devices. While no single individual is credited with its discovery, it is derived from the fundamental laws of electricity and energy that scientists like James Prescott Joule explored in the 19th century
Energy consumed over a period is calculated by multiplying power by time. The formula in its basic form is:
In practical scenarios, particularly in household and industrial electricity usage, we typically measure energy in kilowatt-hours (kWh) instead of joules, and we use hours instead of seconds for time. To align with these units:
Convert power from watts to kilowatts. Since 1 kilowatt (kW) = 1000 watts (W), we divide the power by
Convert time from seconds to hours. Since 1 hour = 3600 seconds, if we have time in hours, we keep it as it is without conversion for this formula.
Using the new units, the energy consumption formula is adapted to:
𝐸=(𝑃 / 1000) × 𝑡
𝐸 = 𝑃 × (𝑡 / 1000)
Here, E now represents the energy in kilowatt-hours (kWh), P is still the power in watts (W), and 𝑡t is the time in hours (h).
Problem: A 60-watt light bulb is used for 5 hours a day. How much energy does it consume in one day?
Solution:
Using the formula 𝐸 = 𝑃 × (𝑡 / 1000):
𝐸 = 60 × (5 / 1000) = 0.3 kWh
Result: The light bulb consumes 0.3 kWh of energy per day.
Problem: A refrigerator with a power rating of 200 watts runs continuously. Calculate its energy consumption for a month (30 days).
Solution:
Using the formula 𝐸 = 𝑃 × (𝑡 / 1000):
𝐸 = 200 × (720 / 1000)=144 kWh
Result: The refrigerator uses 144 kWh of energy in one month.
Problem: An air conditioner with a power rating of 1000 watts runs for 8 hours a day. If the cost of electricity is $0.10 per kWh, calculate the annual cost to operate the air conditioner.
Solution:
Using the formula 𝐸 = 𝑃 × (𝑡/ 1000) :
𝐸 =1000 × (2920 / 1000) = 2920 kWh
To find the cost:
Cost=2920 kWh × $0.10/kWh = $292
Result: It costs $292 annually to operate the air conditioner.
Use the formula: Specific Energy = Total Energy Used / Output. It measures energy efficiency per unit of output.
The kWh consumption formula is 𝐸 = 𝑃 × (𝑡 / 1000), where 𝐸 is energy in kWh.
Multiply daily kWh by 365: 𝐴𝑛𝑛𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑘𝑊ℎ = 𝐷𝑎𝑖𝑙𝑦 𝑘𝑊ℎ × 365. This estimates yearly energy usage.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for calculating electrical energy consumption?
E = P×t
E = V×I
E = I×R
E = V×Q
A 100 W light bulb is used for 5 hours. How much energy does it consume?
100 Wh
500 Wh
50 Wh
5 kWh
If an appliance has a power rating of 1500 W and it runs for 2 hours, what is the energy consumption?
1.5 kWh
0.75 kWh
3 kWh
2.5 kWh
What is the energy consumption of a device that uses 0.5 kW of power over 4 hours?
2 kWh
1.5 kWh
0.2 kWh
4.5 kWh
An air conditioner operates at 2000 W for 3 hours. What is the total energy consumption?
6 kWh
3 kWh
6000 Wh
Both A and C
A 75 W fan runs for 10 hours. What is its energy consumption in kilowatt-hours?
A 75 W fan runs for 10 hours. What is its energy consumption in kilowatt-hours?
0.75 kWh
1.5 kWh
7.5 kWh
0.075 kWh
If a refrigerator has a power rating of 300 W and it runs for 24 hours, what is the energy consumption?
7.2 kWh
3.6 kWh
12 kWh
24 kWh
What is the energy consumption of a device that uses 500 W of power over 6 hours?
0.5 kWh
3 kWh
1.5 kWh
6 kWh
A washing machine operates at 1200 W for 1.5 hours. What is the total energy consumption?
1.2 kWh
1.4 kWh
1.6 kWh
1.8 kWh
If a 60 W light bulb is used for 8 hours a day for 30 days, what is the total energy consumption?
14.4 kWh
16.8 kWh
12 kWh
10 kWh
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

