What is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI)?
Newton
Pascal
Joule
Watt

In physics, force is any interaction that changes the motion of an object when unopposed. It can cause an object to accelerate, described as a push or pull resulting from interaction with another object. Force is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction, and is measured in Newtons (N) in the International System of Units (SI). Key concepts include the Units of Force, the Centripetal Force Formula, the Resultant Force Formula, and the Drag Force Formula.
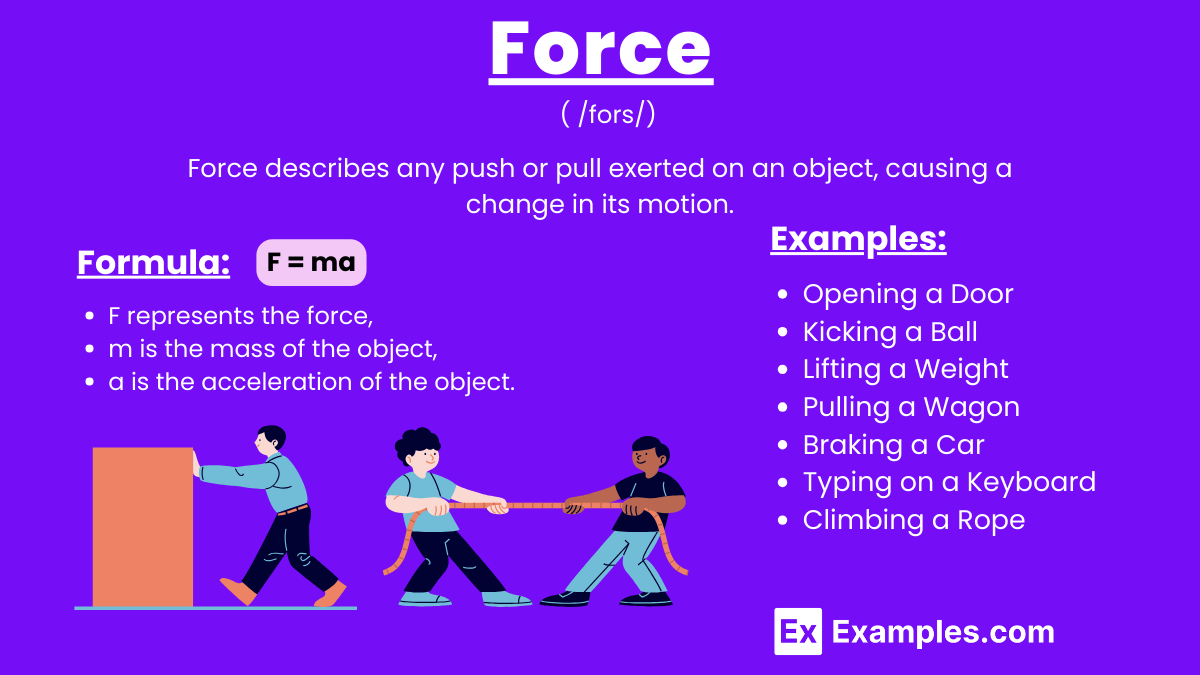
Force is a vector quantity that describes any push or pull exerted on an object, causing a change in its motion. It results from interactions between objects and is measured in newtons (N). The net force is the sum of all individual forces acting on an object, leading to acceleration.
The formula for force is given by Newton’s second law of motion:
where:
The force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared, or kg·m·s⁻².
The force required to accelerate a one-gram mass by one centimeter per second squared, or g·cm·s⁻².
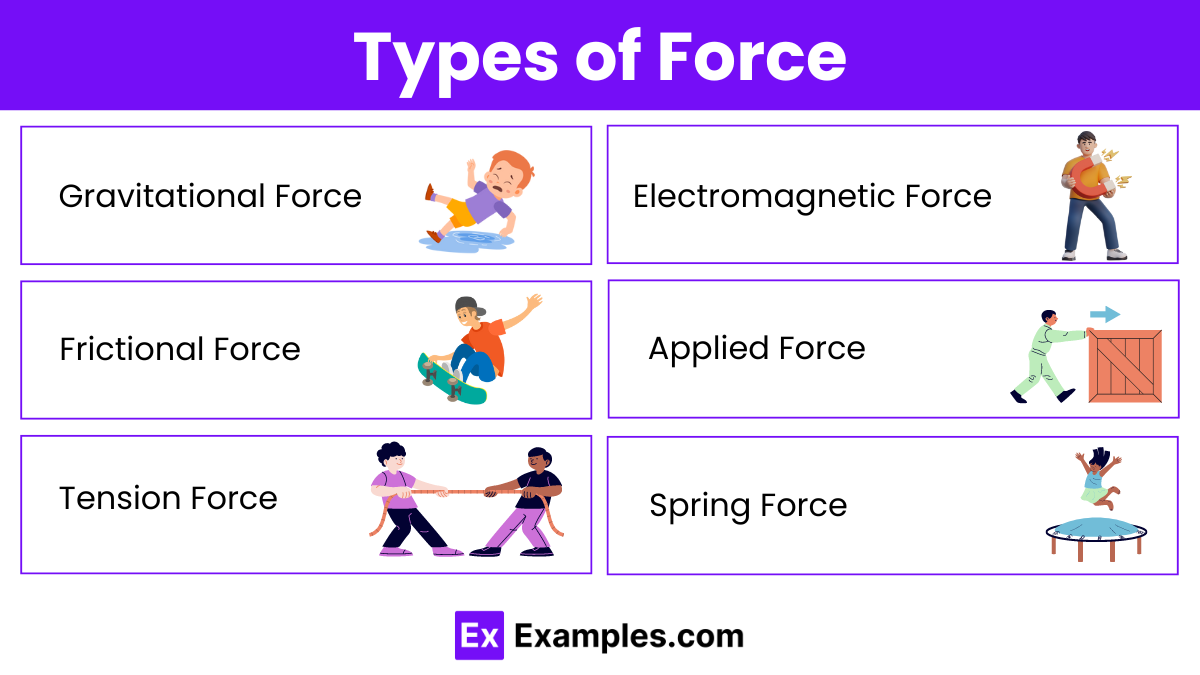
Force can be classified into various types based on the nature of the interaction between objects and the effects they produce. Here are the primary types of forces:
Force is measured in newtons (N) using a force meter or a spring scale, where one newton equals the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass by one meter per second squared.
An object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force, illustrating the concept of inertia.
The acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting upon it and its mass, formulated as F = ma (Force = mass × acceleration).
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, meaning forces always occur in pairs that act on different objects.
Gravitational force is the attractive force between two masses, proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Friction is the force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact, dependent on the nature of the surfaces and the normal force pressing them together.
Tension force is the force transmitted through a string, rope, or wire when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends.
Normal force is the support force exerted upon an object in contact with a stable surface, acting perpendicular to the surface.
Air resistance is the force that opposes the motion of objects through air, depending on the object’s speed, shape, and surface area.
Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass, calculated as weight = mass × gravitational acceleration.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI)?
Newton
Pascal
Joule
Watt
What does Newton's First Law of Motion state about an object at rest?
It will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force
It will start moving with constant velocity
It will accelerate indefinitely
It will change its shape
Which of the following is an example of a contact force?
Gravitational force
Magnetic force
Frictional force
Electromagnetic force
If the net force acting on an object is zero, what happens to its motion?
The object will accelerate
The object will decelerate
The object will continue to move at a constant velocity or remain at rest
The object will change its direction of motion
What is the formula for calculating force?
Force = Mass × Velocity
Force = Mass × Acceleration
Force = Mass / Acceleration
Force = Acceleration / Mass
What is the direction of the force of gravity acting on an object?
Upwards
Downwards
Sideways
Diagonally
If the mass of an object is doubled, what happens to the force required to accelerate it at a constant rate?
The force remains the same
The force is halved
The force is doubled
The force is tripled
Which force acts perpendicular to the direction of motion?
Frictional force
Gravitational force
Normal force
Tension force
What type of force is responsible for holding molecules together in a substance?
Gravitational force
Electromagnetic force
Nuclear force
Frictional force
When two objects collide and stick together, which type of force is primarily involved?
Gravitational force
Normal force
Frictional force
Impact force
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

