What is a gradian?
A unit of distance
A unit of time
A unit of angle
A unit of weight

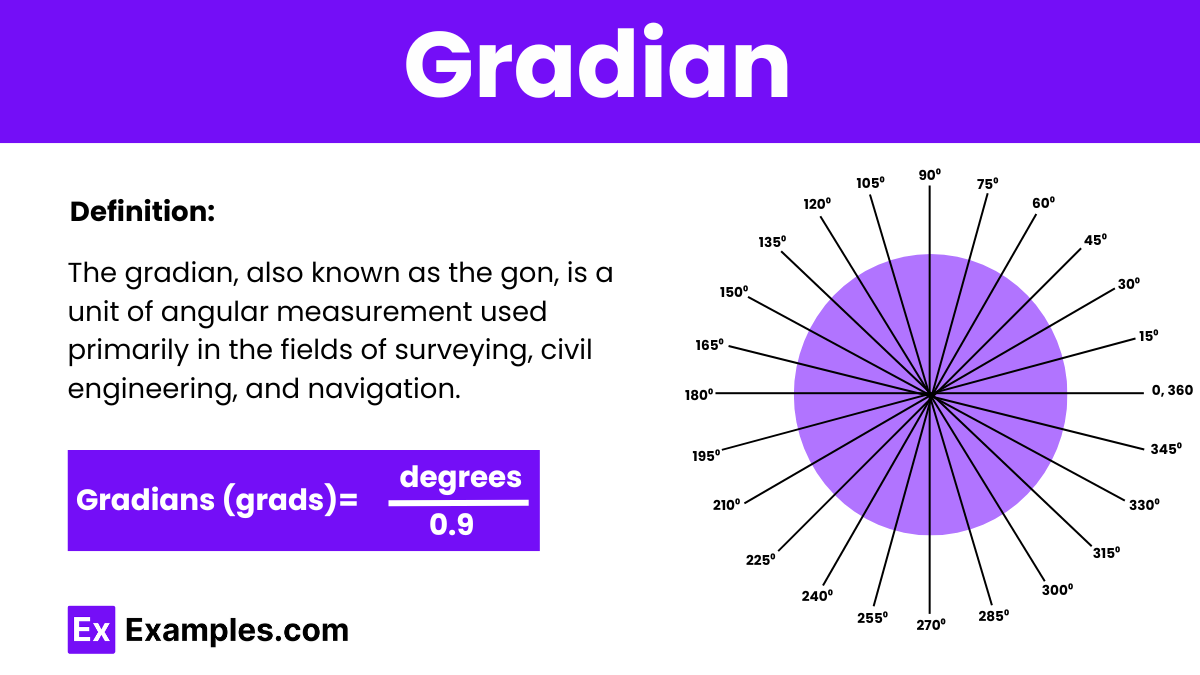
Gradian is a unit of angular measurement equal to 1/400th of a circle, commonly used in surveying, mapping, and some European educational contexts. Each gradian subdivides into 100 centesimal minutes.
From Radians to Gradians
From Gradians to Degrees
From Gradians to Radians
1.Surveying
A land surveyor measures a field boundary angle as 100 gradians to ensure accurate mapping.
2. Civil Engineering
Engineers design a road curve that subtends an angle of 50 gradians for safe and efficient traffic flow.
3. Mathematics Education
A math teacher uses an angle of 25 gradians in a geometry problem to teach students about angular measurements.
4. Mapping
Cartographers might denote a 150-gradian angle on a new map to represent specific landmark orientations.
5. Construction
In constructing a pentagon, each internal angle might be set to approximately 158.4 gradians for precision.
6. Artillery
Military uses, such as calculating the firing angle for an artillery piece, often involve measurements like 75 gradians.
7. Astronomy
Astronomers might use a small angular measurement of 1 gradian to track the movement of a star across the sky.
8. Robotics
A robotic arm might rotate 80 gradians to position itself to pick up an object correctly.
9. Navigation
Navigators might use gradians to measure the bearing between two points in a navigation chart.
10. 0 grad
This represents a zero angle, where no rotation from the reference line is observed.
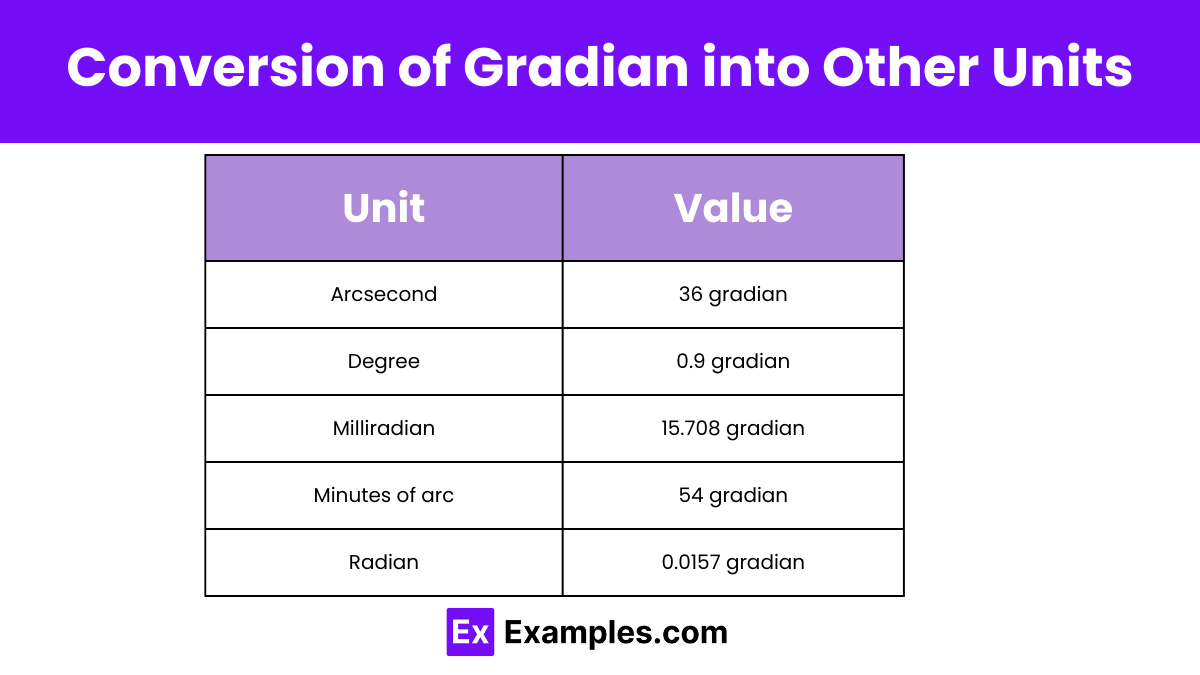
| Arcsecond | 36 gradian |
| Degree | 0.9 gradian |
| Milliradian | 15.708 gradian |
| Minutes of arc | 54 gradian |
| Radian | 0.0157 gradian |
One gradian equals 3600 arcseconds, a unit used in precise angular measurements in astronomy and geodesy.
One gradian equals 0.9 degree, a unit used for measuring angles, especially in surveying and certain educational contexts.
One gradian is equivalent to approximately 15.708 milliradians, used in ballistics, optics, and other precision scientific calculations.
One gradian is equal to 54 minutes of arc, a measurement unit commonly used in astronomy and navigation.
One gradian is equivalent to π/200 radian, a measurement used in angles, particularly beneficial in surveying and geometry.
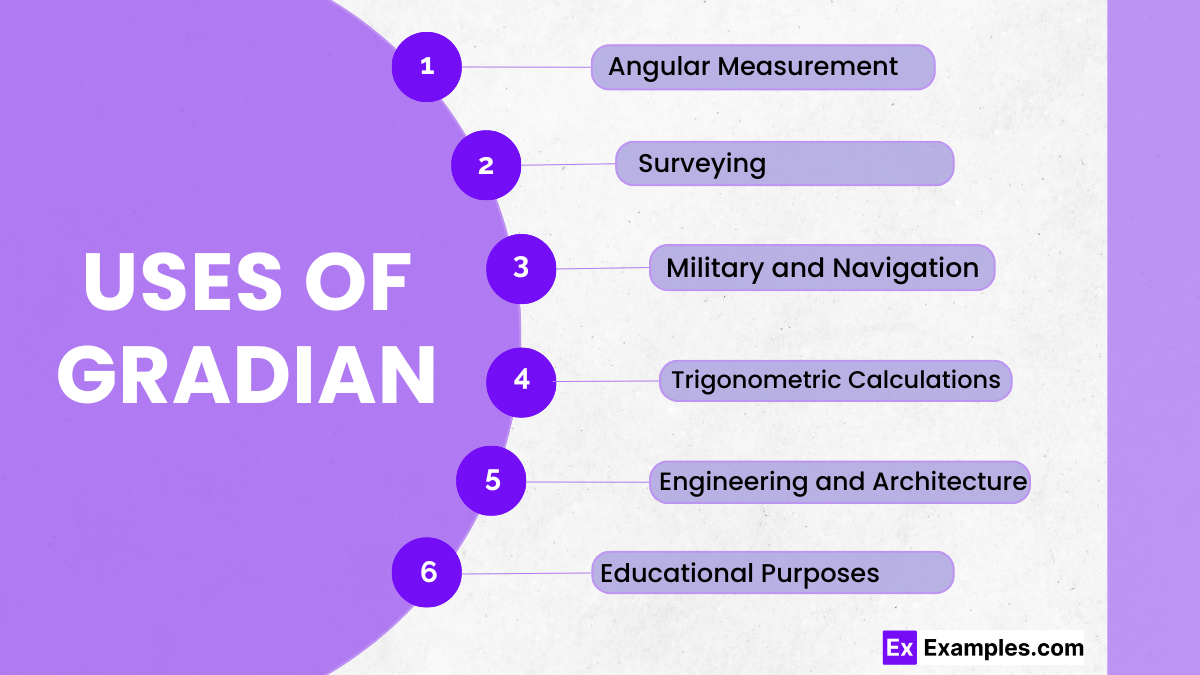
Gradians are commonly used in fields like surveying, navigation, military, and certain trigonometric calculations.
One full rotation in radians is equal to 2π radians, while in gradians it is equal to 400 gradians.
Yes, in certain applications like artillery targeting or compass bearings, gradians offer a simple and precise way to communicate directions and angles.
The abbreviation for Gradians is “grad” or sometimes “gon”.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is a gradian?
A unit of distance
A unit of time
A unit of angle
A unit of weight
How many gradians are there in a right angle?
90
100
200
300
How many gradians are in a full circle?
180
200
360
400
How many gradians are there in a straight angle?
100
200
300
400
onvert 25 gradians to degrees.
15°
20°
22.5°
25°
What is the gradian measure of an angle of 45 degrees?
25 gradians
50 gradians
60 gradians
70 gradians
Convert 400 gradians to degrees.
360°
400°
450°
500°
What is the gradian measure of an angle of 60 degrees?
50 gradians
60 gradians
66.67 gradians
75 gradians
What is the gradian measure of an angle of 270 degrees?
200 gradians
225 gradians
300 gradians
360 gradians
Convert 10 gradians to degrees.
5°
9°
12°
14°
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

