What is the formula for Hubble's Law?
v = H₀d
E = mc²
F = ma
P = IV

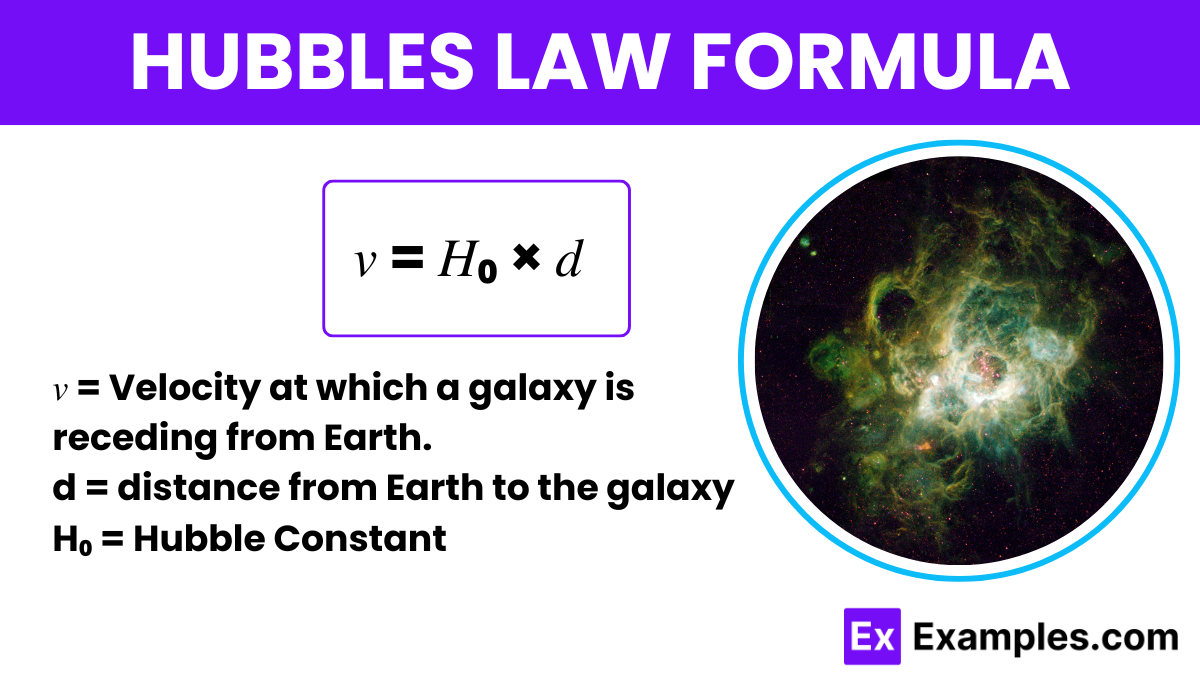
Hubble’s Law describes the relationship between the distance to a galaxy and the speed at which it moves away from us, reflecting the expansion of the universe. Edwin Hubble is an physics scientists, who discovered this phenomenon in 1929, revealing that the universe is expanding.
The formula for Hubble’s Law is:
To derive this formula, Hubble plotted the velocities of galaxies against their distances, establishing a linear relationship. The slope of this line, the Hubble Constant, indicates how fast the universe expands per megaparsec of distance.
This simple yet profound equation means that the farther a galaxy is from us, the faster it moves away. This observation supports the theory that the universe started from a singular event, commonly known as the Big Bang.
Problem: If a galaxy is located 100 megaparsecs (Mpc) away from Earth, and the Hubble Constant (H₀) is estimated to be 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc), what is the recessional velocity of this galaxy?
Solution: To find the recessional velocity (v), use the formula:
v=H₀ × d
Substitute the given values:
𝑣=70 km/s/Mpc×100 Mpc
𝑣=7000 km/s
The galaxy is moving away from Earth at a velocity of 7000 km/s.
Problem: A galaxy is moving away from us at a velocity of 2100 km/s. Using a Hubble Constant of 70 km/s/Mpc, estimate the distance from Earth to this galaxy.
Solution: Rearrange the Hubble’s Law formula to solve for distance (d):
𝑑=𝑣 x 𝐻₀
Substitute the given values:
𝑑= (2100 km/s) / (70 km/s/Mpc)
𝑑=30 Mpcd
The galaxy is approximately 30 megaparsecs away from Earth.
Problem: Astronomers measure the recessional velocity of a galaxy as 2800 km/s. If this galaxy is known to be 40 megaparsecs (Mpc) away from Earth, calculate the Hubble Constant (H₀).
Solution: Rearrange Hubble’s Law to solve for the Hubble Constant 𝐻₀:
𝐻₀=𝑣 / 𝑑
Substitute the given values: 𝐻₀= (2800 km/s) / (40 Mpc)
𝐻₀=70 km/s/Mpc
The Hubble Constant is calculated to be 70 km/s/Mpc.
Problem: Assuming the Hubble Constant remains constant at 70 km/s/Mpc, calculate the future recessional velocity of a galaxy currently 50 megaparsecs away, assuming it moves to 55 megaparsecs away from Earth.
Solution: First, use Hubble’s Law to calculate the current velocity:
𝑣 current=𝐻₀ × 𝑑 current = 70 km/s/Mpc × 50 Mpc
𝑣 current=3500 km/s
Next, calculate the future velocity:
𝑣 future=𝐻₀ × 𝑑 future=70 km/s/Mpc × 55 Mpc
𝑣 future=3850 km/s
The future recessional velocity of the galaxy, when it is 55 Mpc away, will be 3850 km/s.
Measure the slope of the velocity-distance graph for distant galaxies to find Hubble’s constant.
As of the latest observations, Hubble’s constant is approximately 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec.
Hubble’s length, derived from Hubble’s constant, represents the scale of the observable universe, approximately 14 billion light-years.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for Hubble's Law?
v = H₀d
E = mc²
F = ma
P = IV
What does 'v' represent in the Hubble's Law formula v = H₀d?
Volume
Velocity
Voltage
Viscosity
What does 'd' represent in the formula v = H₀d?
Density
Distance
Diameter
Displacement
What is Hubble's constant denoted as in the formula v = H₀d?
H₀
G
c
k
Which physical phenomenon does Hubble's Law describe?
Gravitational attraction
Electromagnetic force
Expansion of the universe
Nuclear fusion
How is the recessional velocity (v) of a galaxy related to its distance (d) according to Hubble's Law?
Inversely proportional
Directly proportional
Exponentially proportional
Unrelated
If the distance to a galaxy is doubled, what happens to its recessional velocity according to Hubble's Law?
It remains the same
It is halved
It doubles
It becomes zero
What is the unit of Hubble's constant (H₀)?
m/s
s⁻¹
km/s/Mpc
m²/s²
Which observation led to the formulation of Hubble's Law?
The motion of planets
The spectrum of light from distant galaxies
The behavior of gases
The rotation of stars
How does Hubble's Law support the Big Bang Theory?
By showing that the universe is static
By showing that the universe is expanding
By showing that the universe is contracting
By showing that the universe is rotating
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

