What is an implosion?
A sudden outward explosion
A rapid inward collapse
An even distribution of force
A slow expansion of material
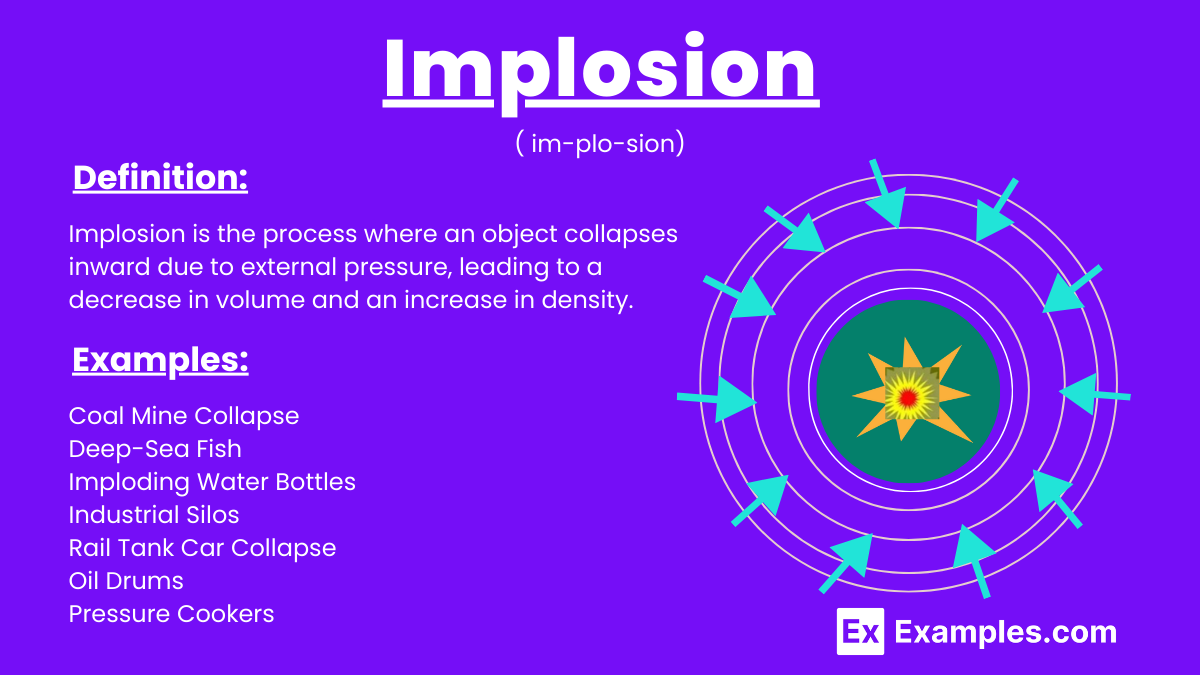
Implosion is the process where an object collapses inward under the influence of external pressure, typically leading to a reduction in volume and an increase in density. Unlike an explosion, where energy is released outward, implosion compresses an object, often resulting in a sudden and forceful inward collapse. This phenomenon is observed in various contexts, such as the collapse of buildings during controlled demolitions, the implosion of underwater structures due to high external pressure, and in astrophysics, where stars can implode to form neutron stars or black holes.
Implosion is the process where an object collapses inward due to external pressure, leading to a decrease in volume and an increase in density. This inward collapse is the opposite of an explosion, which releases energy outward. Implosions can occur in controlled demolitions, underwater structures under high pressure, and in astrophysical events such as the formation of black holes or neutron stars.
| Aspect | Explosion | Implosion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid expansion and release of energy outward | Collapse inward due to external pressure |
| Pressure | Increases pressure inside, causing outward force | Decreases volume by external forces pushing inward |
| Examples | Bomb detonations, volcanic eruptions, supernovae | Controlled demolitions, underwater structure collapses, stellar core collapse |
| Effects | Destruction spreads outward, debris and shockwaves move away from the source | Object compresses and contracts, often creating high-density remnants |
| Applications | Mining, demolition, fireworks, combustion engines | Controlled building demolition, nuclear weapons, astrophysical phenomena like black holes |
Implosion occurs when an object collapses inward due to external pressure that exceeds the internal pressure of the object. Here are the key steps and factors involved in the process:
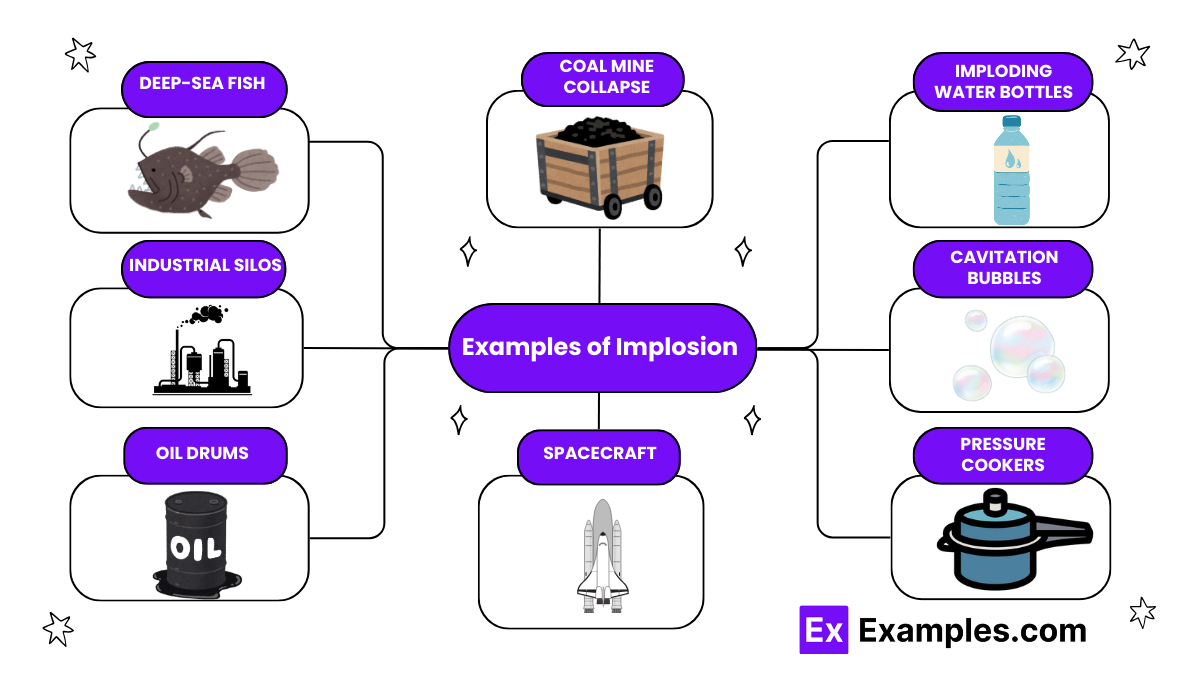
Yes, natural implosions can occur, such as when deep-sea creatures implode due to rapid pressure changes.
Demolition of buildings using controlled explosions to collapse structures inward is a common example of a man-made implosion.
Implosions are used in demolitions to control the collapse, reducing the spread of debris and ensuring safety.
Implosions occur due to a significant pressure difference, where higher external pressure crushes the object inward.
Yes, an implosion can create a temporary vacuum as the internal space rapidly collapses inward.
Implosions can be dangerous, especially if uncontrolled, leading to debris and structural damage.
Air pressure difference is crucial, with external pressure exceeding internal pressure causing the collapse.
Implosions are less likely in space due to the absence of atmospheric pressure, but can occur with rapid decompression in vessels.
Construction, demolition, and military industries use controlled implosions for safe removal of structures and munitions.
Yes, small objects like cans and bottles can implode if external pressure significantly exceeds their internal pressure.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is an implosion?
A sudden outward explosion
A rapid inward collapse
An even distribution of force
A slow expansion of material
Which scenario is an example of an implosion?
A balloon popping when overfilled
A building collapsing in on itself
A rocket launching into space
A bubble expanding in water
What typically causes an implosion in a controlled demolition?
Overloading with external force
Internal combustion
A precise arrangement of explosives
Chemical reaction with the air
In which field is implosion most commonly used for controlled demolitions?
Medicine
Construction
Agriculture
Food processing
Which of the following can result from an implosion?
Increased pressure
Fragmentation outward
A vacuum effect
Uniform expansion
What is the primary difference between an explosion and an implosion?
Direction of force application
Speed of the reaction
Type of material involved
Temperature of the reaction
What type of implosion involves the collapse of a star under its own gravity?
Nuclear implosion
Supernova
Stellar implosion
Gravitational implosion
Which of the following describes a vacuum implosion?
Collapse of an object due to high internal pressure
Collapse of an object due to low external pressure
Expansion of gases inside a container
Sudden release of chemical energy
In the context of implosions, what is meant by "pressure differential"?
The difference between the internal and external pressures
The average pressure in a medium
The uniform pressure throughout a system
The pressure exerted by gravity
Which safety precaution is crucial when performing an implosion in a demolition?
Ensuring a strong external support structure
Using minimal amounts of explosives
Clearing the area of people and sensitive equipment
Increasing the height of the building
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

