What does the instantaneous speed of an object represent?
Average speed over a long period
The rate of change of position at a specific moment
Distance traveled in total
The maximum speed reached

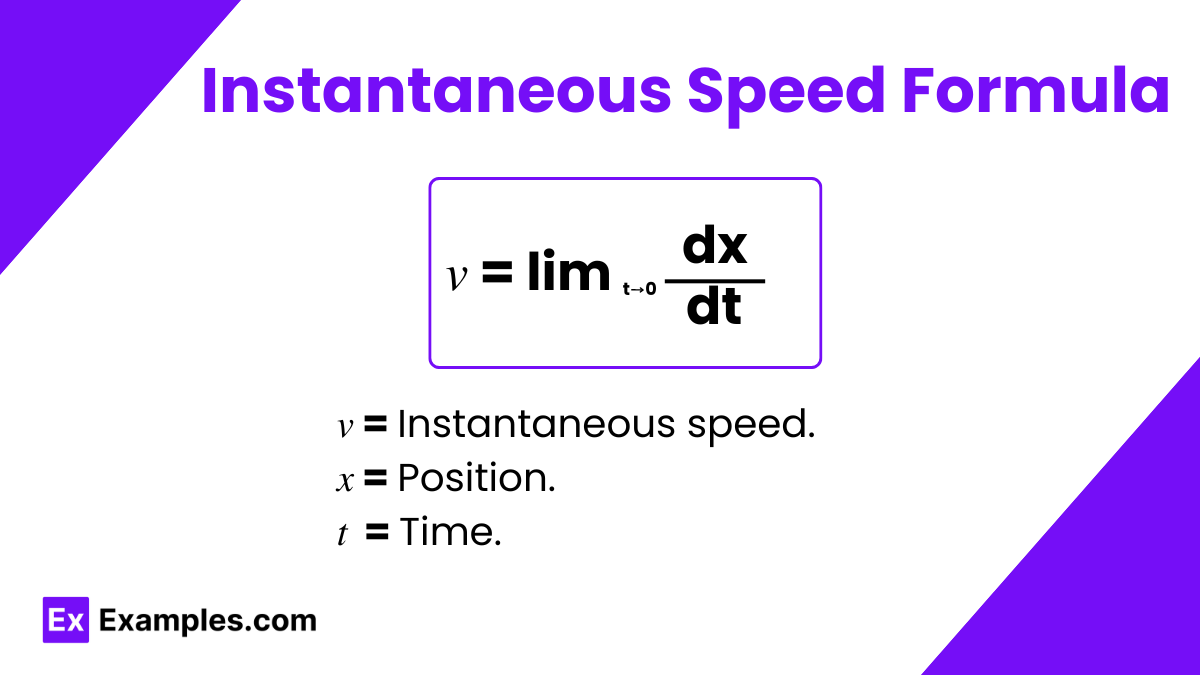
The instantaneous speed formula in physics quantifies the exact speed of an object at a specific moment in time. It is expressed as the limit of the average speed as the time interval approaches zero. In mathematical terms, we represent this formula as the derivative of the position with respect to time, given by
This concept and formula were pioneered through the efforts of Sir Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in the 17th century as part of their development of calculus. Newton’s laws of motion and Leibniz’s mathematical notations provided the tools to calculate how objects move with varying speeds at any given instant. Instantaneous speed is thus a fundamental concept that helps explain how objects behave in dynamic systems, particularly in fields such as mechanics and physics.
Problem: A car travels along a road, and its position at time 𝑡t is given by the equation 𝑥(𝑡)=5𝑡² + 2𝑡 meters, where 𝑡 is in seconds. Find the instantaneous speed of the car at 𝑡= 3 seconds.
Solution: To find the instantaneous speed, take the derivative of the position function with respect to time:
𝑣(𝑡) = 𝑑𝑥 / 𝑑𝑡 = 𝑑 / 𝑑𝑡 ( ( 5𝑡² + 2𝑡 ) ) = 10𝑡 +2
Now, substitute 𝑡=3 seconds into the derivative:
𝑣(3) =10(3) + 2 = 32 m/s
Answer: The car’s instantaneous speed at 3 seconds is 32 meters per second.
Problem: A runner’s position on a track is defined by the function 𝑥(𝑡)=3𝑡³ − 15𝑡² +18𝑡, where 𝑥 is in meters and 𝑡t in seconds. Calculate the runner’s instantaneous speed at 𝑡 = 5 seconds.
Solution: First, differentiate the position function:
𝑣(𝑡) = 𝑑𝑥 / 𝑑𝑡=𝑑 / 𝑑𝑡 ( (3𝑡³ − 15𝑡² +18𝑡) ) = 9𝑡² − 30 𝑡 + 18
Substitute 𝑡=5 seconds:
𝑣(5) = 9(5)² − 30(5) + 18 = 225 − 150 +18 = 93 m/s
Answer: The runner’s instantaneous speed at 5 seconds is 93 meters per second.
Problem: An object is dropped from rest from a height, and its height above the ground after 𝑡 seconds is given by 𝑦(𝑡) = 100 − 4.9𝑡² meters. Determine the instantaneous speed of the object at 𝑡 = 4 seconds.
Solution: The instantaneous speed is the absolute value of the derivative of the height function:
𝑣(𝑡) = ∣𝑑𝑦 / 𝑑𝑡∣ = ∣𝑑 / 𝑑𝑡 ( (100 − 4.9𝑡² )) ∣ = ∣ −9.8𝑡∣
For t = 4 seconds:
𝑣(4) = ∣ −9.8(4) ∣ = 39.2 m/s
Answer: The object’s instantaneous speed at 4 seconds is 39.2 meters per second downward.
No, measuring instantaneous speed directly is not possible. c
The formula for instantaneous force is 𝐹 = 𝑚 (𝑑𝑣 / 𝑑t). Where 𝑚 is mass and 𝑑𝑣 / 𝑑𝑡 is the acceleration.
Calculating instantaneous speed is challenging due to the necessity of precise measurements of time and position changes at very small intervals.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does the instantaneous speed of an object represent?
Average speed over a long period
The rate of change of position at a specific moment
Distance traveled in total
The maximum speed reached
How is instantaneous speed related to instantaneous velocity?
They are always the same
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity
Instantaneous velocity is always zero
They are completely unrelated
What information do you need to calculate instantaneous speed from a position-time graph?
The slope of the tangent line to the curve
The area under the curve
The total distance traveled
The change in position over the entire graph
What does the instantaneous speed of a particle in uniform circular motion represent?
The rate of change of its angular position
The constant rate of change of its radial distance
The constant speed along its circular path
The change in its centripetal force
In calculus, what operation is used to determine instantaneous speed from a position function?
Integration
Differentiation
Multiplication
Addition
For an object with a varying speed, how is the instantaneous speed different from average speed?
Instantaneous speed is the same as average speed
Instantaneous speed varies at different points, while average speed is the total distance divided by total time
Instantaneous speed is always zero
Average speed varies at different points
What type of graph can be used to determine instantaneous speed if you have position vs. time data?
Bar graph
Line graph with tangent lines
Pie chart
Histogram
How do you calculate instantaneous speed if you have a velocity-time graph?
Find the area under the curve
Look at the value of the velocity at a specific time
Differentiate the velocity function
Integrate the velocity function
What does the term 'differentiation' refer to in finding instantaneous speed?
Calculating the area under the curve
Finding the rate of change of a function
Adding values together
Averaging data over a period
Which of the following equations represents the instantaneous speed of an object in uniformly accelerated motion?
v = u + at
v = u² + 2as
v = s / t
v = (s2 - s1) / (t2 - t1)
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

