What is the formula for the Lorentz force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field?
F = qE + q(v × B)
F = qE - q(v × B)
F = q(E + v × B)
F = q(E - v × B)
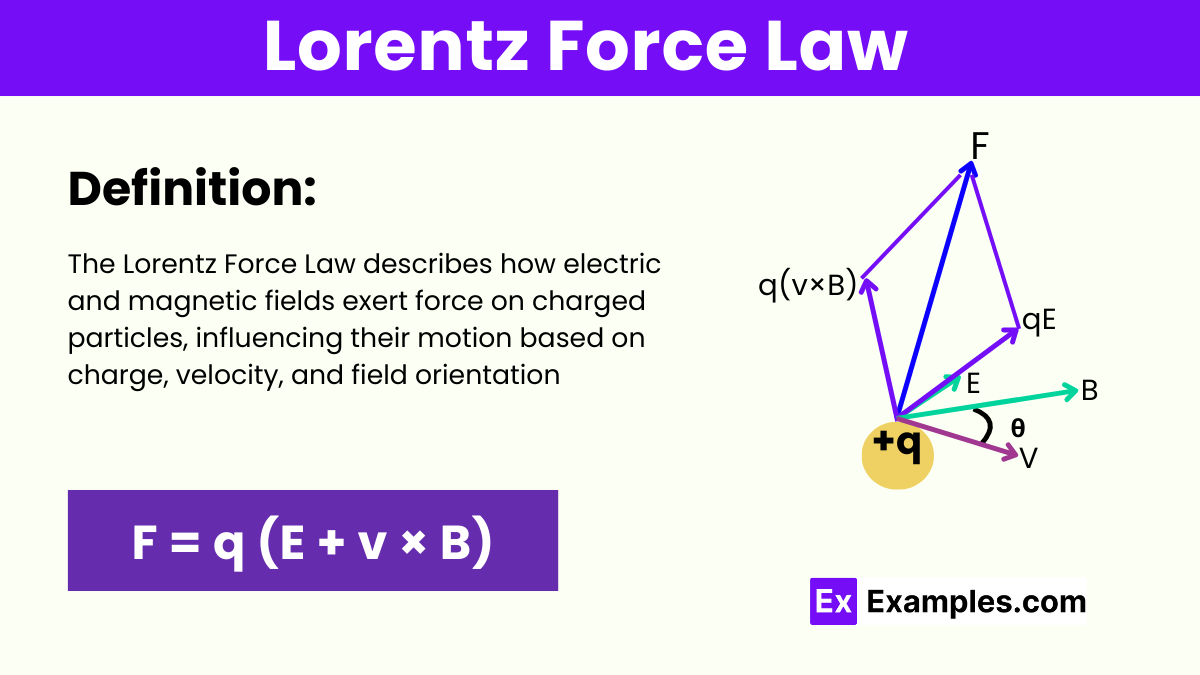
Where:
The SI unit of the Lorentz force is the newton (N). The Lorentz force law describes the force experienced by a charged particle moving through electric and magnetic fields.
In the cgs (centimeter-gram-second) system, the Lorentz force is measured in dynes. The formula for the Lorentz force remains the same, but the units change: charge in statcoulombs, electric field in statvolts per centimeter, velocity in centimeters per second, and magnetic field in gauss. This results in force expressed in dynes.
| Variable | Symbol | Unit | Role in Lorentz Force |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Field | 𝐸 | Volts per meter (V/m) | Generates force on charge regardless of its motion |
| Magnetic Field | 𝐵 | Tesla (T) or Weber per square meter (Wb/m²) | Influences moving charges, perpendicular to motion |
| Charge | 𝑞 | Coulomb (C) | Determines magnitude of the force; sign affects direction |
| Velocity of Charge | 𝑣 | Meters per second (m/s) | Speed and direction of charge; crucial for magnetic force |
| Lorentz Force | 𝐹 | Newton (N) | Resultant force acting on the charge |
The Lorentz force dictates the path that charged particles, like electrons and protons, take when they move through electric and magnetic fields. The direction and speed of their movement are influenced by the characteristics of these fields and the particles’ own properties (such as charge and velocity).
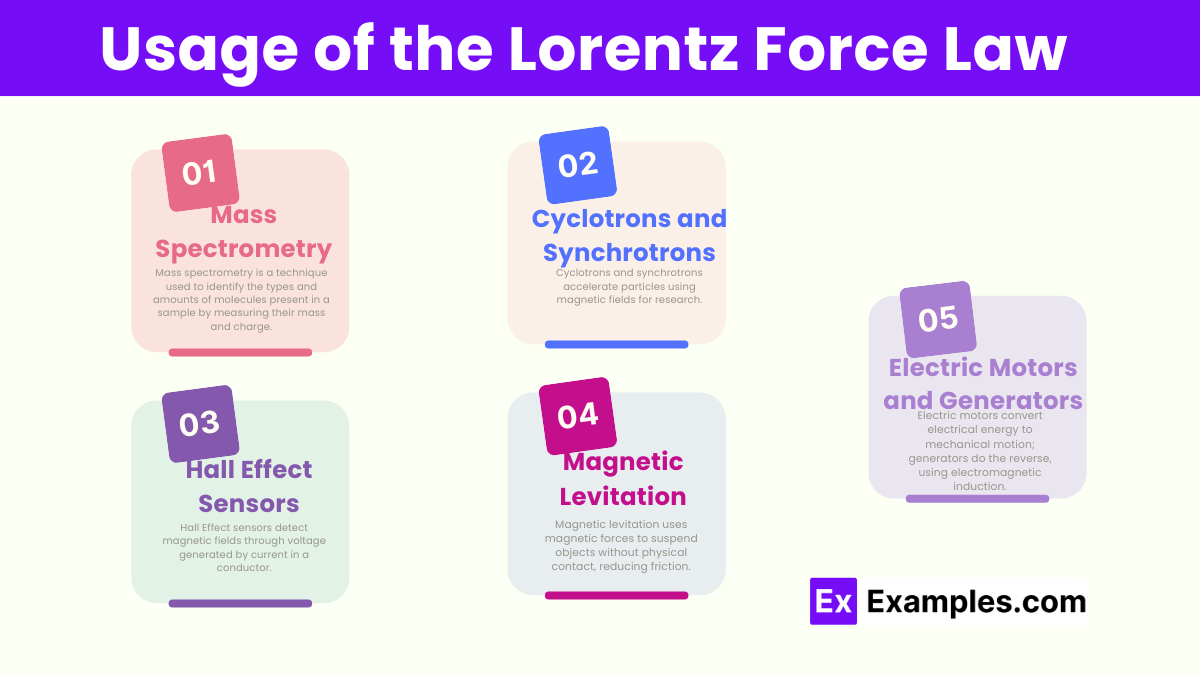
This force is essential in the operation of various technological devices and systems:
The Lorentz force is crucial for experiments and theories in electromagnetism, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It helps scientists understand how charged particles interact, leading to deeper insights into the structure of matter and the fundamental forces that govern the universe.
No, the Lorentz force only acts on particles with an electric charge. Neutral particles do not experience this force directly, although they can still be affected indirectly if they are part of a neutral system that contains charged particles.
The Lorentz force affects the motion of a charged particle by changing its direction and/or speed. In an electric field, the force is along the direction of the field for positive charges and opposite for negative charges. In a magnetic field, the force is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the magnetic field, causing the particle to move in a circular or spiral path.
Yes, the Lorentz force is fundamental in generators, where the motion of a conductor through a magnetic field induces an electromotive force (voltage) across the conductor by the Lorentz force, generating electricity.
No, the magnetic component of the Lorentz force is non-conservative. This means that the work done by the magnetic part of the Lorentz force on a charged particle moving around a closed path is zero, and it does not depend on the path taken by the particle.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for the Lorentz force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field?
F = qE + q(v × B)
F = qE - q(v × B)
F = q(E + v × B)
F = q(E - v × B)
Which component of the Lorentz force is due to the electric field?
qE
q(v × B)
q(E × B)
q(v × E)
Which component of the Lorentz force is due to the magnetic field?
qE
q(v × B)
q(E × B)
q(v × E)
If a charged particle is moving parallel to the magnetic field, what is the magnetic force acting on it?
Zero
qvB
qE
q(E + vB)
What direction does the magnetic force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field act?
Parallel to the velocity
Perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field
Parallel to the magnetic field
Opposite to the velocity
What happens to the magnitude of the Lorentz force if the charge of the particle is doubled?
It remains the same
It is halved
It doubles
It becomes zero
How does the direction of the electric force on a positive charge relate to the direction of the electric field?
Opposite
Same
Perpendicular
No relation
What is the effect of reversing the direction of the magnetic field on the magnetic component of the Lorentz force?
No effect
It doubles
It reverses direction
It halves
If a charged particle is at rest in an electric field, what is the Lorentz force acting on it?
Zero
qE
q(v × B)
q(E + v × B)
In which situation will a charged particle experience the greatest magnetic force?
Moving parallel to the magnetic field
Moving perpendicular to the magnetic field
At rest in the magnetic field
Moving at an angle of 45 degrees to the magnetic field
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

