What is the formula for mass flow rate (ṁ) in terms of density (ρ), velocity (v), and cross-sectional area (A)?
ṁ = ρvA
ṁ = ρv/A
ṁ = ρA/v
ṁ = v/ρA

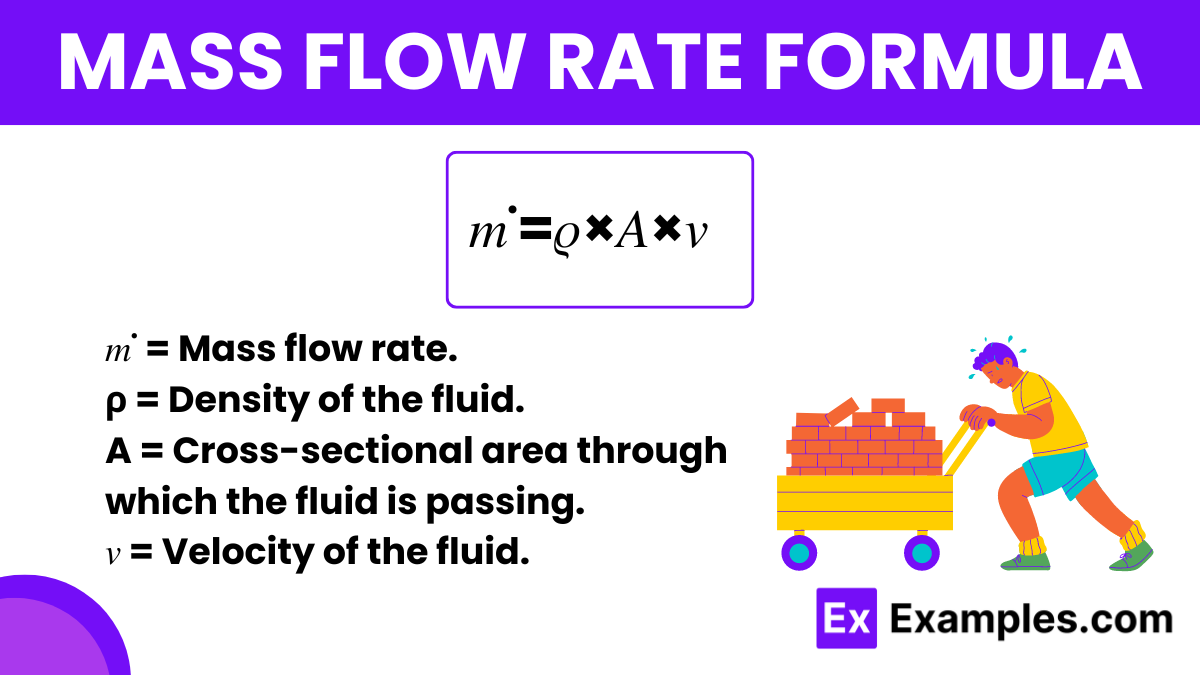
The Mass Flow Rate Formula in physics quantifies the mass of a substance passing through a given surface per unit time. It is a critical concept in various fields such as engineering, physics, and chemistry, providing essential insights into the behavior of fluids and gases in motion. Essentially, this formula helps in calculating how quickly mass is moving through a pipeline, nozzle, or any other kind of conduit. The formula is expressed as:
The concept of mass flow rate is fundamental in the design and analysis of systems involving fluid flow, such as HVAC systems, hydraulic systems, and in various applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
The development of the mass flow rate formula can be traced back to the principles laid down by Sir Isaac Newton, particularly his second law of motion. However, the formula as we use it today has been shaped and refined through contributions from various scientists over centuries who studied fluid dynamics and thermodynamics.
Problem: Water flows through a circular pipe with a radius of 0.1 meters at a velocity of 3 meters per second. The density of water is 1000 kg/m³. Calculate the mass flow rate of water through the pipe.
Solution: First, calculate the cross-sectional area of the pipe using the formula for the area of a circle, 𝐴=𝜋𝑟2:
𝐴 = 𝜋 × (0.1 m)² = 0.0314 m²
Now, apply the mass flow rate formula:
𝑚˙ = 𝜌 × 𝐴 × 𝑣 = 1000 kg/m³ × 0.0314 m² × 3 m/s = 94.2 kg/s
Problem: An HVAC system uses a duct to channel air at a velocity of 5 meters per second. The duct has a diameter of 0.5 meters, and the density of air is approximately 1.2 kg/m³. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the duct.
Solution: Calculate the cross-sectional area of the duct:
𝐴 = 𝜋 x (0.25 m)² = 0.19635 m²
Then, use the mass flow rate formula:
𝑚˙ = 𝜌 × 𝐴 × 𝑣 = 1.2 kg/m³ × 0.19635 m² × 5 m/s = 1.1761 kg/s
Problem: A car engine requires a fuel flow rate of 0.02 kilograms per second to maintain a steady operation. The fuel has a density of 800 kg/m³. If the fuel line leading to the engine has a diameter of 4 millimeters. What is the velocity of the fuel in the line?
Solution: First, calculate the cross-sectional area of the fuel line:
𝐴 = 𝜋 × (0.002 m)² = 0.00001257 m²
Now, rearrange the mass flow rate formula to solve for velocity 𝑣v:
𝑣 = 𝑚˙ / (𝜌 × 𝐴) =0.02 kg/s / (800 kg/m³ × 0.00001257 m²) = 1.98 m/s
The mass flow rate balance equation, 𝑚˙ᵢₙ− 𝑚˙ₒᵤₜ =Δ𝑚˙ₛᵧₛₜₑₘ, ensures mass conservation in a system.
The flow rate formula is 𝑚˙ = 𝜌 × 𝐴 × 𝑣. Where ρ is density, 𝐴 is area, and 𝑣 is velocity.
The unit of mass flow rate is kilograms per second (kg/s), measuring mass flowing per unit time.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for mass flow rate (ṁ) in terms of density (ρ), velocity (v), and cross-sectional area (A)?
ṁ = ρvA
ṁ = ρv/A
ṁ = ρA/v
ṁ = v/ρA
If the density of a fluid is 1000 kg/m³, the velocity is 2 m/s, and the cross-sectional area is 0.5 m², what is the mass flow rate?
1000 kg/s
2000 kg/s
500 kg/s
100 kg/s
In the formula ṁ = ρvA, what does the symbol ṁ represent?
Mass flow rate
Density
Volume flow rate
Velocity
How does the mass flow rate change if the velocity of the fluid is doubled while the density and cross-sectional area remain constant?
It halves
It remains the same
It doubles
It quadruples
If the cross-sectional area of a pipe is reduced by half while the density and velocity remain constant, what happens to the mass flow rate?
It remains the same
It is halved
It is doubled
It is quadrupled
Which of the following correctly describes the units of mass flow rate in the SI system?
kg/m³
m³/s
kg/s
m/s
If the mass flow rate of a fluid is 500 kg/s and the density is 1000 kg/m³, what is the volume flow rate?
0.5 m³/s
5 m³/s
50 m³/s
500 m³/s
If the mass flow rate is 300 kg/s, the velocity is 3 m/s, and the cross-sectional area is 1 m², what is the density of the fluid?
100 kg/m³
300 kg/m³
900 kg/m³
1000 kg/m³
How does the mass flow rate change if the density of the fluid is tripled while the velocity and cross-sectional area remain constant?
It remains the same
It is halved
It is tripled
It is doubled
n a scenario where the velocity of a fluid is decreased by a factor of 4 while the density and cross-sectional area are kept constant, how is the mass flow rate affected?
It decreases by a factor of 4
It remains the same
It increases by a factor of 4
It decreases by a factor of 2
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

