What is the unit of speed in the International System of Units (SI)?
Kilometer per hour
Meter per second
Miles per hour
Feet per second

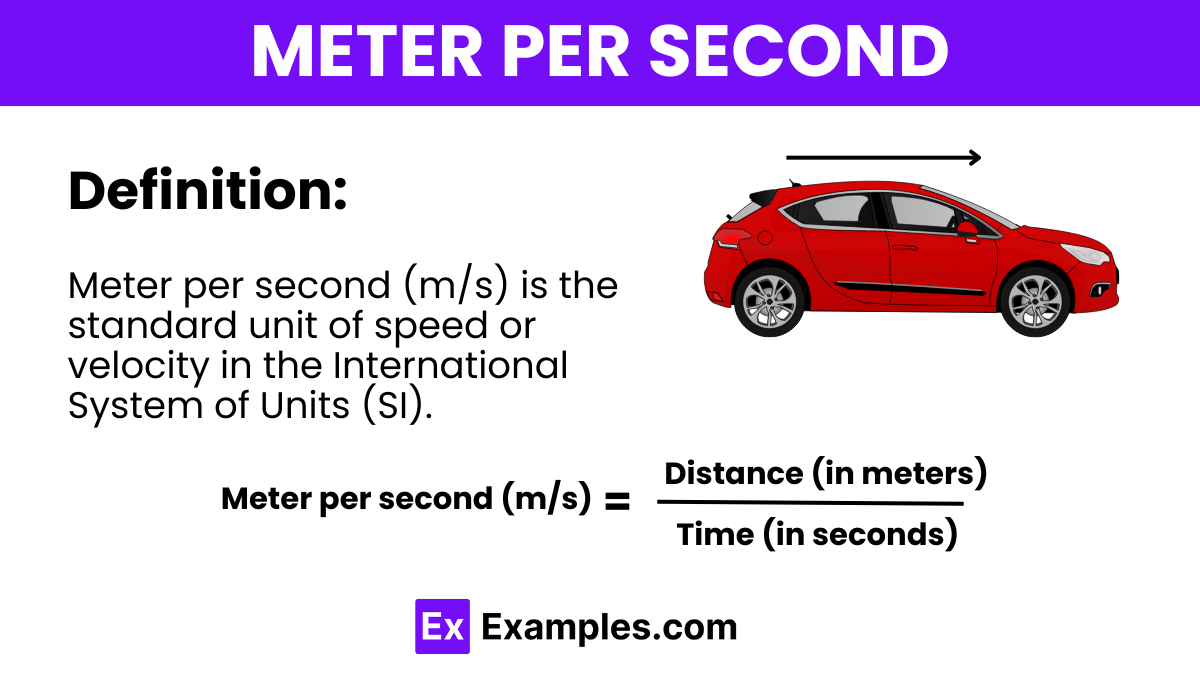
The symbol for meter per second is “m/s“. The formula to calculate meter per second is:
This formula represents the rate of change of distance with respect to time, indicating the speed or velocity of an object in meters per second.
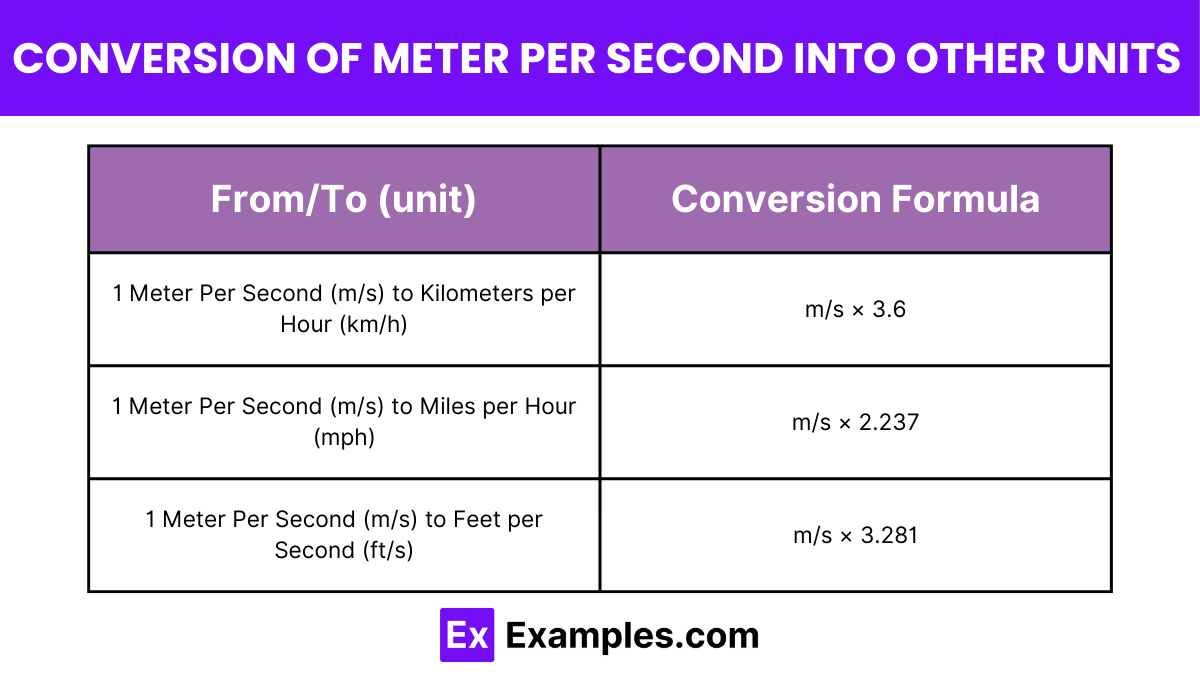
| From/To (unit) | Conversion Formula |
|---|---|
| 1 Meter Per Second (m/s) to Kilometers per Hour (km/h) | m/s × 3.6 |
| 1 Meter Per Second (m/s) to Miles per Hour (mph) | m/s × 2.237 |
| 1 Meter Per Second (m/s) to Feet per Second (ft/s) | m/s × 3.281 |
One meter per second (m/s) is equivalent to 3.6 kilometers per hour (km/h). This conversion factor allows for quick and easy transformation between speed units in everyday calculations.
At a speed of 1 meter per second, you’re moving at a rate equivalent to 2.237 miles per hour, which translates to roughly 3.6 kilometers per hour.
One meter per second (m/s) is equivalent to approximately 3.281 feet per second (ft/s). This conversion is commonly used in physics and engineering calculations involving velocity and speed.
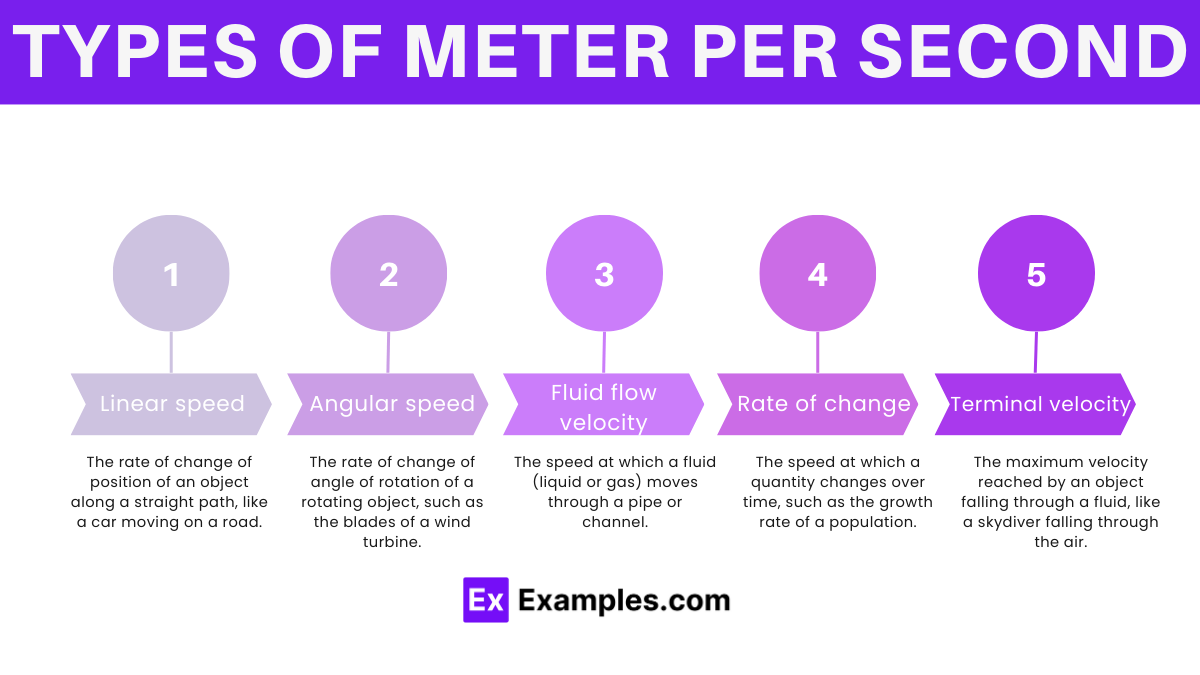
“Meters per second” is the unit of measurement for speed or velocity.
In scientific research, meters per second is used to quantify the speed of various phenomena, from the movement of particles to the flow of fluids, enabling precise analysis and understanding of natural processes.
Meters per second provides a standardized and internationally recognized way to express speed or velocity, making it easy to communicate and compare measurements across different contexts and applications.
Meters per second is calculated by dividing the distance traveled in meters by the time taken in seconds.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the unit of speed in the International System of Units (SI)?
Kilometer per hour
Meter per second
Miles per hour
Feet per second
If an object travels 20 meters in 4 seconds, what is its speed?
4 m/s
5 m/s
6 m/s
8 m/s
Which of the following is equivalent to 1 meter per second?
100 centimeters per second
10 meters per minute
60 meters per hour
3.6 kilometers per hour
What is the speed of a car traveling 90 kilometers in 2 hours in meters per second?
12.5 m/s
15 m/s
20 m/s
25 m/s
Which of the following speeds is the highest?
1 m/s
100 cm/s
0.01 km/s
10 m/min
How long does it take for light to travel 1 meter in a vacuum? (Speed of light = 3 × 10⁸ m/s)
3×10⁻⁹ seconds
3×10⁻⁸ seconds
3×10⁻⁷ seconds
3 × 10⁻⁶ seconds
If a particle travels with a constant speed of 2 meters per second, how far does it travel in 5 seconds?
5 meters
7 meters
10 meters
15 meters
A train is moving at a speed of 20 meters per second. How long will it take to travel 2 kilometers?
50 seconds
100 seconds
150 seconds
200 seconds
If the speed of sound is approximately 343 meters per second, how far does sound travel in 2 seconds?
343 meters
686 meters
1029 meters
1372 meters
An athlete runs at a constant speed of 6 meters per second. How long will it take to run 300 meters?
40 seconds
45 seconds
50 seconds
55 seconds
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

