How many milliradians are in one radian?
100
1000
10
10000

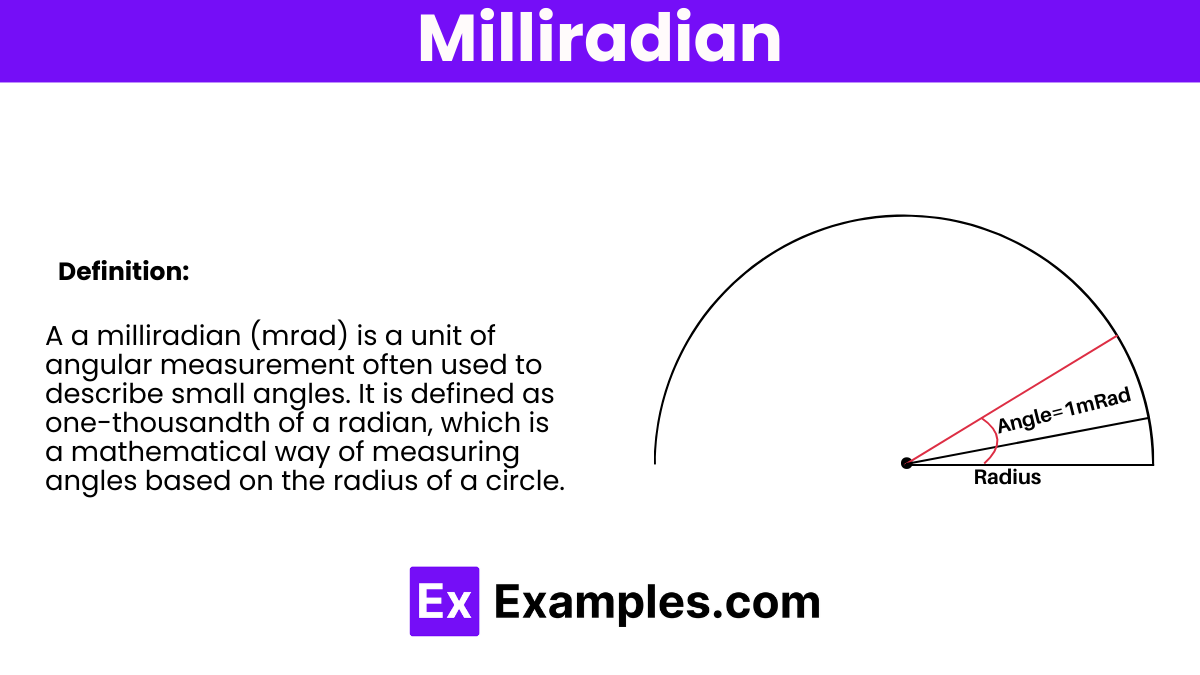
A milliradian, often abbreviated as “mrad” or just “mil,” is a unit of angular measurement used particularly in ballistics and for measuring angles in geographic information systems, among other fields. It is defined as one-thousandth of a radian, which is a mathematical way of measuring angles based on the radius of a circle.
To calculate distance using milliradians:
To find the size of an object:
| SI Prefix | Symbol | Factor | Equivalent in Milliradians | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kilomilliradian | kmrad | 10³ | 1 kmrad = 1,000 mrad | Used for broad angular spans. |
| Decimilliradian | dmrad | 10−¹ | 1 dmrad = 0.1 mrad | Suitable for finer precision in engineering or artillery. |
| Centimilliradian | cmrad | 10−² | 1 cmrad = 0.01 mrad | Used for very precise angular measurements. |
| Micromilliradian | µmrad | 10−³ | 1 µmrad = 0.001 mrad | Utilized in scientific research for ultra-precise measurements. |
Calculating the subtended size of an object at a distance:
This formula is used to determine the physical size or length of an object based on the angle it subtends and the distance to it.
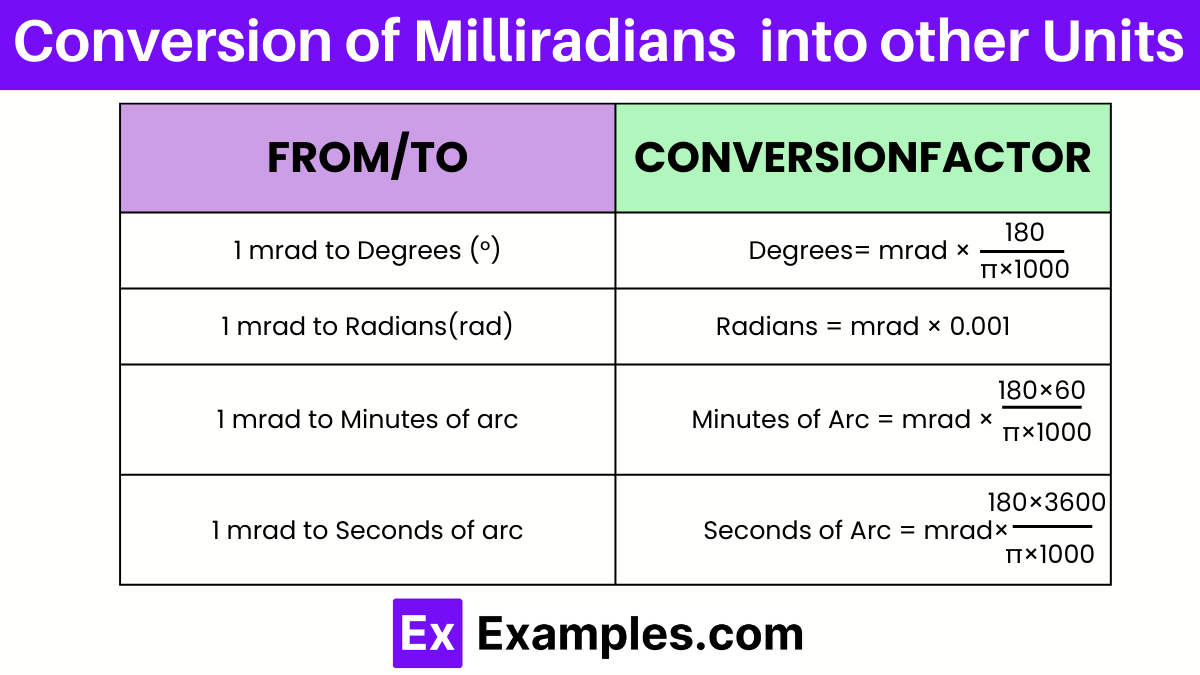
| From Milliradians (mrad) | To Unit | Conversion Formula | Approximate Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mrad | Degrees (°) | Degrees = mrad×(180)/π×1000 | 0.0573° |
| 1 mrad | Radians (rad) | Radians = mrad×0.001 | 0.001 rad |
| 1 mrad | Minutes of arc | Minutes of Arc = mrad×(180×60)/π×1000 | 3.4377′ |
| 1 mrad | Seconds of arc | Seconds of Arc = mrad×(180×3600)/π×1000 | 206.265” |
To understand how to convert milliradians (mrad) into other units of angular measurement, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the key formulas. Here is a detailed overview to assist in these conversions:
Since there are 2π radians in a full circle (360 degrees), and 1000 mrad in a radian, this formula adjusts for these values to convert mrad directly into degrees.
This conversion is straightforward because 1000 milliradians equal one radian by definition.
One degree contains 60 minutes of arc, hence this formula multiplies the degree conversion by 60 to get minutes.
Since one minute of arc contains 60 seconds, this formula converts milliradians first to degrees, then to minutes, and finally to seconds.
These formulas and conversions provide a useful toolset for translating milliradians into more commonly used angular measurements, which can be critical in fields like astronomy, navigation, and surveying. Each conversion allows for precise angular measurements critical in technical applications.

Milliradians (mrad) are a unit of angular measurement commonly used in various fields for their precision and practicality. Here are some of the key uses of milliradians:
1.Military and Shooting Sports: Milliradians are extensively used for artillery, rifle scopes, and other targeting devices in the military and shooting sports. They help shooters calculate the adjustments needed on their sights to hit targets at varying distances. This is particularly useful as it allows for quick and precise adjustments without needing complex calculations.
2.Surveying: In surveying, milliradians assist in the accurate measurement of angles between different points on a site. This precision is crucial for creating reliable maps and executing construction projects with exacting standards.
3.Engineering: Engineers use milliradians in fields such as mechanical and civil engineering to ensure precise angular measurements are maintained in designs and constructions, such as in the alignment of structures or components.
4.Astronomy: Astronomers use milliradians to measure the apparent sizes of celestial bodies and their separation in the sky. This unit allows for a precise understanding of the scale and distance of objects in space relative to one another.
5.Optics: In optics, milliradians are crucial for aligning and calibrating equipment like laser systems, telescopes, and other optical devices. They ensure the precision of angles required for accurate focus and direction of light.
6.Robotics: Robotics applications use milliradians for precise movement and orientation of robotic limbs and tools. Accurate angular measurements ensure that robotic actions are both precise and repeatable, which is vital for automation and manufacturing processes.
At a distance of 1000 meters, 1 milliradian subtends approximately 1 meter. This relationship is derived from the definition of a milliradian as one-thousandth of a radian.
At 100 meters, 1 milliradian subtends approximately 3.937 inches. This calculation is based on the conversion where 1 meter equals approximately 39.37 inches.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
How many milliradians are in one radian?
100
1000
10
10000
Convert 200 milliradians to radians.
0.2 radians
2 radians
0.02 radians
20 radians
What is the measure of 5000 milliradians in radians?
5 radians
0.5 radians
50 radians
500 radians
How many degrees are equivalent to 100 milliradians?
5.73 degrees
57.3 degrees
0.573 degrees
0.0573 degrees
Convert 1 degree to milliradians.
17.45 milliradians
174.5 milliradians
1.745 milliradians
0.1745 milliradians
How many milliradians are in a full circle?
10000
20000
6283
3142
If an angle measures 250 milliradians, what is its measure in degrees?
14.32 degrees
1.432 degrees
143.2 degrees
0.1432 degrees
What is the angular size of an object that spans 1500 milliradians?
1.5 radians
15 radians
0.15 radians
150 radians
Convert 2 radians to milliradians.
200 milliradians
2000 milliradians
20 milliradians
20000 milliradians
How many milliradians are in 45 degrees?
785.4 milliradians
78.54 milliradian
7.854 milliradians
7854 milliradians
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

