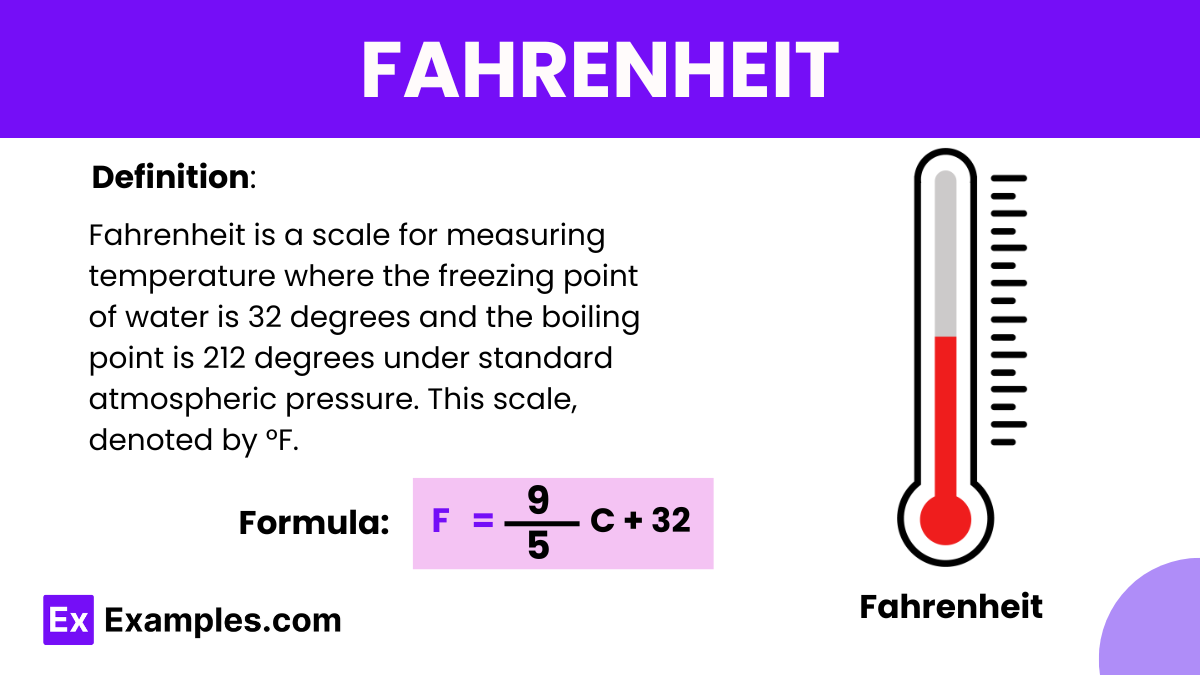
Fahrenheit is a temperature scale named after the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, who proposed it in 1724. In this scale, water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) and boils at 212 degrees Fahrenheit at standard atmospheric pressure. This contrasts with the Celsius scale, commonly used in physics and other sciences, where water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius (°C) and boils at 100 degrees Celsius. The Fahrenheit scale is still commonly used in the United States for weather forecasts and in everyday applications.
What is Fahrenheit?
How to Convert a Temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, you can use the following formula:
Where:
- F represents the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit,
- C represents the temperature in degrees Celsius.
This formula multiplies the Celsius temperature by 9/5 (or 1.8) and then adds 32 to the result to find the equivalent temperature in Fahrenheit..
Example
Let’s say you have a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius and you want to convert it to Fahrenheit. You can use the formula:
F = 9/5C+32
Substituting 𝐶C with 20:
𝐹 = 9/5×20+32
𝐹 = 36+32
𝐹 = 68
So, 20 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 68 degrees Fahrenheit.
Temperature of Fahrenheit
- Fahrenheit Scale: The Fahrenheit temperature scale is a way of measuring temperatures where 32°F is the freezing point of water and 212°F is the boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Daily Use: In everyday situations, especially in the United States, people use Fahrenheit to report weather temperatures. For instance, a comfortable room temperature might be around 68°F to 72°F.
- Conversion: If you need to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, the formula is
C = 95(F−32) Where 𝐶C is the temperature in Celsius and F is the temperature in Fahrenheit.
Difference Between Celsius and Fahrenheit
| Aspect | Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Developed by | Anders Celsius (1701–1744) | Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686–1736) |
| Introduced | Mid-18th century | Early 18th century |
| Base Unit | Degree Celsius | Degree Fahrenheit |
| Freezing Point of Water | 0°C | 32°F |
| Boiling Point of Water | 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure | 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure |
| Increment Size | One degree Celsius is larger; each degree is equal to 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit | One degree Fahrenheit is smaller; it takes more degrees to cover the same change in temperature |
| Usage | Used worldwide, except in the United States and a few other countries | Primarily used in the United States, Bahamas, Belize, and a few other countries |
| Conversion Formula to Other | 𝐹 = 95𝐶+32 (To convert to Fahrenheit) | 𝐶 = 59(𝐹−32) (To convert to Celsius) |
Absolute zero in Fahrenheit
Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature where all molecular motion stops. It’s a theoretical limit in thermodynamics, representing the minimum internal energy a thermodynamic system can have.
In the Fahrenheit scale, absolute zero is approximately -459.67 degrees Fahrenheit (°F). This temperature corresponds to -273.15 degrees Celsius (°C) and zero Kelvin (K), which are equivalent values in other temperature scales. Absolute zero is primarily used in scientific contexts, especially in physics and chemistry, to describe extreme conditions or theoretical states.
Scale of the Fahrenheit
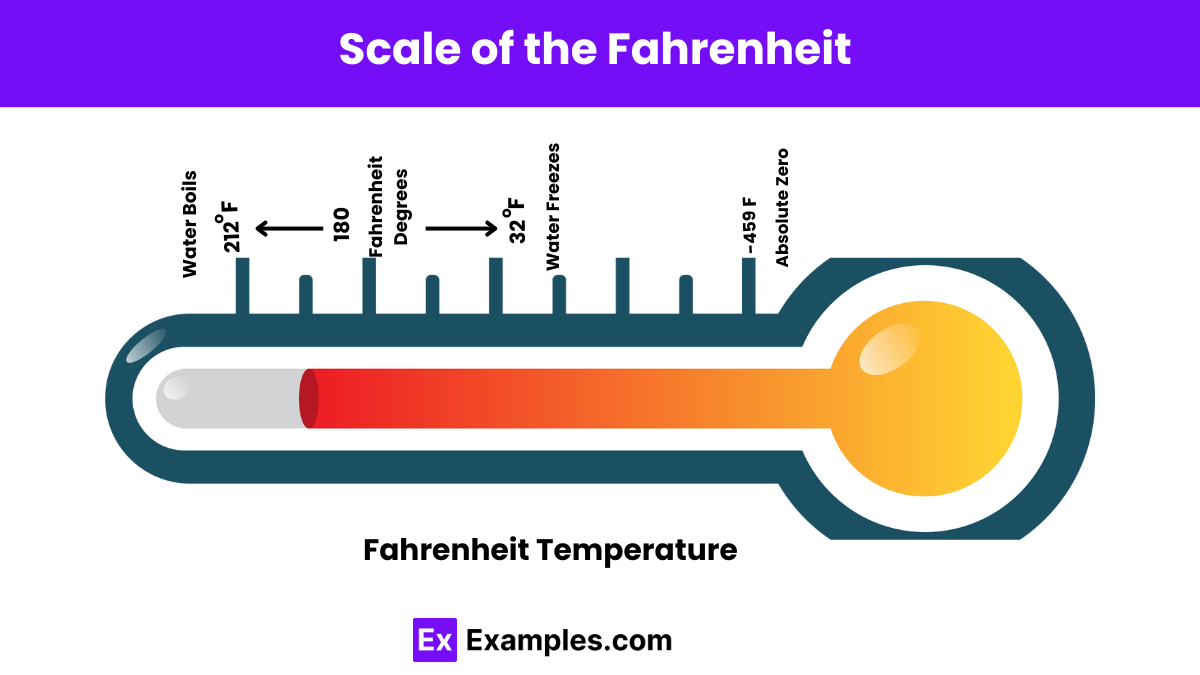
The Fahrenheit scale is marked by several key points that relate to everyday phenomena, particularly in terms of water’s behavior and human comfort levels. Here’s an overview of some significant points on the Fahrenheit scale:
- Absolute Zero: -459.67°F (-273.15°C). This is the theoretical lowest temperature possible, where molecular motion ceases.
- Freezing Point of Water: 32°F (0°C). This is the temperature at which water freezes.
- Body Temperature: Around 98.6°F (37°C). This is considered the normal body temperature for humans.
- Boiling Point of Water: 212°F (100°C) at sea level. This is the temperature at which water boils.
The Fahrenheit scale is divided into degrees, where each degree is 1/180 of the interval between the freezing point and boiling point of water at sea level. Here are some additional common reference points:
- Room Temperature: Typically around 68°F to 72°F (20°C to 22°C).
- Cold Day: Temperatures around or below 32°F (0°C) are typically considered cold, especially in climates accustomed to warmer weather.
- Hot Day: Temperatures around or above 90°F (32°C) are generally considered hot.
Effects of the Fahrenheit
Weather Reporting and Perception
- Public Understanding: In regions where Fahrenheit is used, people are accustomed to interpreting weather conditions based on this scale. For example, temperatures in the 70s (°F) are generally perceived as comfortable, while temperatures dropping to the 30s or rising to the 90s carry specific, commonly understood connotations about the need for heating or cooling.
- Cultural Relevance: In the United States, people often discuss weather and temperature changes in Fahrenheit, making it a culturally relevant scale for everyday conversations.
Science and Education
- International Communication: Scientists typically use Celsius or Kelvin in academic and international contexts. Thus, students in Fahrenheit-using countries need to learn to convert between scales and understand scientific concepts in multiple units, which can add a layer of complexity to science education.
- Precision and Scale: The finer division in the Fahrenheit scale (where a degree Fahrenheit is smaller than a degree Celsius) can be advantageous in fields like meteorology and high-precision manufacturing, as it allows for detailed temperature distinctions without using decimals.
Health and Medicine
- Medical Temperature Readings: In the medical field, especially in the U.S., body temperature is usually measured in Fahrenheit. Thus, a normal body temperature is around 98.6°F, and slight deviations are easily recognizable in this scale.
- Public Health Communication: Health advisories about temperature-related conditions (like hypothermia or heat strokes) are given in Fahrenheit in the U.S., which is crucial for public understanding and safety.
Cooking and Food Safety
- Cooking Instructions: Recipes in the U.S. are usually written with Fahrenheit temperatures. Understanding these temperatures is essential for cooking and baking precision.
- Food Safety Standards: Guidelines for food storage, handling, and cooking temperatures are often communicated in Fahrenheit to ensure safety against foodborne illnesses.
Engineering and Technical Applications
- HVAC Settings: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in the U.S. are calibrated in Fahrenheit, which influences how settings are adjusted in residential and commercial buildings.
- Material Science: The behavior of materials at different temperatures might be tested and documented using the Fahrenheit scale in certain U.S.-based industries.
FAQs
Is the Fahrenheit scale more accurate than Celsius?
The Fahrenheit scale is not inherently more accurate, but it is more precise because it uses a smaller interval between degrees. This can make it useful in fields requiring fine temperature adjustments.
What are the practical advantages of using the Fahrenheit scale?
One practical advantage is its precision without using decimals, which is useful in weather forecasting and HVAC settings. It’s also historically and culturally embedded in the U.S., making it a familiar reference for most residents.
How are extreme temperatures reported in Fahrenheit?
Extreme temperatures, like those in Death Valley or Arctic regions, are reported in Fahrenheit in the U.S., providing immediate context and relevance for residents familiar with the scale.