What is resonant frequency?
The frequency at which a system naturally vibrates
The frequency at which resonance is impossible
The frequency at which damping is maximum
The frequency at which energy transfer is minimal

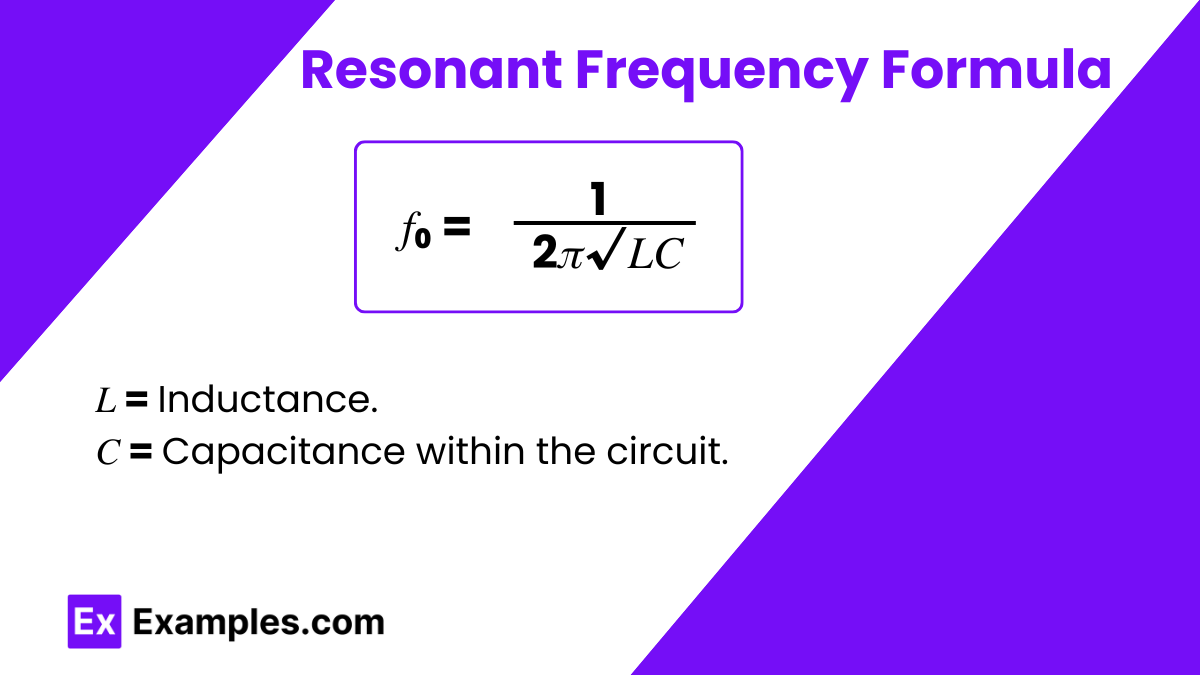
The resonant frequency formula is a fundamental equation in the field of physics, particularly in the study of electrical circuits. his formula calculates the natural frequency at which a circuit will oscillate when no external forces are driving it. It is expressed as:
The concept of the resonant frequency formula was developed in the early 20th century, significantly influenced by the work of the physicist Heinrich Hertz. Hertz was not directly responsible for this specific formula, but his pioneering work on electromagnetic waves set the stage for the further development of electrical resonant systems. The formula is essential for designing circuits in radios, televisions, and other electronic devices that need to filter out specific frequencies from a spectrum of signals. Understanding and applying this formula allows engineers and physicists to precisely control the frequencies at which circuits operate, optimizing performance across a wide range of technologies.
To understand the derivation of the resonant frequency formula in a series RLC circuit (resistor 𝑅, inductor 𝐿, and capacitor 𝐶 connected in series), we start by calculating the total impedance 𝑍 of the circuit when excited by an alternating current (AC) source. The impedance 𝑍 is given by:
where 𝜔ω is the angular frequency, and 𝑗j represents the imaginary unit. Simplifying the imaginary components, we write:
At resonance, the circuit behaves purely resistively, which implies that the imaginary part of the impedance must be zero. This condition ensures that the inductive and capacitive reactances cancel each other out. Thus, setting the imaginary part equal to zero, we get:
Solving for 𝜔ω, the angular frequency at resonance, we find:
𝜔𝐿 = 1 / 𝜔𝐶
𝜔² = 1 / 𝐿𝐶
𝜔=1 / √𝐿𝐶
The angular frequency 𝜔ω is related to the frequency 𝑓f by the relation 𝜔=2𝜋𝑓ω=2πf. Substituting 𝜔ω in the formula for frequency, we derive:
Thus, the resonant frequency 𝑓₀ for the series RLC circuit is given by:
Question: Determine the resonant frequency of a circuit if the inductance 𝐿 is 10 millihenries and the capacitance 𝐶 is 100 picofarads.
Solution:
Convert units: 𝐿=10 millihenries = 10 × 10⁻³ henries, 𝐶=100 picofarads = 100 ×10⁻¹² farads.
Apply the formula:
𝑓₀ = 1/ 2𝜋 √( (10 × 10⁻³) x (100×10⁻¹²) ) =1 / 2𝜋 √10⁻⁶ = 1 / 2𝜋×10⁻³ =10.002 x 𝜋 ≈159.155 kHz
Question: If the inductance in a circuit is fixed at 5 millihenries and the resonant frequency needs to be 200 kHz, what must be the capacitance?
Solution:
Convert the inductance to henries: 𝐿=5 millihenries = 5×10⁻³ henries.
Rearrange the resonant frequency formula to solve for 𝐶:
𝑓₀=1 / 2𝜋 √ 𝐿𝐶
𝐶=1 / (2𝜋𝑓₀ )² 𝐿 =1 / ( 2𝜋 × 200 × 10³ )² × 5 × 10⁻³ ≈31.831 picofarads
Question: A radio tuner circuit requires a resonant frequency of 1 MHz. If the available capacitor is 500 picofarads, what inductance is necessary?
Solution:
Convert the capacitance: 𝐶=500 picofarads = 500 × 10⁻¹² farads.
Rearrange the formula to solve for 𝐿:
𝐿=1 / (2𝜋𝑓₀)² 𝐶 = 1 / (2𝜋 × 1 × 10⁶ )² × 500 × 10⁻¹² ≈ 10.178 microhenries
The resonant frequency of a room depends on its dimensions and reflects the sound frequency most amplified within that space.
Calculate resonant frequency using 𝑓₀ = 1 / 2𝜋√𝐿𝐶, where 𝐿 is inductance and 𝐶 is capacitance.
Yes, all objects have a resonant frequency, which is the frequency at which they naturally oscillate when disturbed.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is resonant frequency?
The frequency at which a system naturally vibrates
The frequency at which resonance is impossible
The frequency at which damping is maximum
The frequency at which energy transfer is minimal
How is resonant frequency related to the natural frequency of a system?
Resonant frequency is always higher than the natural frequency
Resonant frequency is always lower than the natural frequency
Resonant frequency is equal to the natural frequency
Resonant frequency has no relation to the natural frequency
Which type of resonance occurs when there is damping in a system?
Series resonance
Parallel resonance
Critical damping
Forced resonance
What is the unit of resonant frequency?
Hertz (Hz)
Newton (N)
Pascal (Pa)
Watt (W)
How does temperature affect the resonant frequency of a tuning fork?
Resonant frequency decreases with temperature
Resonant frequency increases with temperature
Resonant frequency remains unaffected by temperature
Resonant frequency becomes zero at high temperatures
Which phenomenon describes the increase in amplitude near the resonant frequency?
Damping
Resonance
Interference
Diffraction
What is the condition for resonance in an oscillating system?
The applied frequency is equal to the natural frequency of the system
The applied frequency is zero
The applied force is maximum
The system is in equilibrium
In mechanical systems, what role does resonance play?
It reduces energy loss
It increases damping
It amplifies vibrations
It stabilizes oscillations
How does damping affect the sharpness of resonance in a system?
Damping decreases sharpness of resonance
Damping increases sharpness of resonance
Damping has no effect on resonance sharpness
Damping makes resonance impossible
Which factor does not affect the resonant frequency of a vibrating system?
Stiffness
Mass
Temperature
Damping
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

