What is the formula for calculating the resultant force when two forces F₁ and F₂ act in the same direction?
F = F₁ + F₂
F = F₁ − F₂
F = √F²₁ + F²₂
F = F₁+F₂/2

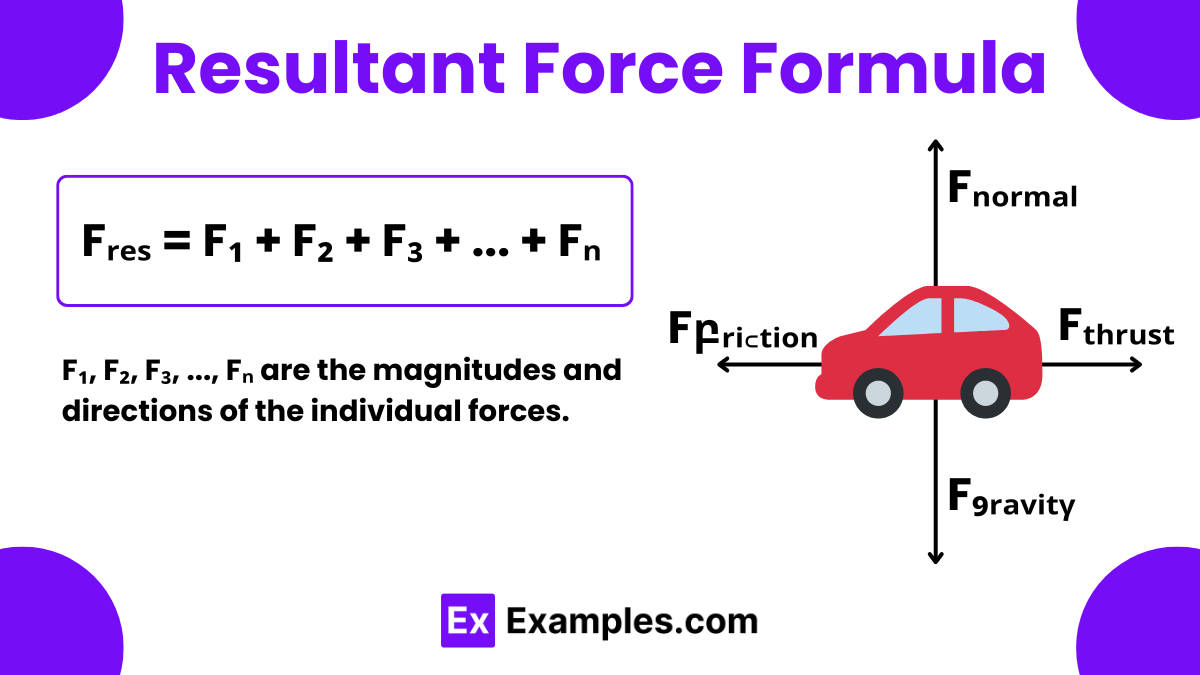
The Resultant Force Formula is a crucial equation in physics that allows us to calculate the single force acting on an object when multiple forces are at play. This formula is fundamental in the study of dynamics, which is the branch of physics concerned with the motion of objects influenced by forces. The formula states that the resultant force (Fᵣ) is the vector sum of all individual forces acting on an object. Mathematically, it can be expressed as
F₁, F₂, F₃, …, Fₙ are the magnitudes and directions of the individual forces.
The concept of the resultant force and its mathematical determination were developed as part of classical mechanics, primarily influenced by the work of Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century. Newton’s laws of motion describe how and why objects move, and his second law, in particular, forms the basis for calculating resultant forces. It establishes the relationship between an object’s mass, its acceleration, and the applied force, leading to the development of the formula for resultant forces.
This formula is essential for solving problems where multiple forces act on a single object, allowing us to predict the object’s motion. By using the resultant force formula, physicists and engineers can determine how forces interact and influence the behavior of physical systems, from simple mechanical devices to complex structures like bridges and spacecraft. Whether calculating the tension in cables, the stability of structures, or the trajectory of moving objects, the resultant force formula is a cornerstone of physical calculations.
Problem: Two people push a stationary car. One applies a force of 200 N to the east. The other applies a force of 150 N to the east. Calculate the resultant force on the car.
Solution:
Problem: A boat is being pulled by two forces. One force of 100 N is directed north and another force of 100 N is directed east. Calculate the resultant force.
Solution:
Problem: A sled is being pulled from opposite sides. One person pulls with a force of 250 N east, while another pulls with a force of 180 N west. Calculate the resultant force.
Solution:
To calculate the resultant force, sum up all individual forces acting on an object, considering both magnitude and direction.
The resultant force of two vectors is the vector sum of both forces, calculated using vector addition.
The formula for resultant moment of force is 𝜏=𝑟×𝐹, where 𝑟 is the position vector and 𝐹 is the force vector.
The formula for resultant acceleration is 𝑎 = 𝐹ₙₑₜ / 𝑚, where 𝐹ₙₑₜ is the net force and 𝑚 is the mass of the object.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for calculating the resultant force when two forces F₁ and F₂ act in the same direction?
F = F₁ + F₂
F = F₁ − F₂
F = √F²₁ + F²₂
F = F₁+F₂/2
If two forces of 5 N and 7 N act in opposite directions, what is the magnitude of the resultant force?
2 N
5 N
7 N
12 N
What is the resultant force when two perpendicular forces of 3 N and 4 N act on an object?
1 N
5 N
7 N
12 N
If a 10 N force acts to the right and a 7 N force acts to the left, what is the resultant force?
3 N to the left
3 N to the right
17 N to the left
17 N to the right
What is the resultant force if two forces of 8 N and 6 N act in the same direction?
2 N
6 N
8 N
14 N
Which of the following statements about resultant force is true?
Resultant force always points in the direction of the larger force
Resultant force is always perpendicular to the forces applied
Resultant force is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object
Resultant force is always equal to the difference of the forces applied
If two forces of equal magnitude act in opposite directions, what is the resultant force?
Zero
Equal to one of the forces
Equal to the sum of the forces
Equal to the product of the forces
Two forces of 7 N and 24 N act at an angle of 90 degrees to each other. What is the magnitude of the resultant force?
17 N
25 N
28 N
31 N
If a 5 N force acts to the left and a 10 N force acts to the right, what is the magnitude and direction of the resultant force?
5 N to the right
5 N to the left
15 N to the right
15 N to the left
A 3 N force acts to the right, and a 4 N force acts upward. What is the magnitude of the resultant force?
5 N
6 N
7 N
8 N
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

