What is the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level?
760 mmHg
500 mmHg
1000 mmHg
600 mmHg

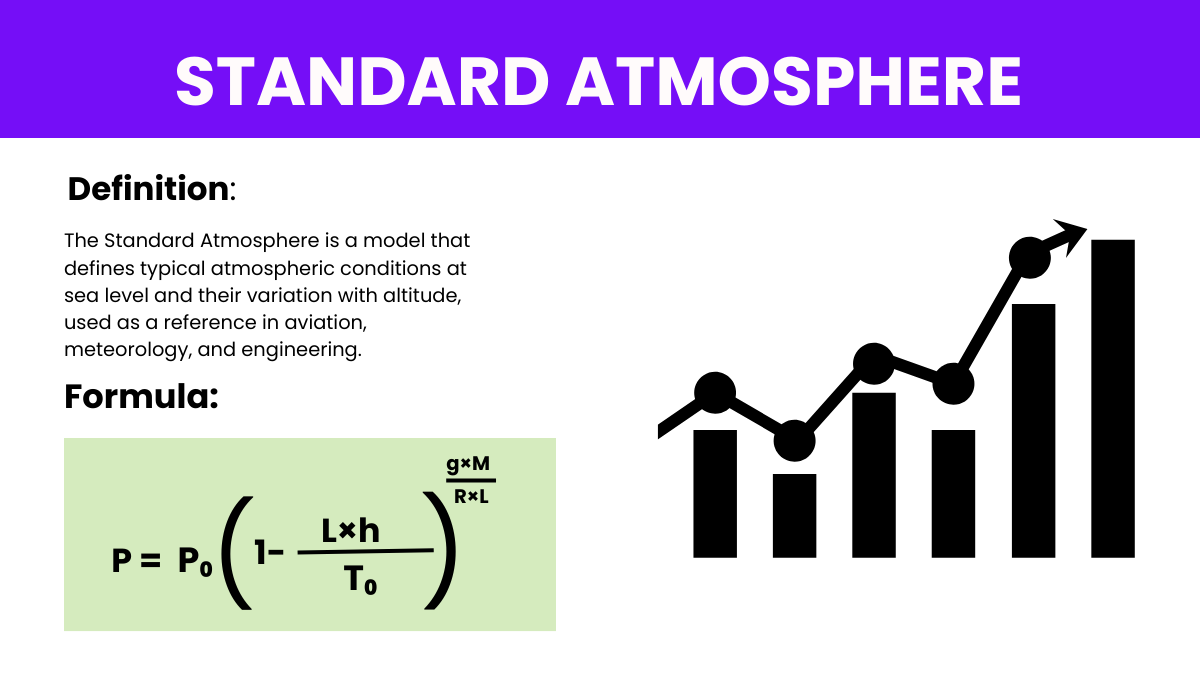
In Physics the standard atmosphere (atm) is a Unit of pressure defined as being equal to the typical atmospheric pressure at sea level on Earth. It is commonly used as a reference point in various scientific contexts and is equivalent to approximately 101,325 pascals (Pa), 1.01325 Bars, or 14.696 pounds per square inch (psi). These units represent different ways to measure pressure, which is a fundamental parameter in both scientific research and industrial applications. Understanding these units is crucial for fields like meteorology, aviation, and engineering to ensure accurate pressure measurement and standardization.
Where:
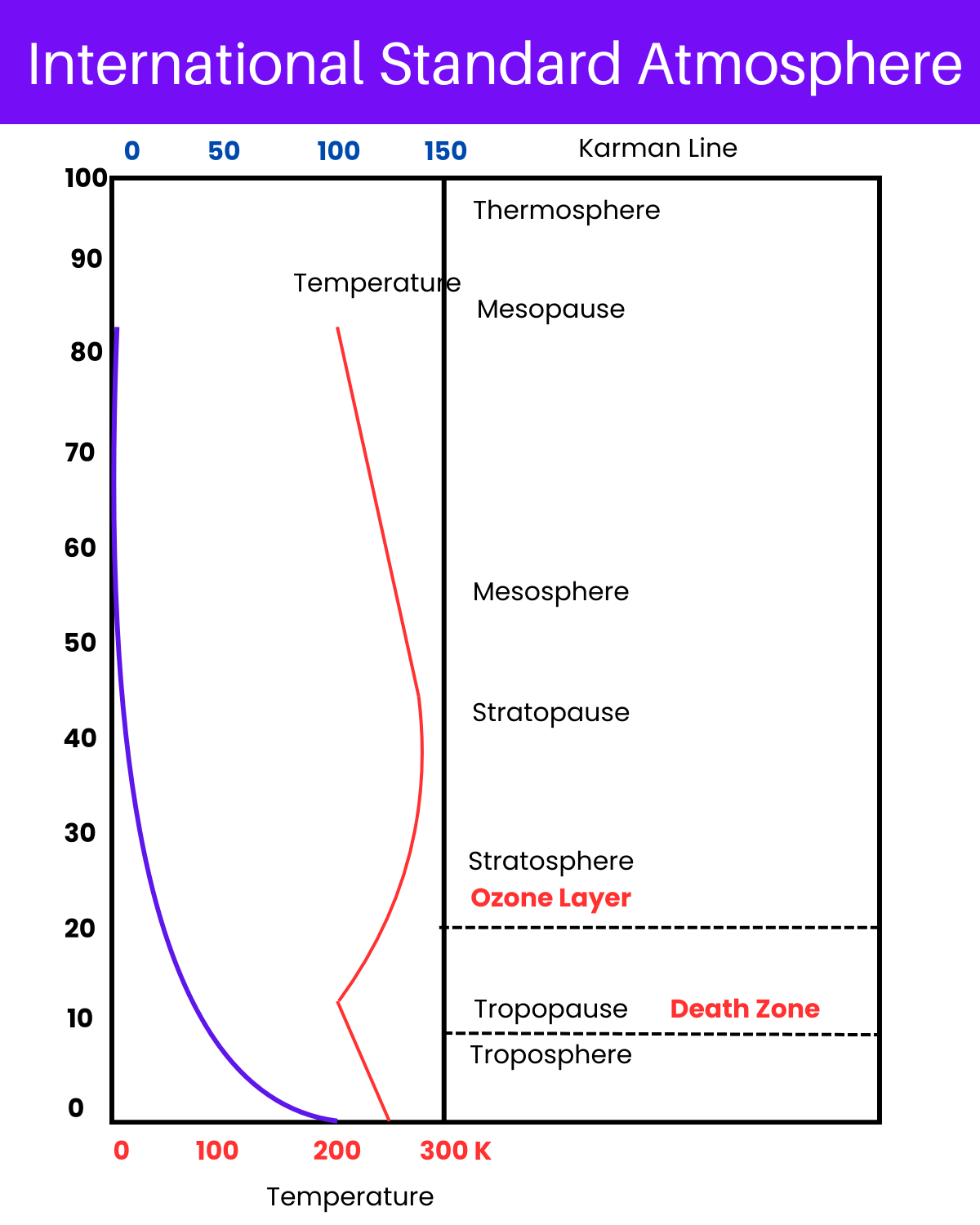
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a model used for calibrating instruments and designing aircraft, among other applications in engineering and meteorology. This model provides a standardized vertical distribution of atmospheric properties under average conditions. The ISA is critical for ensuring consistent measurements and operation standards across the global aviation and meteorological communities.
| Prefix | Symbol | Multiplier | Pressure Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kilo- | kPa | 10³ | 1 kPa = 1,000 Pa |
| Mega- | MPa | 10⁶ | 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa |
| Giga- | GPa | 10⁹ | 1 GPa = 1,000,000,000 Pa |
| Milli- | mPa | 10⁻³ | 1 mPa = 0.001 Pa |
| Micro- | μPa | 10⁻⁶ | 1 μPa = 0.000001 Pa |
| Nano- | nPa | 10⁻⁹ | 1 nPa = 0.000000001 Pa |
| Pico- | pPa | 10⁻¹² | 1 pPa = 0.000000000001 Pa |
| Femto- | fPa | 10⁻¹⁵ | 1 fPa = 0.000000000000001 Pa |
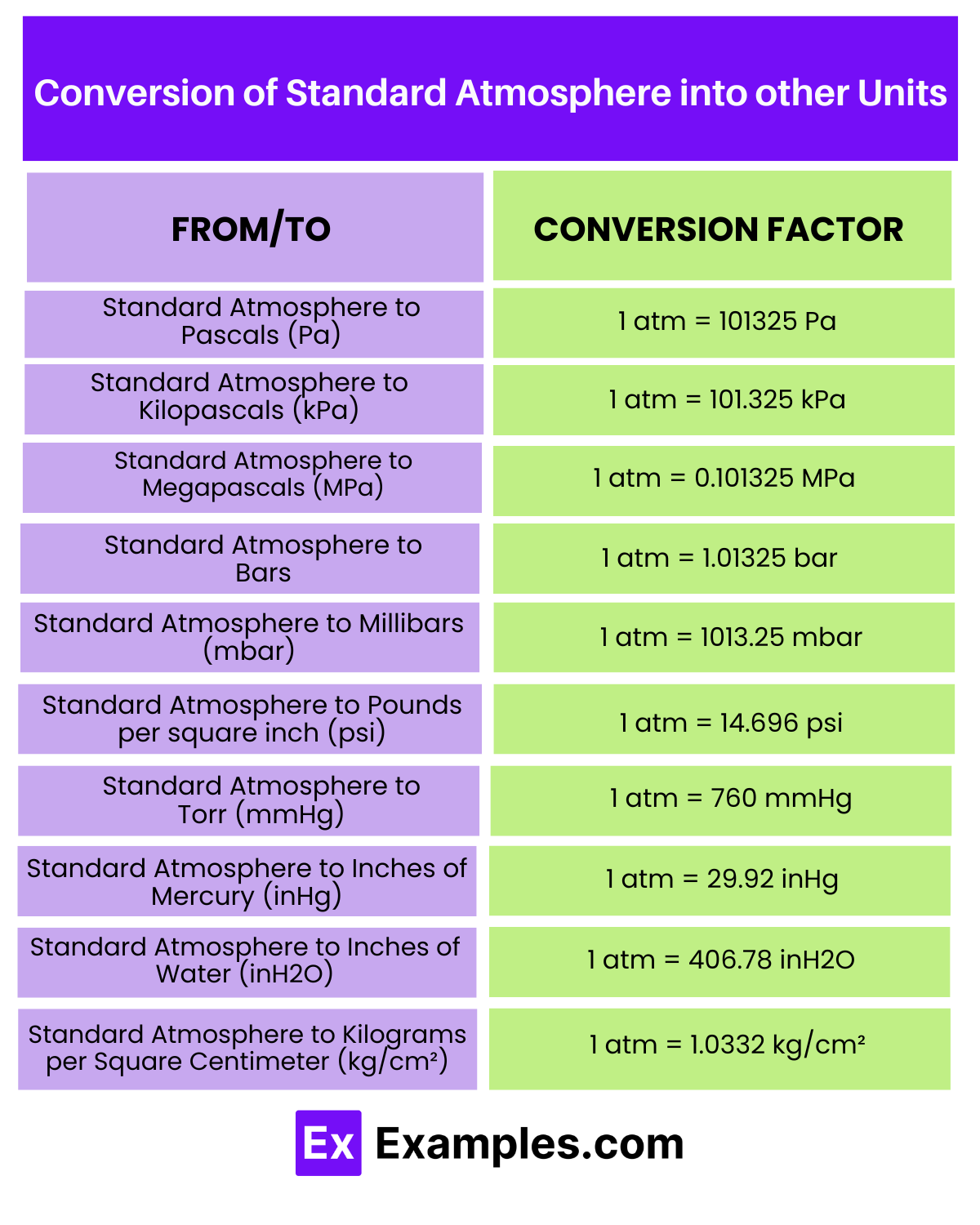
| To Unit | Conversion Factor | Conversion from 10 atm |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Atmosphere to Pascals (Pa) | 1 atm = 101325 Pa | 10 atm = 1,013,250 Pa |
| Standard Atmosphere to Kilopascals (kPa) | 1 atm = 101.325 kPa | 10 atm = 1,013.25 kPa |
| Standard Atmosphere to Megapascals (MPa) | 1 atm = 0.101325 MPa | 10 atm = 1.01325 MPa |
| Standard Atmosphere to Bars | 1 atm = 1.01325 bar | 10 atm = 10.1325 bar |
| Standard Atmosphere to Millibars (mbar) | 1 atm = 1013.25 mbar | 10 atm = 10,132.5 mbar |
| Standard Atmosphere to Pounds per square inch (psi) | 1 atm = 14.696 psi | 10 atm = 146.96 psi |
| Standard Atmosphere to Torr (mmHg) | 1 atm = 760 mmHg | 10 atm = 7,600 mmHg |
| Standard Atmosphere to Inches of Mercury (inHg) | 1 atm = 29.92 inHg | 10 atm = 299.2 inHg |
| Standard Atmosphere to Inches of Water (inH2O) | 1 atm = 406.78 inH2O | 10 atm = 4,067.8 inH2O |
| Standard Atmosphere to Kilograms per Square Centimeter (kg/cm²) | 1 atm = 1.0332 kg/cm² | 10 atm = 10.332 kg/cm² |
The conversion of standard atmospheres (atm) into various other pressure units is essential for a wide range of scientific and engineering applications, ensuring consistent measurements across different systems and scales. When converting from atmospheres to other units such as pascals, kilopascals, megapascals, bars, and millibars, the multiplier varies according to the scale of the unit, from small to very large values. For more localized measurements, such as pounds per square inch or inches of mercury, specific conversion factors.
This SI unit measures small increments of pressure, making it ideal for scientific applications where precision is crucial, such as in laboratory experiments and technical measurements.
These units scale up from pascals to accommodate higher pressure levels, commonly used in industrial and engineering contexts to measure stress in materials and the pressure in hydraulic systems.
These units scale up from pascals to accommodate higher pressure levels, commonly used in industrial and engineering contexts to measure stress in materials and the pressure in hydraulic systems.
The bar is closely aligned with the atmospheric pressure at sea level, making it intuitive for meteorological use, while millibars are especially useful for detailed weather maps and forecasts.
The bar is closely aligned with the atmospheric pressure at sea level, making it intuitive for meteorological use, while millibars are especially useful for detailed weather maps and forecasts.
A familiar unit in the United States for gauging pressure in automotive tires, plumbing systems, and mechanical engineering.
Both units derive from the use of mercury in barometers. Torr is used in vacuum applications, whereas inches of mercury is prevalent in aviation and meteorology.
Both units derive from the use of mercury in barometers. Torr is used in vacuum applications, whereas inches of mercury is prevalent in aviation and meteorology.
This unit is particularly useful in fields like HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), where it helps measure low-pressure levels, such as those found in ductwork and gas lines.
Often used in hydraulic systems and material testing, this unit relates pressure directly to the weight force distributed over a square centimeter, making it easy to visualize and practical for many engineering tasks.
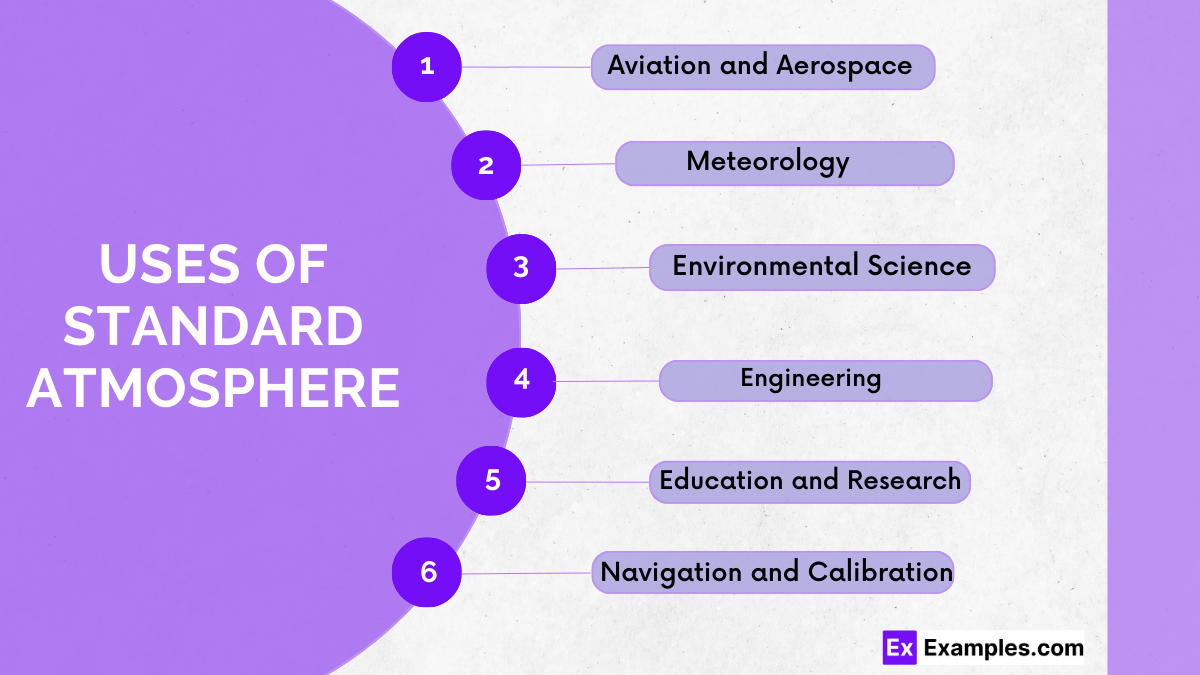
The Standard Atmosphere is a model that simplifies Earth’s atmosphere under average conditions to provide a consistent reference for pressure, temperature, and density up to 100 km above sea level. It’s crucial for applications in aviation, meteorology, and engineering, ensuring uniform measurements and safe operational standards globally.
Aircraft are designed with the Standard Atmosphere in mind to ensure they can handle environmental conditions encountered during flight. This includes calculating lift and fuel efficiency, which vary with atmospheric conditions.
It provides a baseline for measuring deviations caused by pollutants in the atmosphere, thus aiding in environmental monitoring and research into air quality and pollution impacts.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level?
760 mmHg
500 mmHg
1000 mmHg
600 mmHg
What is the value of standard atmospheric pressure in pascals (Pa)?
101325 Pa
100000 Pa
98000 Pa
105000 Pa
How many atmospheres (atm) is 101325 Pa equivalent to?
0.5 atm
1 atm
1.5 atm
2 atm
What is the standard atmospheric pressure in bar?
1.01325 bar
1.0 bar
1.5 bar
2.0 bar
What is the standard temperature in the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA)?
15°C
0°C
25°C
20°C
How is atmospheric pressure measured?
Barometer
Thermometer
Hygrometer
Anemometer
What is the standard lapse rate in the troposphere according to the ISA?
6.5°C per 1000 meters
9.8°C per 1000 meters
5.0°C per 1000 meters
3.6°C per 1000 meters
What is the approximate pressure at an altitude of 5,000 meters in the ISA?
54 kPa
70 kPa
85 kPa
101 kPa
Which gas is most abundant in the Earth's atmosphere?
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Carbon dioxide
Argon
What percentage of the Earth's atmosphere is composed of oxygen?
21%
78%
0.03%
0.9%
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

