What is the Principle of Relativity?
Laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference
Speed of light is constant in all reference frames
Time is absolute and the same in all frames of reference
Gravity affects all objects equally

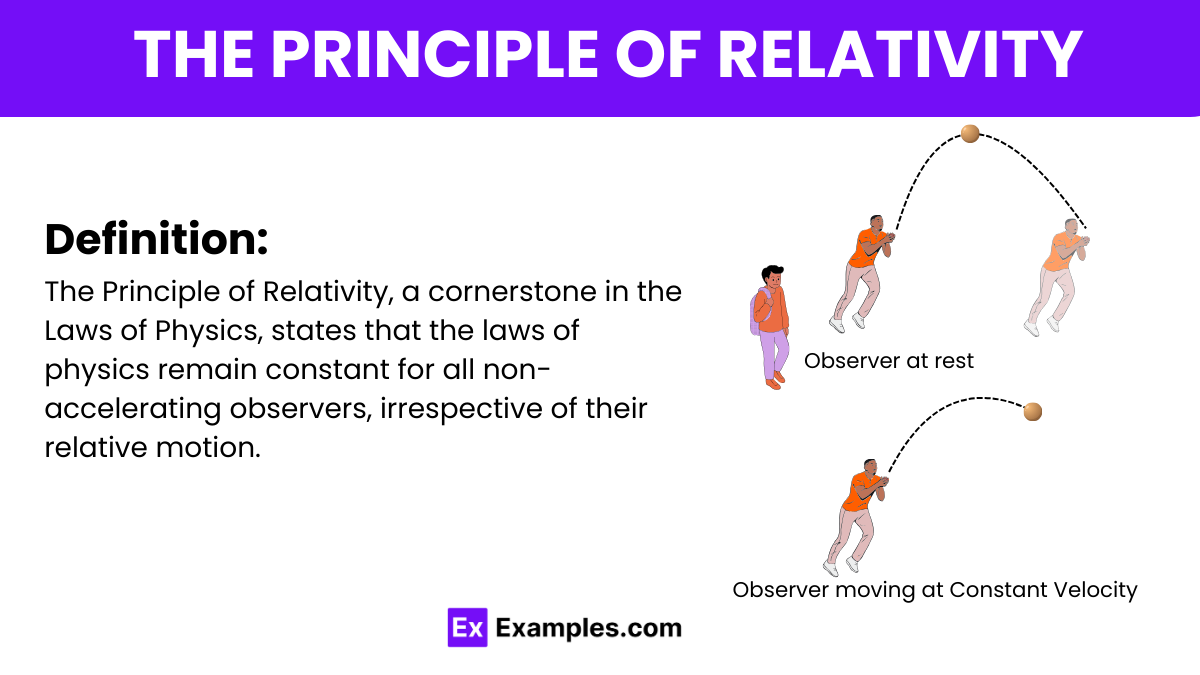
The Principle of Relativity, a cornerstone in the Laws of Physics, states that the laws of physics remain constant for all non-accelerating observers, irrespective of their relative motion. As a result, no experiment within an inertial frame can discern absolute motion, affirming that all motion is relative. This principle is integral to both Newtonian mechanics and Einstein’s theory of relativity, effectively linking classical and modern physics under the unified framework of the Laws of Relativity.
The Principle of Relativity itself doesn’t have a specific formula, as it is a fundamental concept rather than a quantitative equation. However, it underpins several important formulas in physics, especially in Einstein’s theory of relativity, such as:
Lorentz Transformation:
Where 𝛾 is the Lorentz factor 𝛾=1/√1−𝑣²𝑐², v is the relative velocity between observers, and c is the speed of light.
These transformations are crucial for understanding how measurements of time and space differ for observers in different inertial frames, reflecting the core principles of relativity.
Deriving the core concepts of the Principle of Relativity, particularly as formalized by Albert Einstein, involves considering the behavior of light and the constancy of the speed of light in all inertial frames of reference. This derivation lays the foundation for both the special and general theories of relativity. Here is a simplified explanation focusing on the derivation of Special Relativity:
Einstein’s derivation begins with two fundamental postulates:
Step 2: Analyzing Light in Moving Frames
Imagine two observers, one stationary and one moving at a constant velocity. If a light signal is emitted, according to the second postulate, both observers must measure the speed of the light as ‘c’. This scenario raises questions about how time and distance are measured in different frames, leading to the concepts of time dilation and length contraction.
Step 3: Lorentz Transformations
To reconcile how events are timed and positioned differently in moving frames while keeping the speed of light constant, Lorentz transformations are derived:
Here, 𝛾 is the Lorentz factor, 𝛾=1/√1−𝑣²𝑐², where ‘v’ is the velocity of the moving observer relative to the stationary one, and ‘c’ is the speed of light.
Step 4: Implications of Lorentz Transformations
These transformations show that as the velocity of the moving frame approaches the speed of light, time stretches (time dilation) and lengths contract (length contraction) along the direction of motion. These effects are not noticeable at everyday speeds but become significant at speeds close to the speed of light.
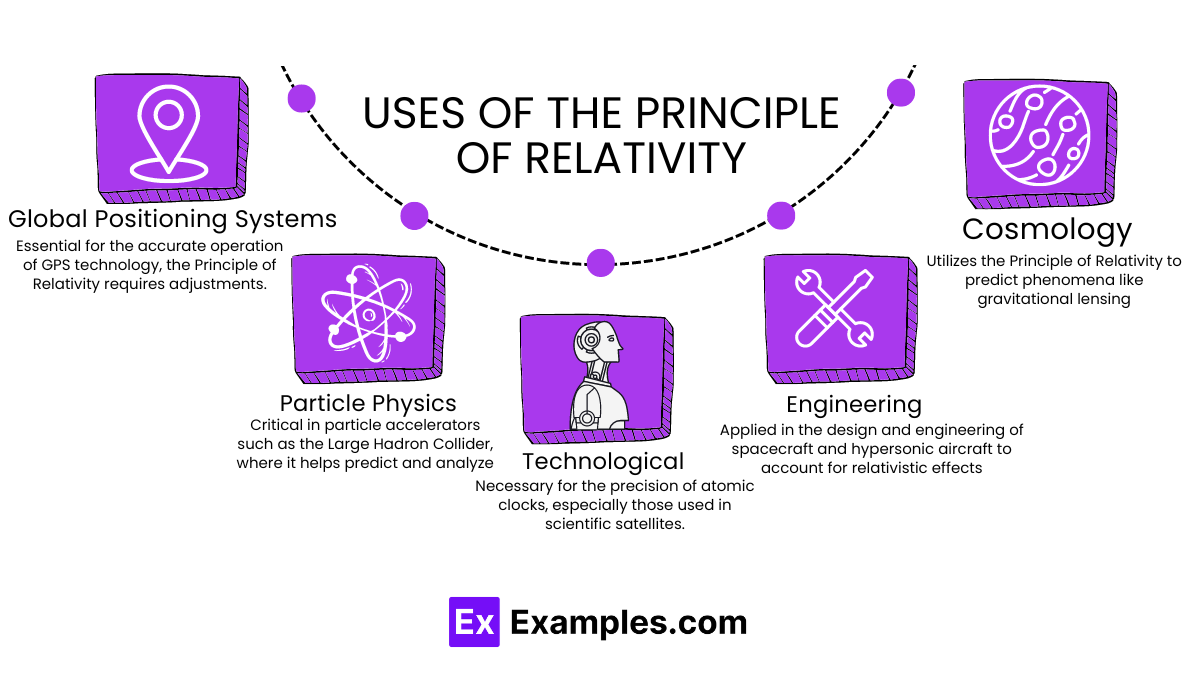
The Principle of Relativity profoundly impacts various scientific and technological fields, demonstrating its far-reaching applications:
Astrophysics and Cosmology:
Global Positioning Systems (GPS):
Particle Physics:
Technological Advancements in Timekeeping:
Engineering and Design of High-Speed Vehicles:
The principle of relativity states that the laws of physics remain consistent across all non-accelerating frames, meaning no absolute motion can be detected.
Special relativity explains how time and space aren’t absolute but vary according to the observer’s speed, showing that time slows and lengths contract at high speeds.
Yes, the theory of relativity has been repeatedly confirmed through experiments and observations, such as GPS accuracy, light bending during solar eclipses, and atomic clocks on airplanes.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the Principle of Relativity?
Laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference
Speed of light is constant in all reference frames
Time is absolute and the same in all frames of reference
Gravity affects all objects equally
Who formulated the Principle of Relativity?
Isaac Newton
Albert Einstein
Galileo Galilei
James Clerk Maxwell
In which theory is the Principle of Relativity a fundamental concept?
Quantum Mechanics
General Relativity
Special Relativity
Thermodynamics
How does the Principle of Relativity relate to the speed of light?
Speed of light is variable in different inertial frames
Speed of light is constant in all inertial frames
Speed of light depends on the observer's motion
Speed of light is infinite in all frames
What does the Principle of Relativity imply about time and space in different inertial frames?
Time and space are absolute and the same for all observers
Space is absolute, but time is relative
Time is absolute, but space is relative
Time and space are relative and can vary between observers
Which concept is directly challenged by the Principle of Relativity?
Conservation of energy
Absolute time
Conservation of momentum
Gravitational force
What is the significance of the Lorentz transformation in the context of the Principle of Relativity?
It describes the change in gravitational force
It provides the mathematical framework for transforming between inertial frames
It explains the behavior of particles at high temperatures
It measures the energy of a system
How does the Principle of Relativity affect the concept of simultaneity?
Events that are simultaneous in one frame are simultaneous in all frames
Simultaneity is absolute and independent of the observer
Events that are simultaneous in one frame may not be simultaneous in another
Simultaneity only applies to stationary observers
Which experiment provided crucial evidence supporting the Principle of Relativity and the constancy of the speed of light?
Michelson-Morley experiment
Cavendish experiment
Young's double-slit experiment
Rutherford's gold foil experiment
What does the Principle of Relativity say about the laws of physics in non-inertial frames?
Laws of physics are identical in non-inertial frames
Laws of physics are different in non-inertial frames
Principle of Relativity does not apply to non-inertial frames
Laws of physics are arbitrary in non-inertial frames
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

