What is the SI unit of electric current?
Volt
Coulomb
Ampere
Ohm

Electric current, fundamentally essential in both scientific and practical contexts, is measured in various units. The primary unit is the ampere. Known as the amp, symbolized as A, it quantifies the flow of electrical charge per second through a conductor. One ampere represents the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
The ampere, often shortened to “amp,” is recognized globally as the SI unit of electric current. It provides a standard measure for the flow of electric charge through a conductor. Specifically, one ampere corresponds to the flow of one coulomb of charge passing through a point in one second.
In the Centimeter –Gram-Second (CGS) system of units, the primary unit for measuring electric current is the biot, also known as the abampere. This unit differs notably from the more commonly used ampere of the SI system. Specifically, one biot is equal to ten amperes, demonstrating a larger base unit for current in the CGS system.
| Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Ampere | A |
| Milliampere | mA |
| Microampere | μA |
| Biot (Abampere) | biot |
| Statampere | statA |
| Coulomb per second | C/s |
The ampere is the SI unit of electric current, named after André-Marie Ampère. It quantifies the flow of electric charge through a conductor at a rate of one coulomb per second. This unit is universally employed in science and engineering to measure electrical flow.
This unit is extensively used in electronic applications, particularly for measuring small currents in circuits. It represents one-thousandth of an ampere, enabling precise current measurements in delicate electronic devices.
A microampere is a unit used to measure extremely low electrical currents. This precision is crucial in microelectronic applications, such as in the operation of transistors and other semiconductor devices.
The biot, also known as abampere, is the CGS unit of current. It measures the amount of current when ten amperes are flowing through a conductor, often utilized in certain scientific contexts where the CGS system remains relevant.
A statampere is the CGS electrostatic unit of current, used primarily in theoretical physics. It quantifies a small but significant flow of charge derived from electrostatic units of charge.
Coulomb per second is another expression for the ampere, emphasizing the rate of charge flow. It is directly equivalent to an ampere, reinforcing the fundamental relationship between charge and current in electrical measurements.
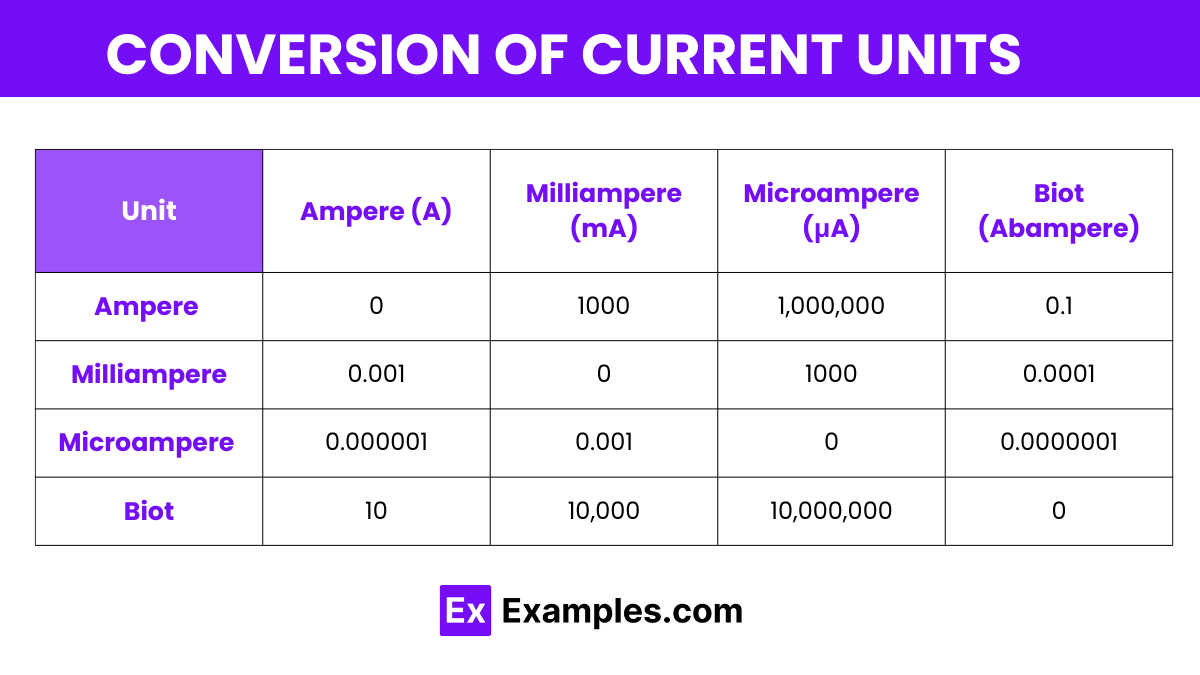
Here is a table format for different units of electric current, presented in a manner similar to the energy conversion factors you provided. Each cell after the unit’s name shows the conversion factors to other current units, such as from amperes to milliamperes, microamperes, and biots (abamperes).
| Current Unit | Ampere (A) | Milliampere (mA) | Microampere (μA) | Biot (Abampere) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampere (A) | 0 | 1000 | 1,000,000 | 0.1 |
| Milliampere (mA) | 0.001 | 0 | 1000 | 0.0001 |
| Microampere (μA) | 0.000001 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.0000001 |
| Biot (Abampere) | 10 | 10,000 | 10,000,000 | 0 |
Conversion: 1 A = 1000 mA
Example: To convert 2 amperes to milliamperes, multiply by 1000.
2 A × 1000 = 2000 mA
Conversion: 1 A = 1,000,000 μA
Example: To convert 0.5 amperes to microamperes, multiply by 1,000,000.
0.5 A × 1,000,000 = 500,000 μA
Conversion: 1 mA = 0.001 A
Example: To convert 1500 milliamperes to amperes, divide by 1000.
1500 mA / 1000 = 1.5 A
Conversion: 1 mA = 1000 μA
Example: To convert 3 milliamperes to microamperes, multiply by 1000.
3 mA × 1000 = 3000 μA
Conversion: 1 μA = 0.000001 A
Example: To convert 2000000 microamperes to amperes, divide by 1,000,000.
2000000 μA / 1,000,000 = 2 A
Conversion: 1 μA = 0.001 mA
Example: To convert 1000 microamperes to milliamperes, divide by 1000.
1000 μA / 1000 = 1 mA
Conversion: 1 biot = 10 A
Example: To convert 3 biots to amperes, multiply by 10.
3 biots × 10 = 30 A
Conversion: 1 A = 0.1 biot
Example: To convert 50 amperes to biots, multiply by 0.1.
50 A × 0.1 = 5 biots
Electric current is measured using instruments like ammeters, which directly record the flow of electrical charge through a conductor.
The units for measuring electric current are amperes, commonly abbreviated as amps.
To measure electric current, devices called ammeters are used, effectively measuring the charge flow in circuits.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of electric current?
Volt
Coulomb
Ampere
Ohm
Which unit is equivalent to one ampere?
One coulomb per second
One volt per second
One ohm per second
One joule per second
What is the unit of electric current in the cgs (centimeter-gram-second) system?
Abampere
Biot
Coulomb
Statampere
How is the unit milliampere (mA) related to the ampere (A)?
1 mA = 0.001 A
1 mA = 0.01 A
1 mA = 0.1 A
1 mA = 1 A
What is the relationship between microampere (µA) and ampere (A)?
1 µA = 0.01 A
1 µA = 0.001 A
1 µA = 0.000001 A
1 µA = 0.0001 A
Which of the following units is used to measure small electric currents?Kiloampere
Kiloampere
Megaampere
Milliampere
Gigaampere
If a current of 2 A flows through a conductor for 10 seconds, how much charge has passed?
20 C
2 C
0.2 C
200
What is the equivalent of 1 kiloampere (kA) in amperes (A)?
10 A
100 A
1000 A
10000 A
How many amperes are there in 1 megaampere (MA)?
1000 A
10000 A
100000 A
1000000 A
What is the unit used to measure alternating current (AC) in household circuits?
Volt
Ohm
Ampere
Coulomb
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

