What is the SI unit of electric charge?
Coulomb
Volt
Ampere
Ohm

Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract. When charges are in motion, they produce an electric current, which can be harnessed for various purposes. Charge conservation states that the total electric charge in an isolated system remains constant over time, implying that charge cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or redistributed between objects.
where ‘n’ represents the number of elementary charges (usually electrons or protons) and ‘e’ represents the elementary charge, which is approximately equal to 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
| Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Coulomb | C |
| Statcoulomb | statC |
| Microcoulomb | μC |
| Nanocoulomb | nC |
| Picocoulomb | pC |
| Abcoulomb | abC |
| Franklin | Fr |
| Faraday (chemical) | F |
| Elementary charge | e |
Microcoulomb (μC): One microcoulomb is equal to one millionth of a coulomb (10^-6 C). It’s commonly used in measurements of small charges, such as those in electronics and biology.
Nanocoulomb (nC): One nanocoulomb is equal to one billionth of a coulomb (10^-9 C). Nanocoulombs are often used to measure very small electric charges in nanotechnology and semiconductor physics.
Picocoulomb (pC): One picocoulomb is equal to one trillionth of a coulomb (10^-12 C). This unit is used to quantify extremely small charges, such as those found in certain types of sensors and detectors.
Abcoulomb (abC): The abcoulomb is a unit of electric charge in the CGS system, equivalent to ten coulombs. While not commonly used, it’s occasionally encountered in older literature or specialized applications.
Franklin (Fr): Named after Benjamin Franklin, the franklin is an obsolete CGS unit of electric charge. One franklin is equal to the charge of approximately 3.33564 x 10^-10 coulombs.
Faraday (chemical): In electrochemistry, the faraday is a unit of electric charge representing the amount of charge carried by one mole of electrons. Its value is approximately 96,485.34 coulombs, often used in calculations involving electrolysis and chemical reactions.
Elementary charge (e): The elementary charge is the electric charge carried by a single proton or electron. Its value is approximately 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs, and it serves as the fundamental unit of electric charge in particle physics and quantum mechanics.
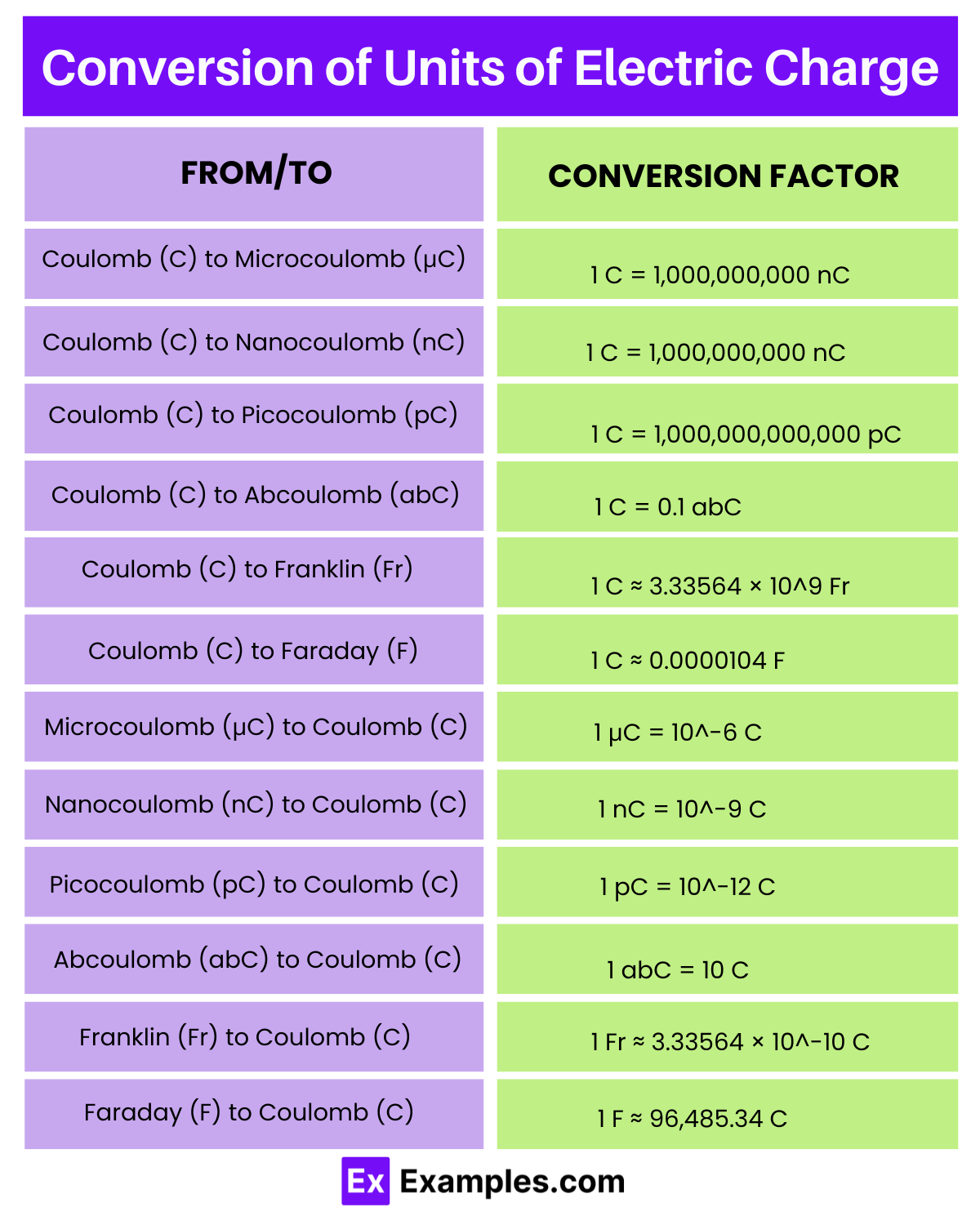
| From (Unit) | To (Unit) | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Coulomb (C) | Microcoulomb (μC) | 1 C = 1,000,000 μC |
| Coulomb (C) | Nanocoulomb (nC) | 1 C = 1,000,000,000 nC |
| Coulomb (C) | Picocoulomb (pC) | 1 C = 1,000,000,000,000 pC |
| Coulomb (C) | Abcoulomb (abC) | 1 C = 0.1 abC |
| Coulomb (C) | Franklin (Fr) | 1 C ≈ 3.33564 × 10^9 Fr |
| Coulomb (C) | Faraday (F) | 1 C ≈ 0.0000104 F |
| Microcoulomb (μC) | Coulomb (C) | 1 μC = 10^-6 C |
| Nanocoulomb (nC) | Coulomb (C) | 1 nC = 10^-9 C |
| Picocoulomb (pC) | Coulomb (C) | 1 pC = 10^-12 C |
| Abcoulomb (abC) | Coulomb (C) | 1 abC = 10 C |
| Franklin (Fr) | Coulomb (C) | 1 Fr ≈ 3.33564 × 10^-10 C |
| Faraday (F) | Coulomb (C) | 1 F ≈ 96,485.34 C |
Electrical charge is measured using instruments such as electrometers or charge meters, which detect and quantify the amount of charge present on an object or in a system.
The unit of electric charge in electron volts (eV) is typically used in particle physics, where 1 electron volt equals the charge of approximately 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
The largest unit of charge is typically considered the Coulomb (C), which represents a significant accumulation of charge and is commonly used in practical applications of electromagnetism.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of electric charge?
Coulomb
Volt
Ampere
Ohm
What is the symbol for the unit Coulomb?
Q
C
E
A
Which of the following is not a unit of electric charge?
Coulomb
Ampere-hour
Volt
Faraday
How many Coulombs are in one Ampere-hour?
3600 C
1800 C
7200 C
5400 C
What is the relationship between charge (Q), current (I), and time (t)?
Q = I/t
Q = It
Q = t/I
Q = I²t
How many microcoulombs are there in one Coulomb?
1000 μC
1 μC
10⁶ μC
10³ μC
How many nanocoulombs are in one Coulomb?
10³ nC
10⁶ nC
10⁹ nC
10¹² nC
f a current of 2 A flows for 3 seconds, how much charge is transferred?
5 C
3 C
6 C
9 C
If a battery supplies a current of 0.5 A for 1 hour, how much charge is delivered?
1800 C
3600 C
900 C
1800 C
What unit is commonly used to express smaller amounts of electric charge?
Milliampere
Nanocoulomb
Kilowatt-hour
Megajoule
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

