What is the SI unit of momentum?
Newton
Joule
Kilogram meter per second
Newton meter


The formula for momentum is a key concept in physics that describes the motion of an object. Momentum (p) is calculated as the product of an object’s mass (𝑚) and its velocity (v). This relationship can be expressed through the equation:
Mass (𝑚): This is the amount of matter in an object, usually measured in kilograms (kg). The mass is a scalar quantity, meaning it has magnitude but no direction.
Velocity (v): Velocity is the speed of the object in a specific direction, making it a vector quantity. It is typically measured in meters
The units of momentum are expressed as kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s). This unit derivation comes from the momentum formula p=m×v, where 𝑚 represents mass measured in kilograms (kg) and v denotes velocity measured in meters per second (m/s). The resulting unit, kg·m/s, indicates the product of an object’s mass and its velocity, providing a measure of its momentum which is fundamental in understanding motion dynamics and the effects of forces in physics.
The CGS (Centimeter-Gram-Second) units of momentum are gram centimeters per second (g·cm/s). This unit arises from using the CGS system’s base units for mass and velocity, where mass is measured in grams and velocity in centimeters per second.
| Unit Name | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Kilogram meters per second | kg·m/s |
| Gram centimeters per second | g·cm/s |
| Slug feet per second | slug·ft/s |
| Pound feet per second | lb·ft/s |
The kilogram meter per second is the SI unit of momentum. It represents the momentum carried by a mass of one kilogram moving at one meter per second. It is widely used in physics to describe the quantity of motion of an object
The gram centimeter per second is the CGS unit of momentum. It measures the momentum of a mass of one gram moving at one centimeter per second. This unit is often used in smaller-scale physics calculations and laboratory settings.
A slug foot per second is a unit of momentum used in the imperial system. It quantifies the momentum of a mass of one slug moving at one foot per second. This unit is prevalent in regions that utilize the imperial system, such as the United States.
The pound foot per second is another imperial unit of momentum. It describes the momentum of a mass of one pound moving at one foot per second. This unit is commonly used in various engineering and scientific applications within the United States
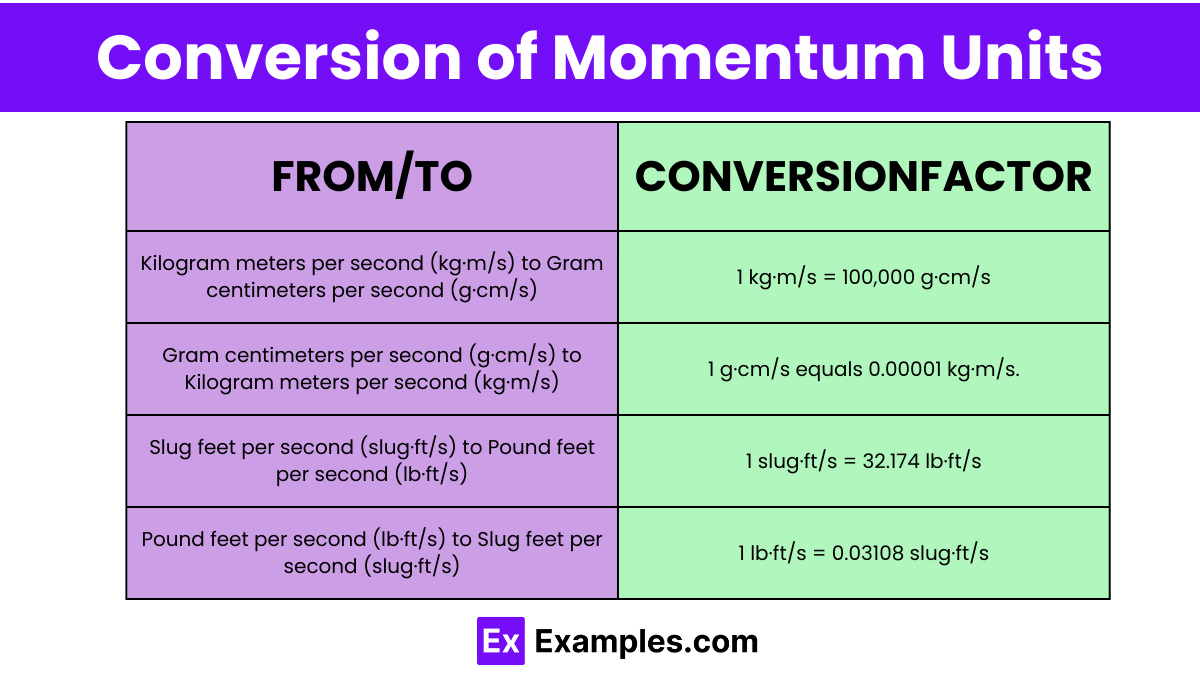
| From Unit | To Unit | Conversion Factor | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s) | Gram centimeters per second (g·cm/s) | 1 kg·m/s = 100,000 g·cm/s | value in kg\cdotpm/s×100,000value in kg\cdotpm/s×100,000 |
| Gram centimeters per second (g·cm/s) | Kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s) | 1 g·cm/s = 0.00001 kg·m/s | value in g\cdotpcm/s×0.00001value in g\cdotpcm/s×0.00001 |
| Slug feet per second (slug·ft/s) | Pound feet per second (lb·ft/s) | 1 slug·ft/s = 32.174 lb·ft/s | value in slug\cdotpft/s×32.174value in slug\cdotpft/s×32.174 |
| Pound feet per second (lb·ft/s) | Slug feet per second (slug·ft/s) | 1 lb·ft/s = 0.03108 slug·ft/s | value in lb\cdotpft/s/32.174value in lb\cdotpft/s/32.174 |
Example: If the momentum is 2 kg·m/s, it converts to 200,000 g·cm/s.
Example: If the momentum is 200,000 g·cm/s, it converts to 2 kg·m/s.
Example: If the momentum is 3 slug·ft/s, it converts to 96.522 lb·ft/s.
Example: If the momentum is 96.522 lb·ft/s, it converts to approximately 3 slug·ft/s.
Momentum is measured in units such as kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s) in the SI system and gram centimeters per second (g·cm/s) in the CGS system. These units reflect the product of an object’s mass and its velocity.
The units for momentum are typically expressed in kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s) in the International System of Units (SI) and gram centimeters per second (g·cm/s) in the Centimeter-Gram-Second (CGS) system. These units reflect the product of an object’s mass and its velocity.
In particle physics, momentum is often measured in electronvolts per speed of light (eV/c), adapting energy units to describe particle velocities close to light speed.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of momentum?
Newton
Joule
Kilogram meter per second
Newton meter
Which of the following is the formula for momentum?
p = mv
p = ma
p = m/v
p = m/a
What does the momentum of an object depend on?
Mass and acceleration
Mass and velocity
Force and time
Velocity and time
What is the unit of mass in the momentum formula?
Kilogram
Newton
Joule
Meter
What is the unit of velocity in the momentum formula?
Meter per second squared
Kilogram
Newton
Meter per second
Which of the following best defines momentum?
The force applied to an object
The product of an object's mass and its velocity
The rate of change of velocity
The energy stored in an object
Which unit is NOT associated with momentum?
Kilogram meter per second
Newton second
Joule second
Meter per second
In which type of collision is momentum conserved?
Elastic collision
Inelastic collision
Both elastic and inelastic collision
Neither elastic nor inelastic collision
What is the term for the change in momentum?
Force
Impulse
Acceleration
Work
Which physical quantity has the same units as momentum?
Force
Work
Impulse
Energy
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

