What is the SI unit of power?
Joule
Watt
Volt
Ampere

Power is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred over time. Understanding units of power is essential for gauging the efficiency of machines and energy systems in various contexts, from household appliances to large-scale industrial operations.
Transitioning to larger scales, the kilowatt (kW), which equals 1,000 watts, frequently measures the energy consumption of appliances and entire households, providing a clear picture of energy usage.
The SI (International System of Units) unit of power is the watt (W). Defined as one joule per second, the watt measures the rate at which energy is used or produced. It is a crucial unit for quantifying the energy conversion in electrical appliances, vehicles, and power systems, allowing for precise calculations of energy efficiency and consumption in various scientific, engineering, and everyday contexts.
The CGS (Centimeter-Gram-Second) unit of power is the erg per second. An erg is a small unit of energy in the CGS system, where one erg is defined as the work done by a force of one dyne exerted over a distance of one centimeter. Therefore, one erg per second represents the power involved when one erg of energy is transferred in one second. This unit, though less commonly used today compared to the SI unit of power, the watt, is still relevant in specific scientific fields such as physics and astrophysics for detailed micro-scale energy measurements.
| Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Watt | W |
| Kilowatt | kW |
| Megawatt | MW |
| Gigawatt | GW |
| Horsepower | hp |
| Metric Horsepower | PS |
| British Thermal Unit per hour | BTU/h |
| Foot-pound per minute | ft-lb/min |
The Watt is the SI unit of power named after James Watt. It measures the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred when one joule is expended in one second. It is universally used in science, engineering, and everyday electrical appliances to quantify power.
A kilowatt equals one thousand watts and is commonly used to express the power output of engines and the power usage of appliances. It represents the energy production or consumption at a rate of one thousand joules per second.
A megawatt is a unit of power typically used to describe the capacity of large power plants or the amount of electricity required by large equipment. It equates to one million watts of power.
The gigawatt is used in major energy production or consumption contexts, such as national power grids or large data centers, representing one billion watts.
Horsepower is traditionally used in the automotive industry and mechanical engineering to measure engine power. It originated as a unit to compare the power of steam engines with that of draft horses.
Metric horsepower, or PS (Pferdestärke), is slightly different than the mechanical horsepower and is used primarily in Europe to denote the power output of motor engines.
This unit is often used in heating and air conditioning industries in the United States to measure the power of HVAC systems.
This unit measures the power in terms of mechanical work done when a force of one pound-force is exerted along one foot in one second. It is used in mechanical engineering and in the U.S. for various applications.
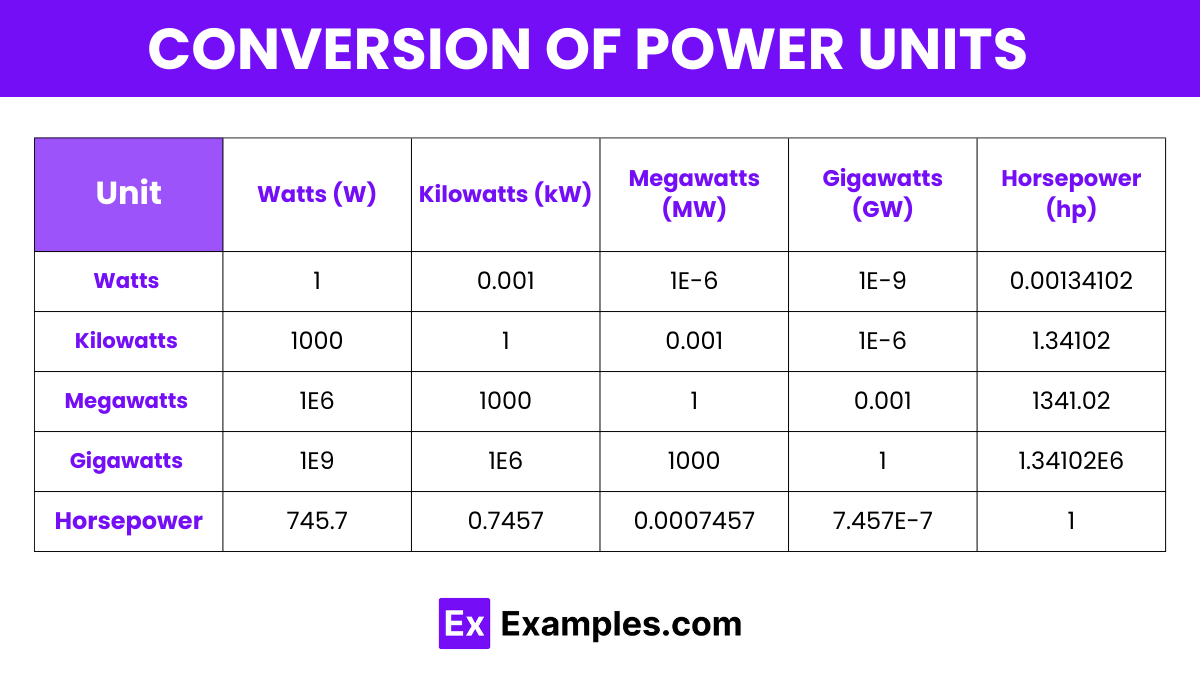
Here’s a conversion table for various units of power, formatted to provide clear conversion factors between watts, kilowatts, megawatts, gigawatts, and horsepower:
| Unit | Watts (W) | Kilowatts (kW) | Megawatts (MW) | Gigawatts (GW) | Horsepower (hp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Watts (W) | 1 | 0.001 | 1E-6 | 1E-9 | 0.00134102 |
| Kilowatts (kW) | 1000 | 1 | 0.001 | 1E-6 | 1.34102 |
| Megawatts (MW) | 1E6 | 1000 | 1 | 0.001 | 1341.02 |
| Gigawatts (GW) | 1E9 | 1E6 | 1000 | 1 | 1.34102E6 |
| Horsepower (hp) | 745.7 | 0.7457 | 0.0007457 | 7.457E-7 | 1 |
1500 W / 1000 = 1.5 kW2000000 W / 1000000 = 2 MW3000000000 W / 1000000000 = 3 GW250 kW * 1000 = 250000 W5 kW / 1000 = 0.005 MW6000 kW / 1000000 = 0.006 GW1 MW * 1000000 = 1000000 W2 MW * 1000 = 2000 kW3 MW / 1000 = 0.003 GW1 GW * 1000000000 = 1000000000 W4 GW * 1000000 = 4000000 kW5 GW * 1000 = 5000 MWPower units, such as watts, kilowatts, and horsepower, quantify the rate at which energy is transferred or work is performed over time.
Power is measured in terms of energy output per unit of time, typically represented by units like watts, indicating the rapidity of energy conversion.
In the context of energy, power describes the speed at which energy is used or generated, essentially reflecting the efficiency and capability of energy systems.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of power?
Joule
Watt
Volt
Ampere
Which of the following units is equivalent to one watt?
One joule per second
One volt per ampere
One newton meter
One coulomb per second
How many watts are in one kilowatt?
10
100
1000
10000
Which unit is used to measure the rate of energy consumption in households?
Kilowatt-hour
Ampere-hour
Volt-hour
Joule-hour
A device uses 500 watts of power for 2 hours. How much energy does it consume?
500 Wh
1000 Wh
1500 Wh
2000 Wh
Which unit is commonly used to measure the power output of engines?
Watt
Horsepower
Joule
Newton
How many watts are in one horsepower?
550
746
1000
1500
Which of the following represents one megawatt?
1000 watts
10,000 watts
100,000 watts
1,000,000 watts
What is the unit of power in the metric system used to express large-scale energy production?
Watt
Kilowatt
Megawatt
Gigawatt
Which unit is used to measure the power consumption of small electronic devices?
Milliwatt
Kilowatt
Megawatt
Gigawatt
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

