How many seconds are there in one minute?
30 seconds
45 seconds
60 seconds
90 seconds

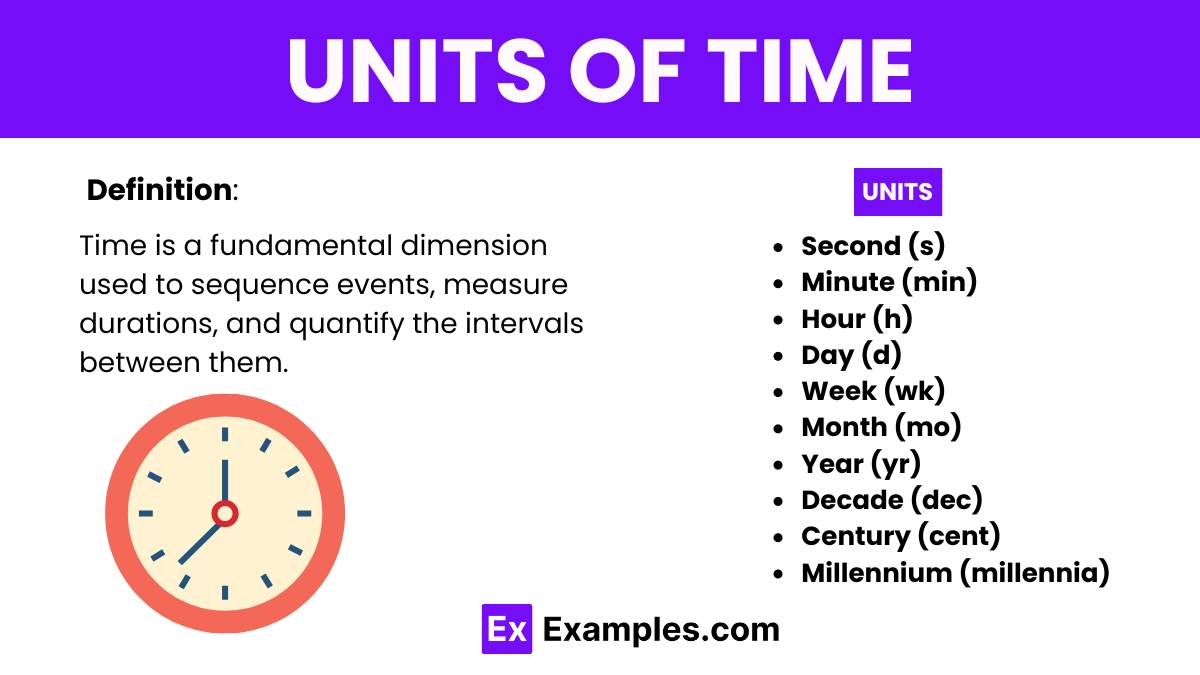
Time is a fundamental dimension used to sequence events, measure durations, and quantify the intervals between them. Essential in all aspects of life, from the simplest daily activities to complex scientific research, time allows us to plan, analyze, and understand the dynamics of the world around us.
Transitioning to larger intervals, the minute (min) and hour (h) serve as critical measures in everyday life, organizing our schedules and activities into manageable segments.
On a larger scale, the day, week, month, and year structure longer periods, vital for planning, agriculture, business, and cultural activities. These units, from seconds to years, are integral to coordinating human endeavors and scientific investigations, helping us synchronize and plan effectively across different scales of time.
The second (s) is the SI unit of time, serving as the foundational measure for quantifying the duration of events. Defined by the oscillation of cesium atoms, the second ensures a high level of precision in timing. This precision is pivotal in various scientific fields such as physics and astronomy, where accurate time measurement is crucial for experiments and observations.
In the CGS (centimeter-gram-second) system, the unit of heat is the calorie (cal). A calorie is defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. This unit is especially prevalent in chemistry and nutrition, where it helps quantify the energy content of reactions and foods, respectively.

| Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Second | s |
| Minute | min |
| Hour | h |
| Day | d |
| Week | wk |
| Month | mo |
| Year | yr |
| Decade | dec |
| Century | cent |
The second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), defined by the oscillation of cesium atoms. It is universally used in science and everyday life to measure durations and intervals.
A minute is commonly used across the globe for personal scheduling, broadcasting, and in various forms of media. It serves as a fundamental unit for recording time in everyday contexts.
The hour is a longer unit of time traditionally used for civil and scientific purposes. It is integral for planning daily activities and is a standard time measurement in business and social settings.
A day is based on the Earth’s rotation cycle and is widely recognized in calendars and for organizing daily human activities. It is crucial for agricultural, social, and economic activities.
A week is a standard unit of time used universally for planning and is a common cycle in business and personal organization.
Months are used in the Gregorian calendar for civil purposes and cultural celebrations. They approximate the lunar cycle and vary in length.
The year corresponds to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, used for long-term planning, historical records, and legal documentation.
Decades are popular in historical and cultural discussions to denote significant periods of time.
Century are used to delineate extended periods in history, helping to organize and contextualize large spans of time in human history.
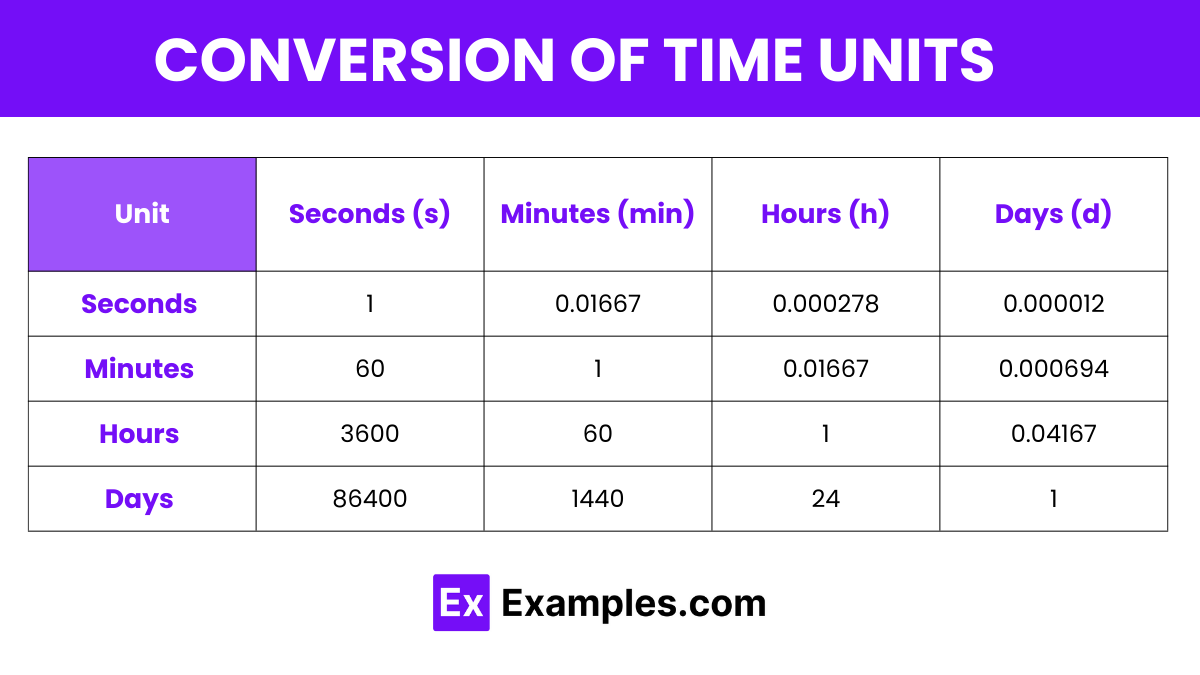
Here is a table format for the conversion factors between various units of time such as seconds, minutes, hours, and days. The values provided represent how many of one unit are contained in another:
| Unit | Seconds (s) | Minutes (min) | Hours (h) | Days (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seconds (s) | 1 | 0.01667 | 0.000278 | 0.000012 |
| Minutes (min) | 60 | 1 | 0.01667 | 0.000694 |
| Hours (h) | 3600 | 60 | 1 | 0.04167 |
| Days (d) | 86400 | 1440 | 24 | 1 |
120 s / 60 = 2 min7200 s / 3600 = 2 h172800 s / 86400 = 2 d30 min × 60 = 1800 sConversion: 1 hour = 60 minutes.
Example: To convert 120 minutes to hours, divide by 60.
120 min / 60 = 2 h
2880 min / 1440 = 2 d2 h × 3600 = 7200 s2 h × 60 = 120 min48 h / 24 = 2 d2 d × 86400 = 172800 s2 d × 1440 = 2880 min2 d × 24 = 48 hSeconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, years, decades, centuries, and millennia organize time from the briefest moments to expansive historical periods.
Yes, the Planck time is considered the smallest measurable unit of time in physics, representing the time it takes light to travel one Planck length.
The attosecond, which equals 10^-18 of a second, is currently one of the fastest units of time used to measure the speed of electron movements inside atoms.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
How many seconds are there in one minute?
30 seconds
45 seconds
60 seconds
90 seconds
How many weeks are there in one month (assuming 4 weeks per month)?
3 weeks
4 weeks
5 weeks
6 weeks
How many decades are there in one century?
5 decades
10 decades
15 decades
20 decades
How many fortnights are there in one year?
20 fortnights
24 fortnights
26 fortnights
30 fortnights
How many days are there in February during a leap year?
28 days
29 days
30 days
31 days
How many months have 31 days?
5 months
6 months
7 months
8 months
How many microseconds are there in one second?
10³ microseconds
10⁴ microseconds
10⁵ microseconds
10⁶ microseconds
How many seconds are there in one day?
86400 seconds
72000 seconds
90000 seconds
100000 seconds
How many centuries are there in one millennium?
5 centuries
10 centuries
15 centuries
20 centuries
How many minutes are there in one day?
720 minutes
1140 minutes
1440 minutes
1800 minutes
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

