What is the SI unit of work?
Joule
Newton
Watt
Erg


Work is a physical concept in physics that describes the transfer of energy when a force moves an object over a distance. It is crucial for understanding energy transfer mechanisms across various scientific and engineering fields.
The SI (International System of Units) unit of work is the joule (J). Defined as the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces an object one meter in the direction of the force, the joule serves as a crucial measure in various scientific and engineering disciplines.
The CGS (Centimeter-Gram-second) unit of pressure is the dyne per square centimeter , often referred to as the barye. Defined as the force of one dyne exerted per square centimeter of area, this unit measures how much force is applied over a specific area within the CGS system.
The formula for work is simple and provides a clear measure of energy transfer when a force moves an object. Work (W) is calculated using the equation:
Here, F represents the force applied, d is the distance over which the force is applied, and θ is the angle between the force and the direction of movement.
Thus, work is simply the product of the force exerted on the box and the distance it moves, reflecting the total energy exerted through the movement.
| Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Joule | J |
| Kilowatt-hour | kWh |
| Calorie | cal |
| Kilocalorie | kcal |
| Electronvolt | eV |
| British Thermal Unit | BTU |
| Foot-pound | ft-lb |
The Joule is the SI unit of work, named after James Prescott Joule. It quantifies the work done or energy transferred when a force of one newton is applied to move an object one meter in the direction of the force. It’s widely used across all fields of science and engineering to measure energy, work, or heat.
A kilowatt-hour is a larger unit of work commonly used to measure electrical energy in commercial and residential settings. It represents the amount of work done when a power of one kilowatt is sustained for one hour.
Originally defined in terms of heating water, a calorie is a unit of work that indicates the energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius at atmospheric pressure. It is often used in chemistry and nutrition.
Also known as a food calorie, the kilocalorie is used to express the energy content in foods, equivalent to 1,000 calories. This unit is crucial in dietary energy measurements.
An electronvolt is a unit of work used primarily in the field of particle physics. It measures the amount of work done when an electron is moved through an electric potential difference of one volt.
The British Thermal Unit is used mainly in the heating and cooling industries in the United States. It defines the amount of work required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
This unit measures the work done when a force of one pound-force is exerted over a distance of one foot. It is commonly used in the United States for applications in mechanical engineering and physics.
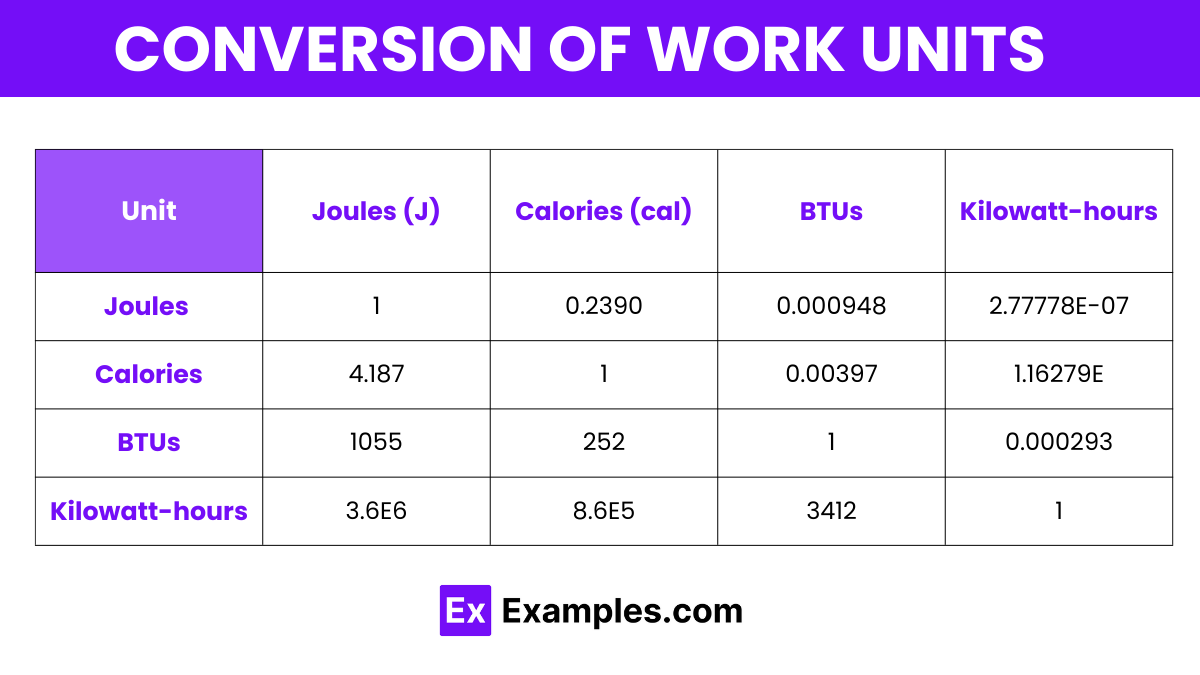
Here’s a conversion table for various units of work, formatted to show how different units such as Joules, Calories, BTUs, and Kilowatt-hours relate to each other:
| Unit | Joules (J) | Calories (cal) | British Thermal Units (BTU) | Kilowatt-hours (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joules (J) | 1 | 0.2390 | 0.000948 | 2.77778E-07 |
| Calories (cal) | 4.187 | 1 | 0.00397 | 1.16279E-06 |
| BTUs | 1055 | 252 | 1 | 0.000293 |
| Kilowatt-hours | 3.6E6 | 8.6E5 | 3412 | 1 |
100 J / 4.187 = 23.88 cal500 J / 1055 ≈ 0.474 BTU18000 J / 3.6×10^6 ≈ 0.005 kWh50 cal × 4.187 = 209.35 J100 cal × 0.00397 = 0.397 BTU1000 cal / 860,000 ≈ 0.00116 kWh2 BTU × 1055 = 2110 J5 BTU × 252 = 1260 cal10 BTU / 3412 ≈ 0.00293 kWh1 kWh × 3.6×10^6 = 3.6×10^6 J0.5 kWh × 860,000 = 430,000 cal0.1 kWh × 3412 = 341.2 BTUIn physics, work does not have a unit in kilograms; rather, it’s measured in joules, where 1 joule equals 1 newton-meter.
In educational contexts, “unit of work” typically refers to a segment of the curriculum or a structured plan, not measured in standard units.
Work describes the process of energy transfer when a force moves an object over a distance, essentially quantifying the energy exerted in doing so.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of work?
Joule
Newton
Watt
Erg
Which unit is equivalent to one joule?
One watt per second
One newton per meter
One newton meter
One meter per second squared
What unit is commonly used to measure work in the CGS (centimeter-gram-second) system?
Dyne
Erg
Newton
Joule
Which of the following is a larger unit of work than a joule?
Erg
Calorie
Dyne
Newton
What is the work done when a force of 1 newton moves an object 1 meter?
1 joule
1 watt
1 newton
1 erg
Which unit is not typically associated with measuring work?
Joule
Newton meter
Watt
Erg
What is the relationship between joules and ergs?
1 joule = 10⁷ ergs
1 joule = 10⁶ ergs
1 joule = 10⁵ ergs
1 joule = 10⁴ ergs
Which of the following is not a unit of work?
Joule
Erg
Watt
Newton meter
What does 1 newton meter represent?
1 joule
1 watt
1 erg
1 dyne
Which unit of work is equivalent to lifting a 1 kg object to a height of 1 meter against gravity?
1 joule
1 watt
1 newton meter
1 erg
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

