What is a US therm used to measure?
Length
Volume
Energy
Temperature

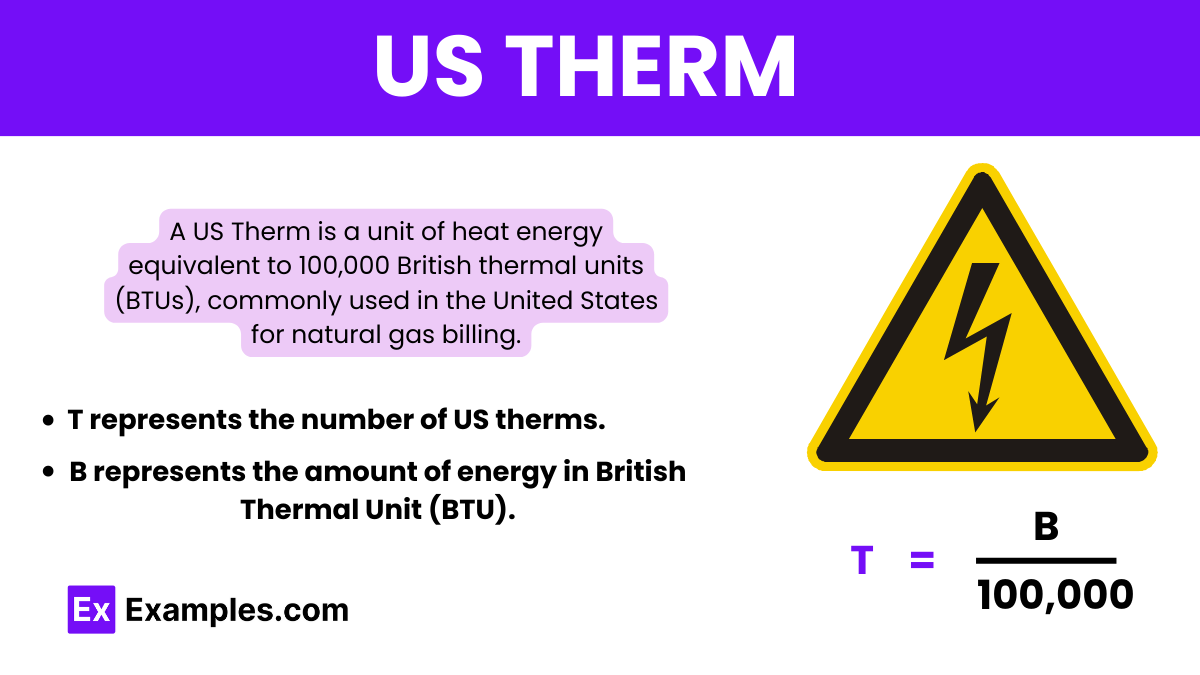
A US therm is a unit of heat energy equal to 100,000 British thermal units (BTUs). It’s commonly used in the United States for billing purposes, particularly in natural gas sales. One US therm can raise the temperature of one pound of water by 1°F when burned.
The formula to calculate the number of US therms is:
T = B/100,000

| From / To | Conversion Factor | Example |
|---|---|---|
| US Therm to British Thermal Unit (BTU) | 1 US Therm = 100,000 | 10 US Therm = 1,000,000 BTU |
| US Therm to kilowatt-hour (kWh) | 1 US Therm = 29.3071 | 10 US Therm ≈ 293.071 kWh |
| US Therm to megawatt-hour (MWh) | 1 US Therm = 0.0293071 | 10 US Therm ≈ 0.293071 MWh |
| US Therm to Joules | 1 US Therm = 105,506,000 | 10 US Therm ≈ 1,055,060,000 J |
| US Therm to Calorie | 1 US Therm = 25,200,000 | 10 US Therm ≈ 252,000,000 Cal |
| US Therm to Cubic feet of natural gas | 1 US Therm = 100 | 10 US Therm = 1,000 Cubic feet |
| US Therm to Liters of gasoline equivalent | 1 US Therm = 28.3 | 10 US Therm ≈ 283 Liters |
1 US Therm is equivalent to a certain number of British Thermal Units (BTUs), which is a common unit of energy.
Kilowatt-hours are commonly used for electricity billing. This conversion tells you how many kWh are equivalent to 1 US Therm of energy.
Megawatt-hours are used for large-scale energy measurements, often in industrial settings or for power generation. This conversion gives you the equivalent energy in MWh.
Joules are the standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). This conversion helps in understanding the energy equivalence in joules.
Calories are another unit of energy commonly used in nutrition and dietetics. This conversion shows the energy equivalence in terms of calories.
This conversion relates the energy content of 1 US Therm to the volume of natural gas it represents, which is useful for understanding the physical volume of gas consumed.
This conversion compares the energy content of 1 US Therm to the volume of gasoline it would be equivalent to, aiding in understanding energy usage in terms of gasoline consumption.
In residential settings, understanding US therms helps homeowners manage heating costs more efficiently. For instance, a homeowner can track their monthly gas consumption in US therms to budget effectively. HVAC professionals use US therms to size heating systems accurately, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. Utility companies bill customers based on US therms consumed, reflecting actual energy usage. Government agencies and policymakers use US therms as a standard metric for energy consumption analysis and policy development.
Health:
Safety:
Yes, US therms can quantify renewable energy usage, especially in systems like biomass or biogas. However, their primary association is with fossil fuel consumption, so it’s essential to differentiate.
Energy efficiency ratings often consider US therms as a baseline for comparison. Higher efficiency means fewer therms needed for the same output, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Yes, various countries use similar units such as the UK therm or the metric ton of oil equivalent (Mtoe). These units allow for global energy comparisons and standardization.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is a US therm used to measure?
Length
Volume
Energy
Temperature
What is the equivalent of one US therm in British thermal units (BTU)?
100 BTU
1000 BTU
10,000 BTU
100,000 BTU
What is the primary use of the US therm?
Measuring electrical energy
Measuring gas energy
Measuring mechanical energy
Measuring thermal energy in water
How does the US therm relate to cubic feet of natural gas?
1 US therm = 100 cubic feet
1 US therm = 10 cubic feet
1 US therm = 1,000 cubic feet
1 US therm = 100,000 cubic feet
If a household consumes 5 therms of natural gas, how many BTUs have been used?
50,000 BTU
500,000 BTU
5,000 BTU
50,000,000 BTU
How is the cost of natural gas typically billed?
Per cubic foot
Per gallon
Per therm
Per pound
What is the significance of the US therm in energy billing?
It standardizes the measurement of electrical energy
It provides a consistent unit for billing gas energy consumption
It measures the power of appliances
It calculates the energy efficiency of buildings
What does the term "therm" originate from?
Greek word fo
Latin word for power
English word for temperature
German word for energy
Which sector commonly uses the US therm for energy measurement?
Transporta
Agriculture
Residential heating
Telecommunicati
What is the equivalent of 1 therm in kilowatt-hours (kWh)?
29.3 kWh
2.93 kWh
293 kWh
0.293 kWh
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

