What is the formula to calculate the wavelength (λ) of a wave if the speed (v) and frequency (f) are known?
λ = v / f
λ = vf
λ = f / v
λ = v + f

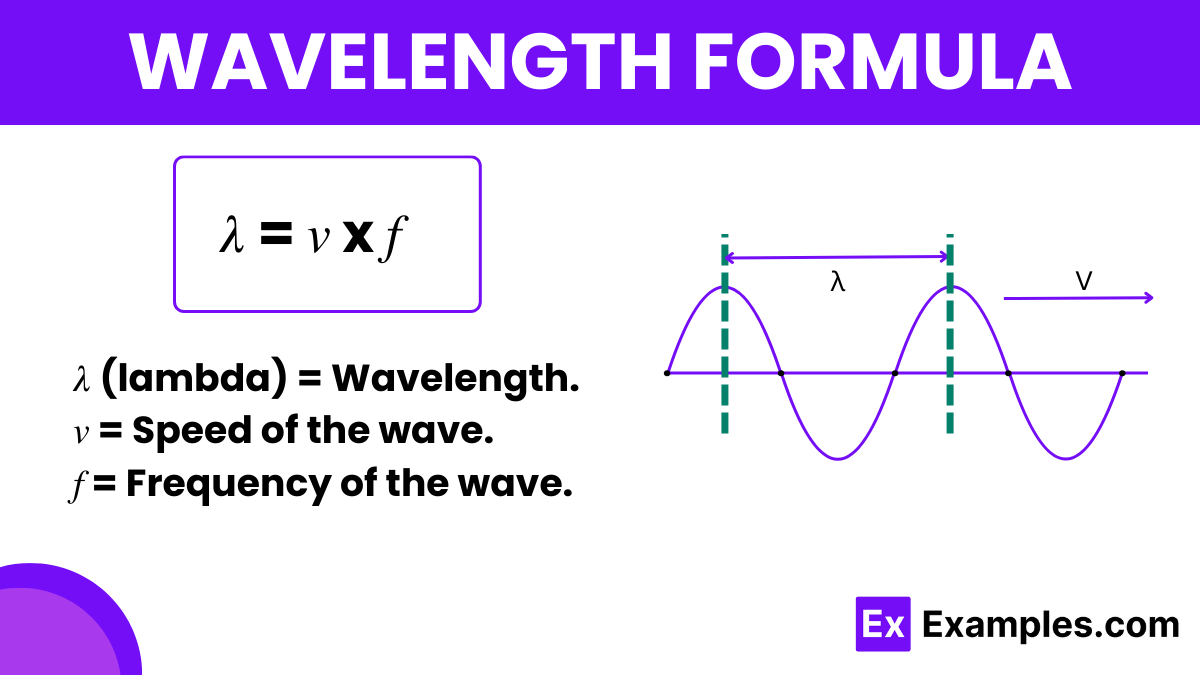
The wavelength formula is essential in physics for calculating the distance between repeating units of a wave pattern. It is commonly symbolized by the Greek letter lambda (λ) and is crucial in various fields of science, especially in optics, acoustics, and electromagnetic theory. This formula helps in determining the physical properties of waves, such as their speed and frequency.
The wavelength formula is defined as
This means that the wavelength is the ratio of the speed at which the wave propagates through a medium to the frequency with which the wave cycles occur. Essentially, it tells us how long one cycle of the wave is in physical space.
The concept of wavelength was first rigorously analyzed by physicists such as Isaac Newton and Thomas Young, but the precise formulation of the wavelength formula as we know it today was developed through the work of multiple scientists over time.
Step 1: Understanding Basic Wave Properties
First, let’s define the terms involved in the formula:
Step 2: Relating Speed, Frequency, and Wavelength
Consider a wave moving through a medium. The speed of the wave tells us how fast a single point on the wave, such as a crest, travels through the medium. In one second, the wave travels a distance equal to its speed, 𝑣v.
Now, if we consider the frequency, f, it indicates how many complete waves pass a point in one second. If each wave has a length of 𝜆λ, then the total distance covered by 𝑓 waves in one second is
According to the definition of speed, this distance must also equal the speed of the wave:
Step 3: Solving for Wavelength
To find the formula for wavelength, we rearrange the equation above:
This equation shows that the wavelength is the speed of the wave divided by its frequency. This relationship is crucial because it allows physicists to calculate any one of these three variables if the other two are known.
This derivation not only highlights the interconnected nature of speed, frequency, and wavelength in wave physics but also provides a clear mathematical framework for analyzing waves in various mediums. Whether it’s sound waves in air or electromagnetic waves in a vacuum, this formula remains a key tool in the field of physics.
Problem Statement: A sound wave travels through air at a speed of 340 m/s with a frequency of 1700 Hz. What is the wavelength of this sound wave?
Solution: Using the wavelength formula 𝜆=𝑣 x 𝑓
𝜆 = 340 m/s x 1700 Hz = 0.2 meters
Problem Statement: The wavelength of a light wave in a vacuum is 500 nm (nanometers), and the speed of light is approximately 3×1083×108 m/s. What is the frequency of this light wave?
Solution: First, convert the wavelength from nanometers to meters:
500 nm = 500×10⁻⁹.
Now, apply the formula to find the frequency f,
𝑓 = 𝑣 / 𝜆=3×108 m/s / (500×10⁻⁹ m) = 6×10¹⁴ Hz
Problem Statement: An FM radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 90.5 MHz. If the wavelength of these radio waves is 3.3 meters, what is the speed of the waves?
Solution: First, convert MHz to Hz:
90.5 MHz = 90.5 × 10⁶ Hz.
Using the wavelength formula to calculate speed 𝑣,
𝑣 = 𝜆 × 𝑓= 3.3 m × 90.5×10⁶ Hz=298.65×10⁶ m/s =
To calculate wavelength (λ) from frequency (f), use the formula: 𝜆=𝑣 / 𝑓, where 𝑣 is the wave speed.
In physics, λ (lambda) represents the wavelength of a wave, indicating the distance over which the wave’s shape repeats.
No, wavelength is not equal to frequency. Wavelength is the distance a wave travels per cycle, while frequency is the number of cycles per second.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula to calculate the wavelength (λ) of a wave if the speed (v) and frequency (f) are known?
λ = v / f
λ = vf
λ = f / v
λ = v + f
If a wave travels at a speed of 340 m/s and has a frequency of 170 Hz, what is its wavelength?
1 m
2 m
0.5 m
0.2 m
How does the wavelength change if the frequency of a wave increases, while the speed remains constant?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
What is the unit of wavelength in the SI system?
Meter
Hertz
Second
Newton
A wave has a speed of 300,000 km/s and a frequency of 3 x 10⁸ Hz. What is its wavelength?
0.1 m
0.01 m
1 m
10 m
Which quantity remains constant for all electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
Wavelength
Frequency
Speed
Amplitude
What is the wavelength of a sound wave traveling at 343 m/s with a frequency of 343 Hz?
1 m
10 m
100 m
0.1 m
How is the wavelength of a wave affected if the wave speed is doubled while the frequency remains the same?
It is halved
It remains the same
It doubles
It becomes zero
A wave on a string has a speed of 10 m/s and a wavelength of 2 m. What is its frequency?
5 Hz
10 Hz
15 Hz
25 Hz
If the wavelength of a wave is decreased by a factor of 2, how does its frequency change assuming constant speed?
It is doubled
It is halved
It remains the same
It becomes zero
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

