Effortlessly convert watt-hours to electronvolts and vice versa using Examples.com. Simply input your numbers for accurate and immediate results.
Wh to eV
Formula: Energy in Electronvolts (eV) = Energy in Watt Hours (Wh) x 2.247 × 1022
Watt Hour :
Electronvolt :
| Watt Hours | Electronvolts |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2.247e+22 |
eV to Wh
Formula: Energy in Watt Hours (Wh) = Energy in Electronvolts (eV) x 4.450 × 10-23
Electronvolt :
Watt Hour :
| Electronvolts | Watt Hours |
|---|---|
| 1 | 4.45e-23 |
Energy Converters to Watt hour
Energy Converters to Electronvolt
Conversion Factors:
- Watt-Hours to Electronvolts: 1 watt-hour (Wh) = 2.247×1022 electronvolts (eV)
- Electronvolts to Watt-Hours: 1 electronvolt (eV) = 4.450×10−23 watt-hours (Wh)
How to Convert Watt-Hours to Electronvolts:
To convert watt-hours to electronvolts, multiply the number of watt-hours by 2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=Watt-Hours (Wh)×2.247×1022
Example: Convert 1 watt-hour to electronvolts.
Electronvolts (eV)=1 Wh×2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=2.247×1022 eV
How to Convert Electronvolts to Watt-Hours:
To convert electronvolts to watt-hours, multiply the number of electronvolts by 4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=Electronvolts (eV)×4.450×10−23
Example: Convert 1×1022 electronvolts to watt-hours.
Watt-Hours (Wh)=1×1022 eV×4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=0.445 Wh
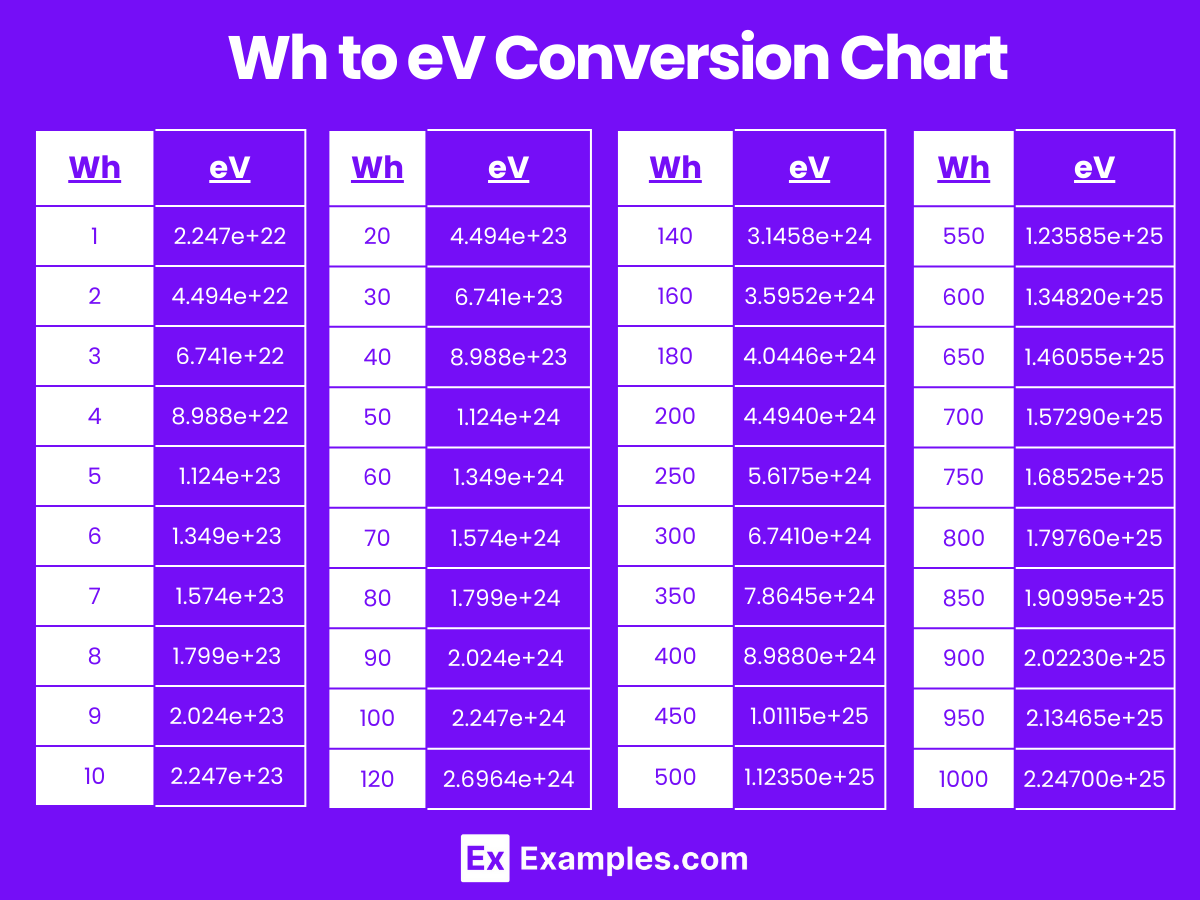
Watt-Hours to Electronvolt Conversion Table
| Watt-Hours (Wh) | Electronvolts (eV) |
|---|---|
| 1 Wh | 2.247e+22 eV |
| 2 Wh | 4.494e+22 eV |
| 3 Wh | 6.741e+22 eV |
| 4 Wh | 8.988e+22 eV |
| 5 Wh | 1.124e+23 eV |
| 6 Wh | 1.349e+23 eV |
| 7 Wh | 1.574e+23 eV |
| 8 Wh | 1.799e+23 eV |
| 9 Wh | 2.024e+23 eV |
| 10 Wh | 2.247e+23 eV |
| 20 Wh | 4.494e+23 eV |
| 30 Wh | 6.741e+23 eV |
| 40 Wh | 8.988e+23 eV |
| 50 Wh | 1.124e+24 eV |
| 60 Wh | 1.349e+24 eV |
| 70 Wh | 1.574e+24 eV |
| 80 Wh | 1.799e+24 eV |
| 90 Wh | 2.024e+24 eV |
| 100 Wh | 2.247e+24 eV |
Wh to eV Conversion Chart
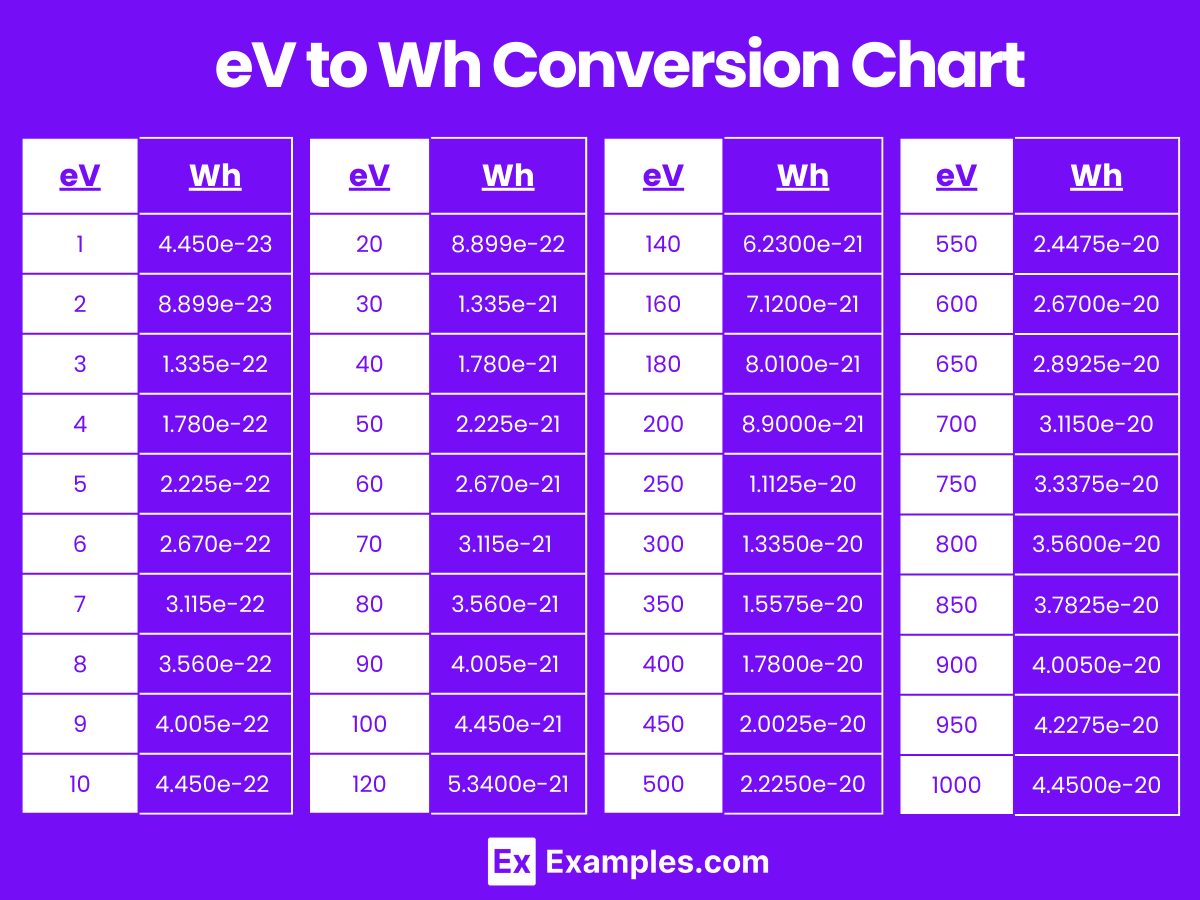
Electronvolt to Watt-Hours Conversion Table
| Electronvolts (eV) | Watt-Hours (Wh) |
|---|---|
| 1 eV | 4.450e-23 Wh |
| 2 eV | 8.899e-23 Wh |
| 3 eV | 1.335e-22 Wh |
| 4 eV | 1.780e-22 Wh |
| 5 eV | 2.225e-22 Wh |
| 6 eV | 2.670e-22 Wh |
| 7 eV | 3.115e-22 Wh |
| 8 eV | 3.560e-22 Wh |
| 9 eV | 4.005e-22 Wh |
| 10 eV | 4.450e-22 Wh |
| 20 eV | 8.899e-22 Wh |
| 30 eV | 1.335e-21 Wh |
| 40 eV | 1.780e-21 Wh |
| 50 eV | 2.225e-21 Wh |
| 60 eV | 2.670e-21 Wh |
| 70 eV | 3.115e-21 Wh |
| 80 eV | 3.560e-21 Wh |
| 90 eV | 4.005e-21 Wh |
| 100 eV | 4.450e-21 Wh |
eV to Wh Conversion Chart
Difference Between Watt-Hours to Electronvolt
| Aspect | Watt-Hours (Wh) | Electronvolts (eV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A unit of energy commonly used in electrical contexts | A unit of energy commonly used in atomic and particle physics |
| Usage | Measures energy consumption or production in electrical systems | Measures energy at the atomic or subatomic level |
| Conversion Factor | 1 Wh = 2.247e+22 eV | 1 eV = 4.450e-23 Wh |
| Measurement Context | Used for household appliances, electrical devices, and power generation | Used for individual particles, atoms, and molecules |
| Symbol | Wh | eV |
| Common Applications | Billing electricity, battery capacity, power generation | Determining particle energy, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics |
| Energy Content | Represents a significant amount of energy in daily life | Represents a very small amount of energy |
| Fields of Use | Electrical engineering, energy industry, power systems | Physics, chemistry, material science |
| Practical Example | 1 Wh is the energy consumed by a 1-watt device running for 1 hour | 1 eV is the energy gained by an electron when accelerated through a potential difference of 1 volt |
| Scale of Energy | Macro-scale energy measurement | Micro-scale energy measurement |
1. Solved Examples on Converting Watt-Hours to Electronvolt
Example 1:
Convert 1 watt-hour to electronvolts.
Calculation: Electronvolts (eV)=1 Wh×2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=2.247×1022 eV
Example 2:
Convert 2 watt-hours to electronvolts.
Calculation: Electronvolts (eV)=2 Wh×2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=4.494×1022 eV
Example 3:
Convert 5 watt-hours to electronvolts.
Calculation: Electronvolts (eV)=5 Wh×2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=1.124×1023 eV
Example 4:
Convert 10 watt-hours to electronvolts.
Calculation: Electronvolts (eV)=10 Wh×2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=2.247×1023 eV
Example 5:
Convert 20 watt-hours to electronvolts.
Calculation: Electronvolts (eV)=20 Wh×2.247×1022
Electronvolts (eV)=4.494×1023 eV
2. Solved Examples on Converting Electronvolts to Watt-Hours
Example 1:
Convert 1 electronvolt to watt-hours.
Calculation: Watt-Hours (Wh)=1 eV×4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=4.450×10−23 Wh
Example 2:
Convert 10 electronvolts to watt-hours.
Calculation: Watt-Hours (Wh)=10 eV×4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=4.450×10−22 Wh
Example 3:
Convert 100 electronvolts to watt-hours.
Calculation: Watt-Hours (Wh)=100 eV×4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=4.450×10−21 Wh
Example 4:
Convert 1,000 electronvolts to watt-hours.
Calculation: Watt-Hours (Wh)=1,000 eV×4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=4.450×10−20 Wh
Example 5:
Convert 10,000 electronvolts to watt-hours.
Calculation: Watt-Hours (Wh)=10,000 eV×4.450×10−23
Watt-Hours (Wh)=4.450×10−19 Wh
Are there any online tools for converting watt-hours to electronvolts?
Yes, there are numerous online conversion tools available that can easily convert watt-hours to electronvolts and vice versa. Websites such as unit converters, energy calculators, and educational resources offer these tools.
Can watt-hours and electronvolts be used for calculating energy consumption?
Yes, both watt-hours and electronvolts can be used for calculating energy consumption, but in different contexts. Watt-hours are more suitable for measuring energy consumption in electrical systems, while electronvolts are used to measure energy at the atomic or subatomic level.
What is the practical use of converting electronvolts to watt-hours?
Converting electronvolts to watt-hours is practical for understanding the energy consumption of electronic devices and systems that operate on atomic or subatomic energy levels. It provides a way to quantify and compare energy usage in different contexts.
What is the significance of converting watt-hours to electronvolts in scientific research?
Converting watt-hours to electronvolts is significant in scientific research as it allows for comparisons and calculations across different scales of energy measurement. It is particularly useful in fields such as physics and material science where different units of energy are used.
How accurate is the conversion between watt-hours and electronvolts?
The conversion between watt-hours and electronvolts is precise based on the defined conversion factors. However, the practical accuracy depends on the precision of the measurement tools and methods used.
Are watt-hours and electronvolts used interchangeably?
No, watt-hours and electronvolts are used in different contexts and represent different scales of energy. Watt-hours are typically used in electrical and energy consumption contexts, while electronvolts are used in atomic and particle physics to describe very small amounts of energy.

